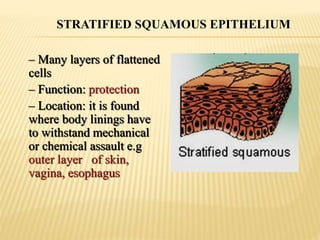
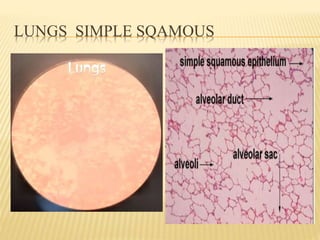
Epithelial tissue lines body surfaces and cavities. It is classified based on cell shape (squamous, cuboidal, columnar) and number of cell layers (simple, stratified, pseudostratified). Simple squamous epithelium is a single layer of flattened cells found in the lungs, blood vessels, and heart. Stratified squamous epithelium has multiple layers of flattened cells and protects surfaces like skin and esophagus. Pseudostratified epithelium appears layered but is a single cell layer with irregularly placed nuclei, found in the respiratory tract.