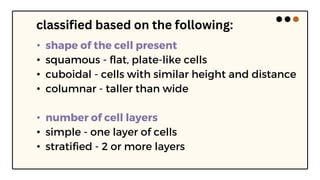
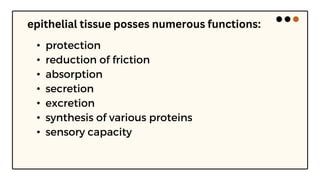
This document summarizes the key characteristics of epithelial tissue. It notes that epithelial tissue is avascular and made up of sheets of cells with little intercellular material. Epithelial tissue can be simple with one cell layer, or stratified with two or more layers. The shape and arrangement of cells and nuclei define different types of epithelia like squamous, cuboidal, columnar, and pseudostratified. Epithelial tissue has functions like protection, absorption, secretion, and sensation.