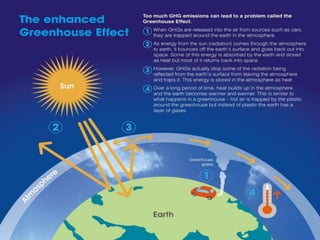
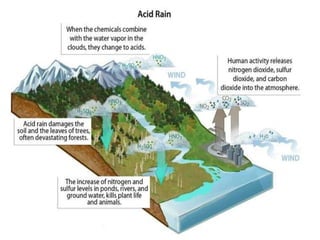
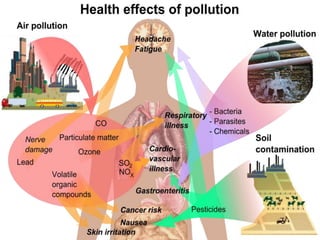
This document discusses various topics related to environment protection. It defines environment protection and discusses key issues like the greenhouse effect, acid rain, wildlife extinction, deforestation, pollution, and ecology. It specifically examines selective collection and recycling, noting that selective collection is one stage of recycling that separates waste to transform it into useful products. Recycling reduces energy consumption and excessive use of natural resources. The document also defines environmental pollution as an undesirable change in the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of air, land, and water. Pollutants are categorized as either biodegradable or non-biodegradable. Biodegradable pollutants are broken down by microorganisms while non-biodegradable poll