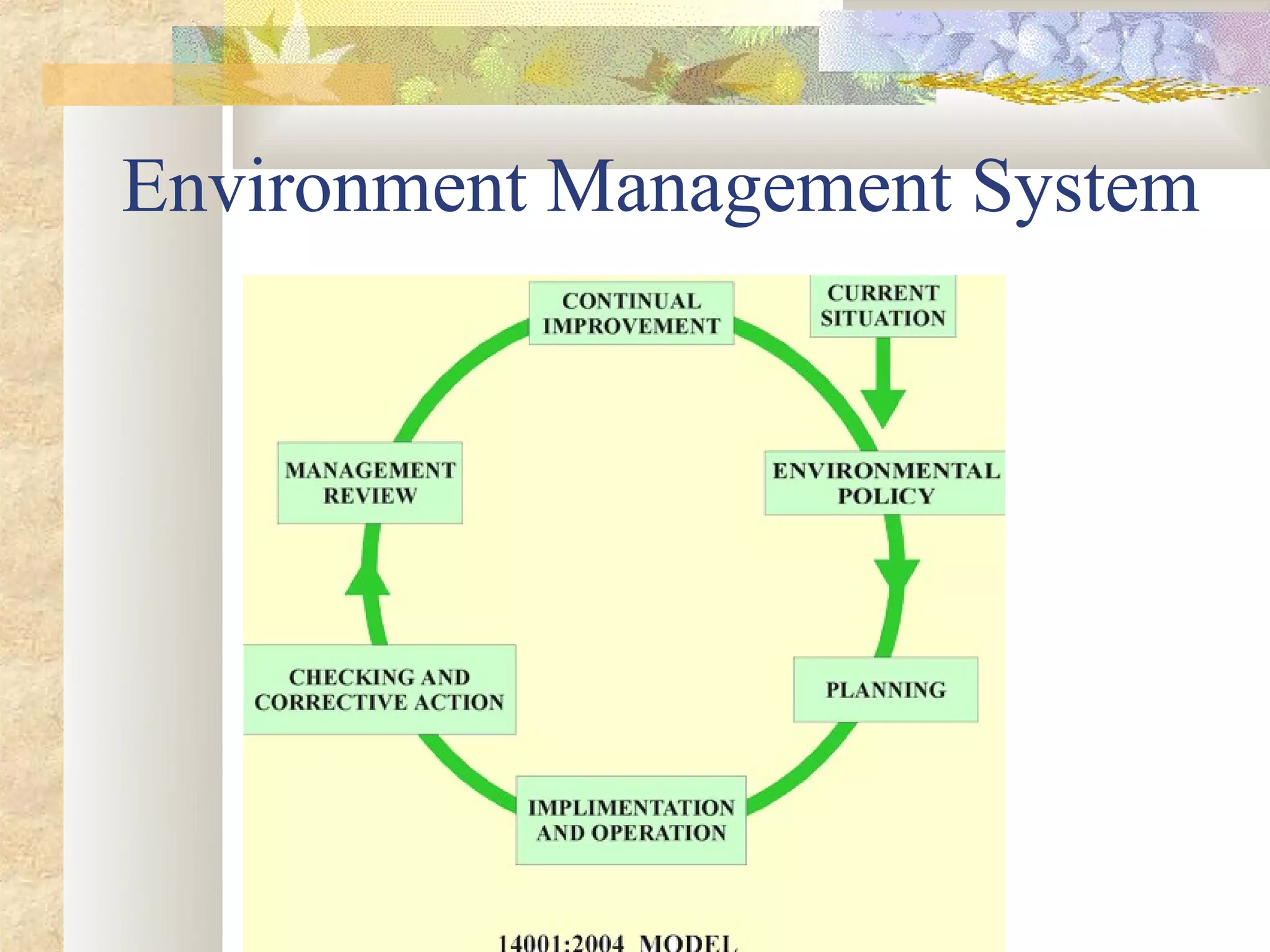
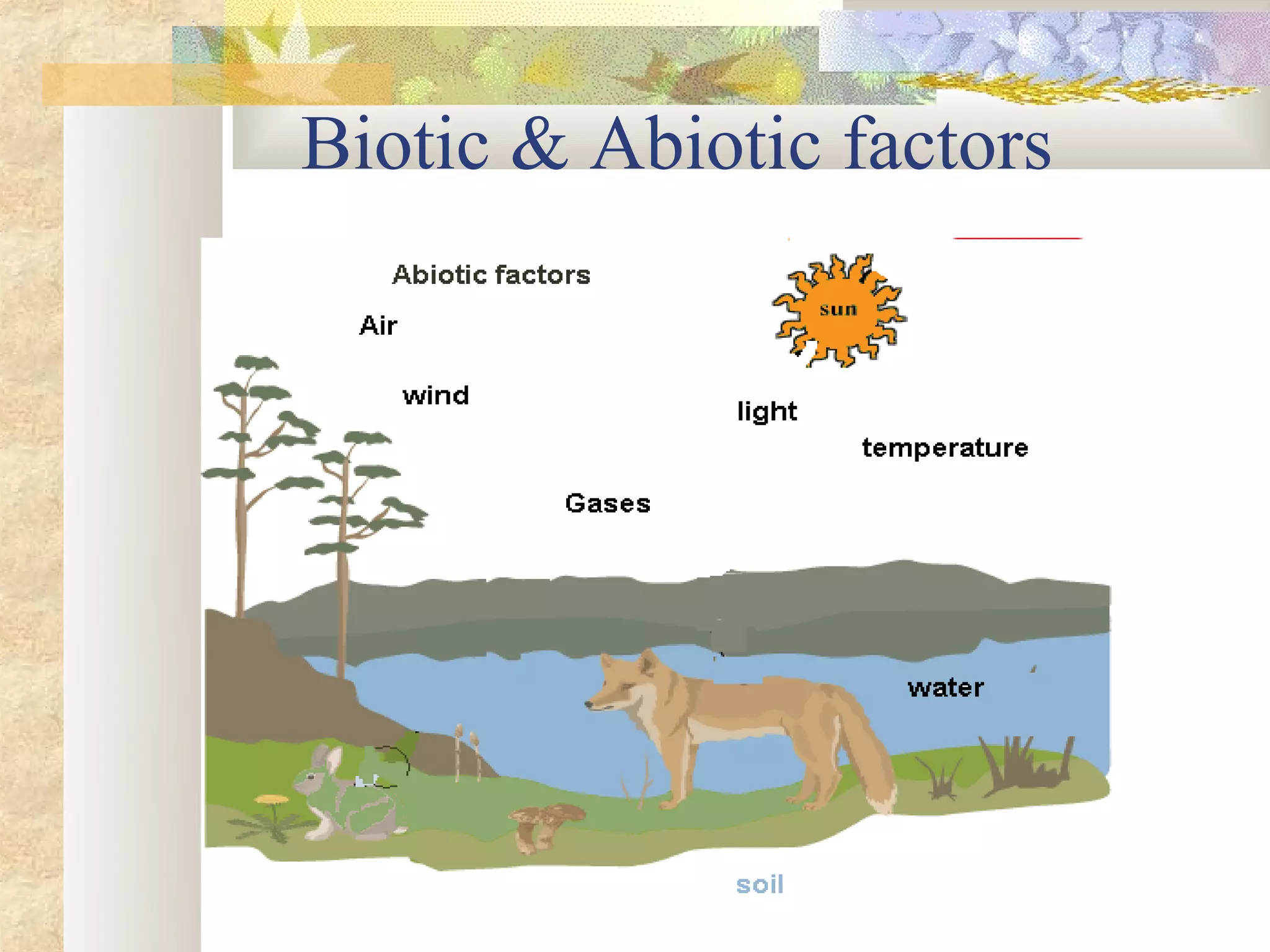
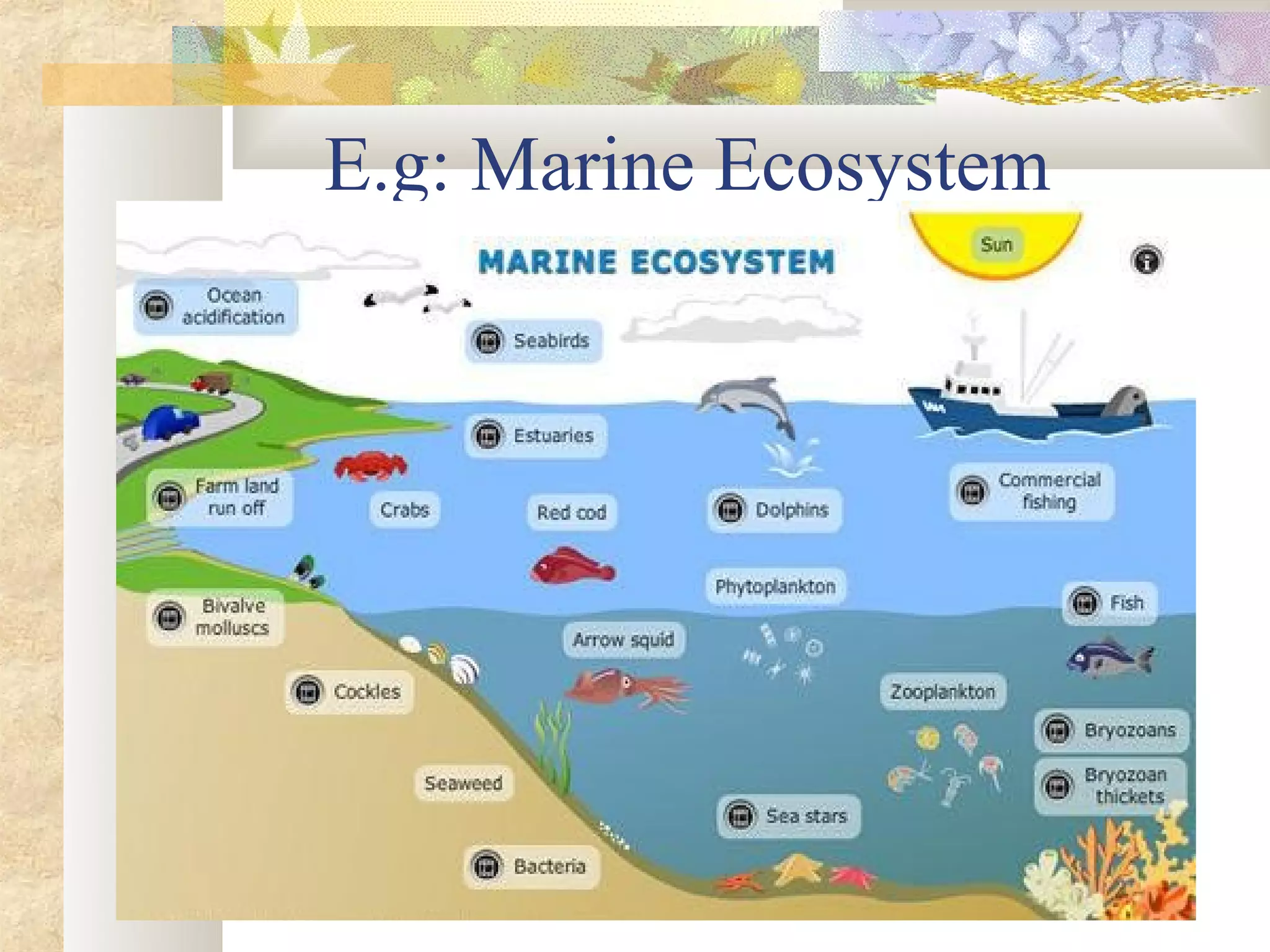
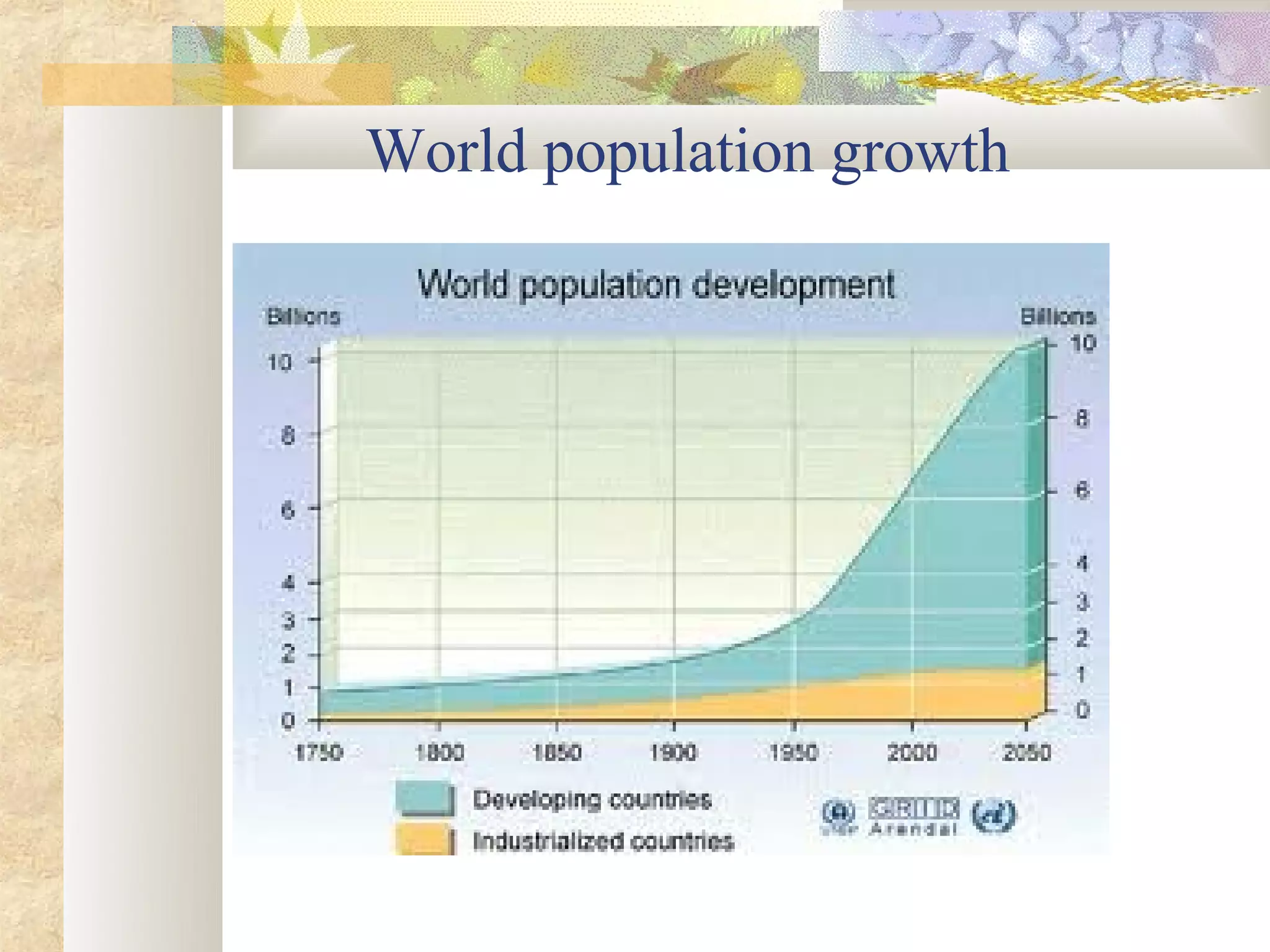
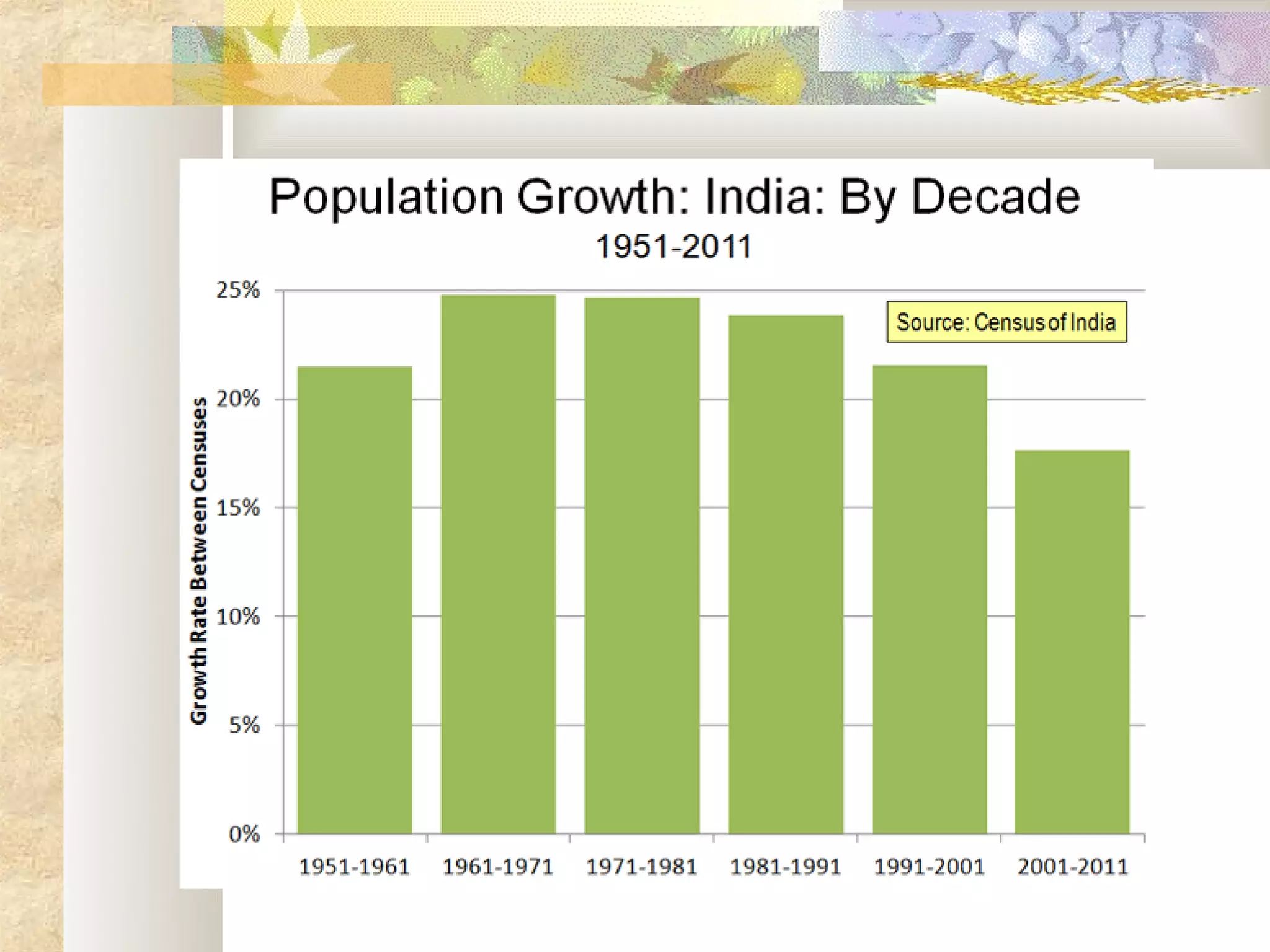
This document provides an overview of environment management. It discusses key topics like what environment management is, the environment management system, definitions of environment and ecosystem, causes of pollution like population growth and fossil fuel usage. It also summarizes important issues in India like air pollution from industries and vehicles, the Bhopal gas tragedy, and causes of water and soil pollution. The objectives of the course are to understand human impacts on the environment and means for sustainable development.