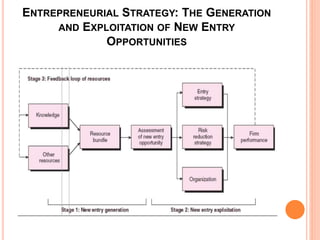
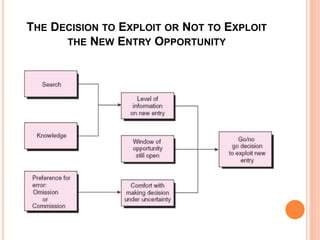
This document discusses strategies for new market entry and exploitation. It defines new entry as offering a new product, an established product to a new market, or creating a new organization. An entrepreneurial strategy generates and exploits new entry opportunities over time. Generating opportunities involves creating a valuable, rare, and inimitable bundle of resources using market and technological knowledge. Exploiting opportunities considers being a first mover and managing risks through narrow or broad market scope strategies or imitation strategies like franchising. Managing newness involves addressing liabilities of inexperience while leveraging advantages of flexibility.