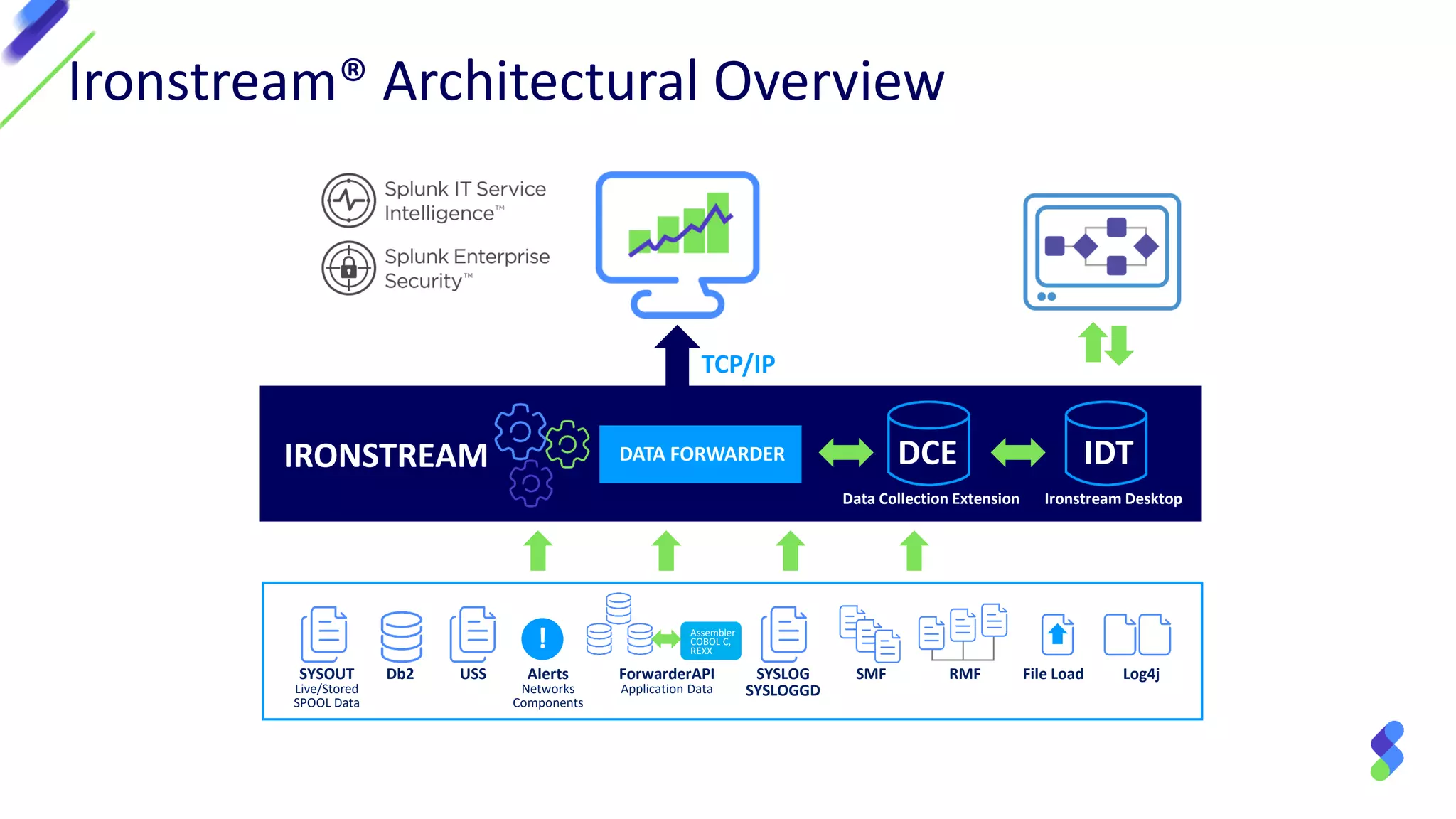
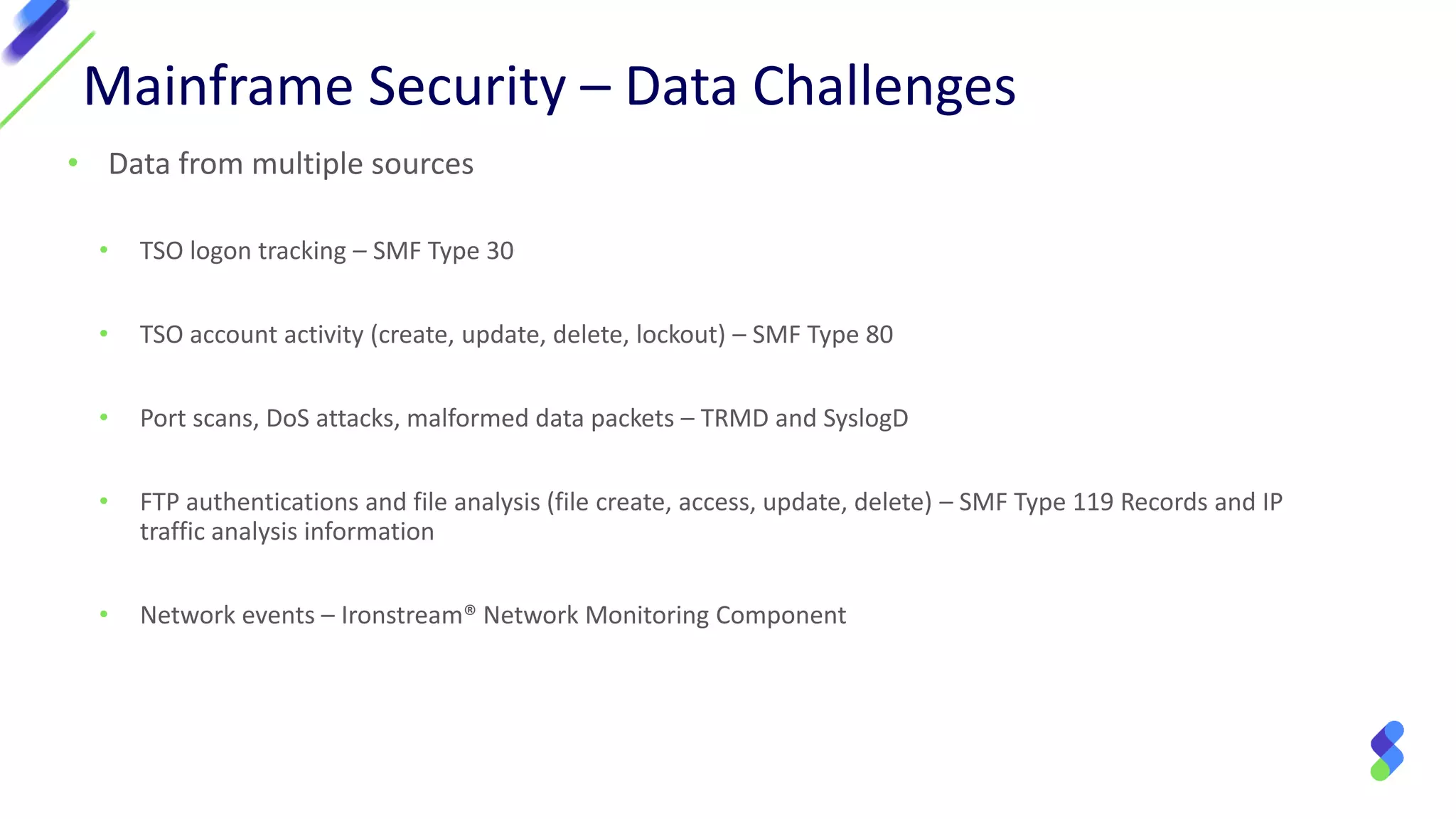
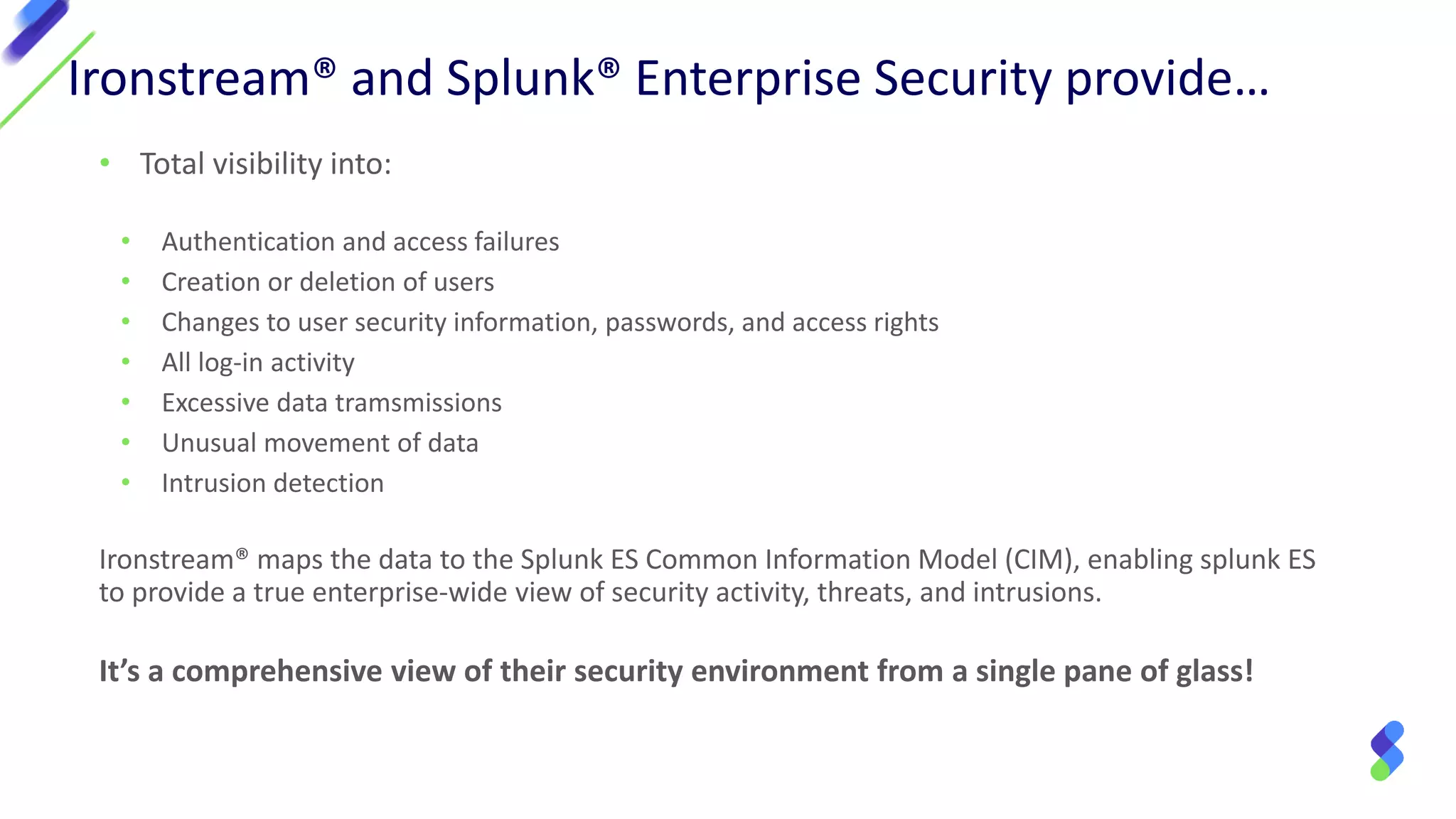
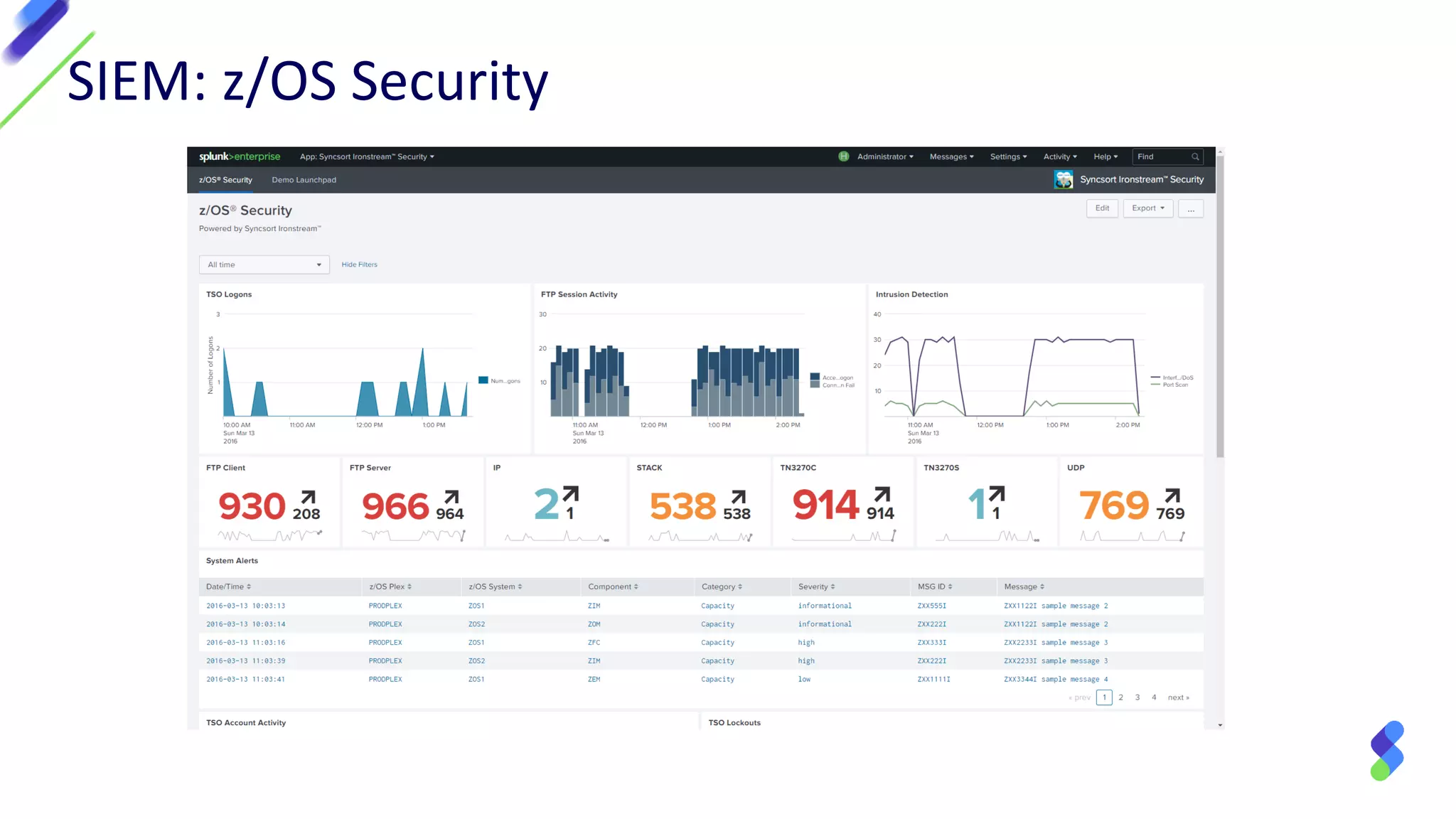
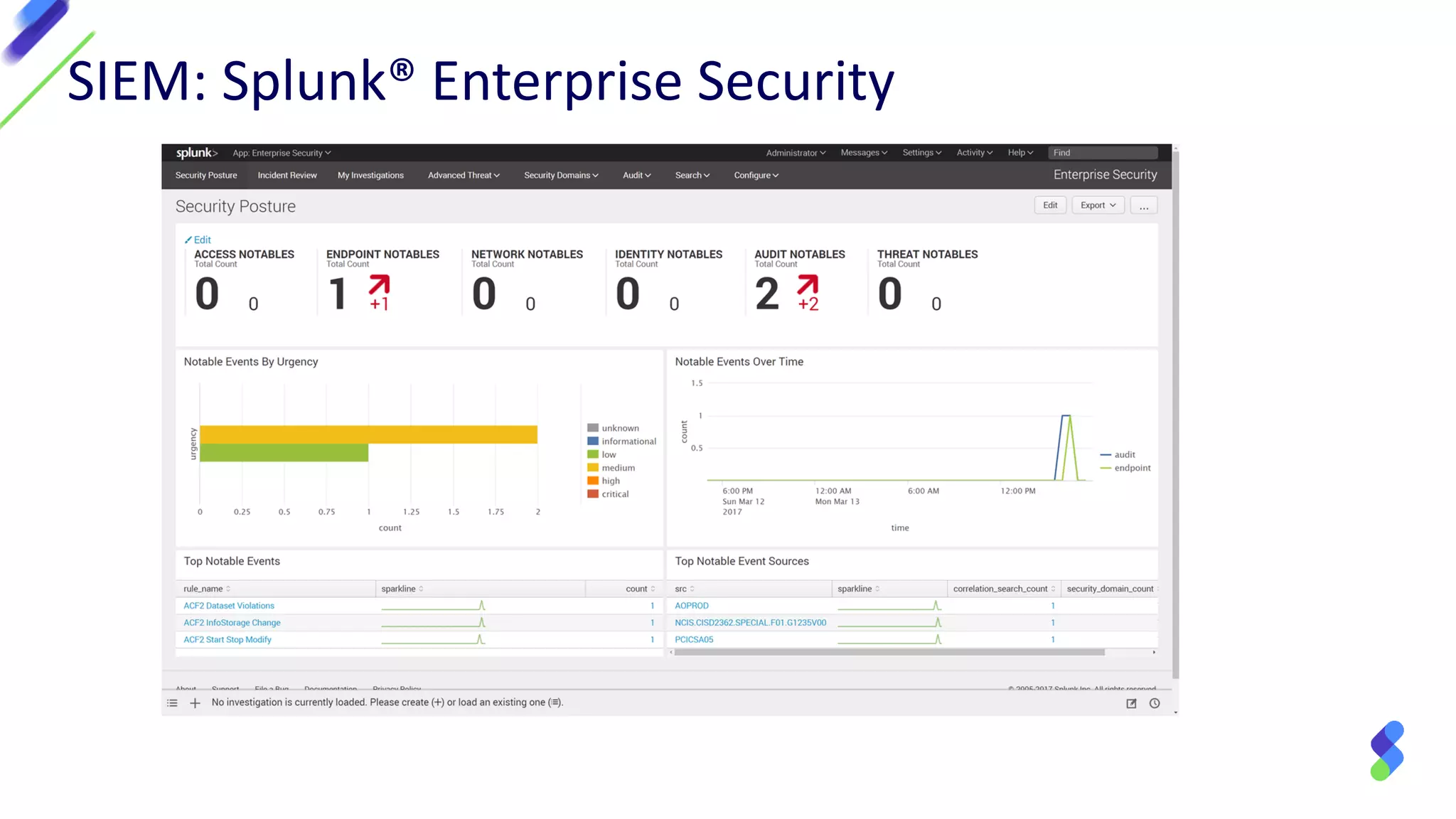
The document discusses enterprise security in mainframe-connected environments, focusing on the use of security information and event management (SIEM) for real-time analysis and vulnerability management. It highlights challenges related to log analysis on mainframes, including complex data structures and the need for timely information extraction. Ironstream® is presented as a solution that normalizes mainframe data for effective use in analytics, offering visibility into IT operations, security threats, and compliance needs.