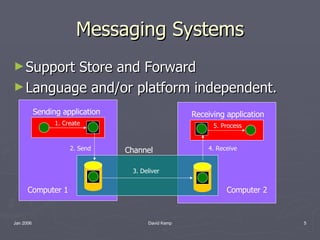
The document introduces the book Enterprise Integration Patterns by Gregor Hohpe and Bobby Woolf. It discusses how enterprise integration often involves messaging as an alternative to remote procedure invocation, file transfer, and shared databases. Messaging involves program-to-program communication through asynchronous messages sent over channels. Messaging systems support store and forward capabilities and can be language/platform independent. Reasons for using messaging include integration, asynchronous communication, disconnected operation, improved thread utilization, reliability, and throttling. Challenges include complex programming, sequence issues, performance, limited platform support, and vendor lock-in. An example order processing system is described using messaging between different systems. The book covers various messaging patterns.