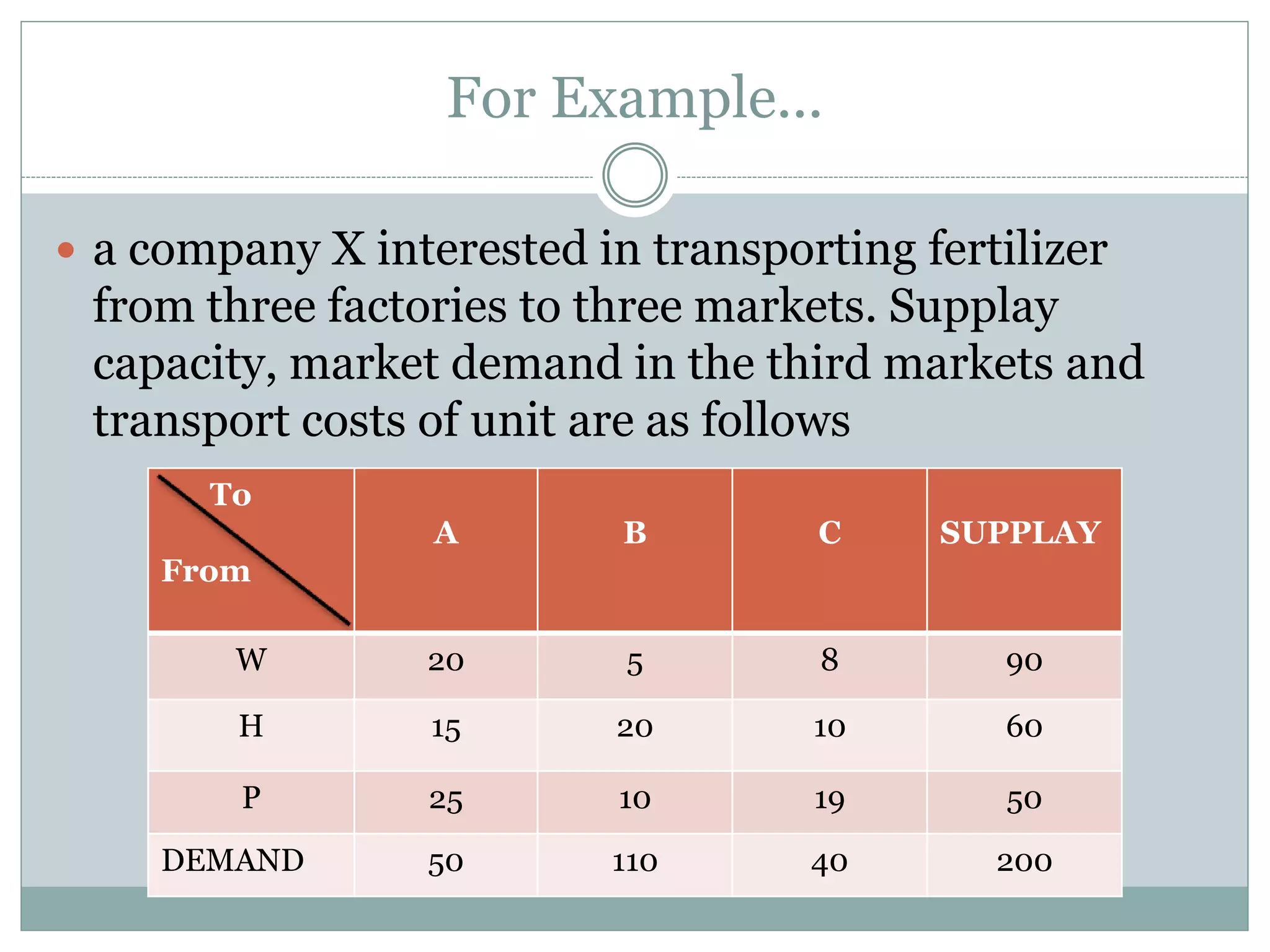
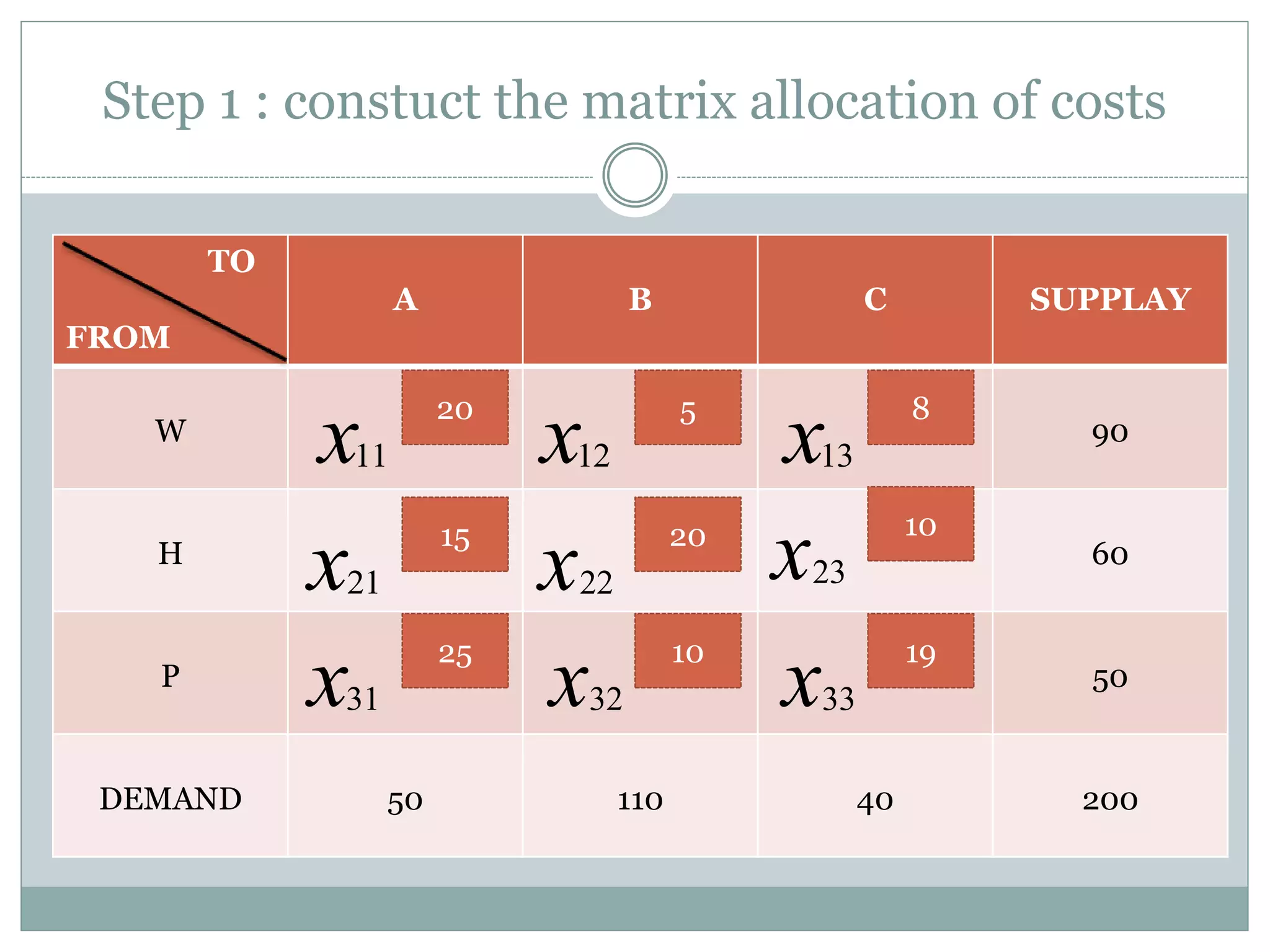
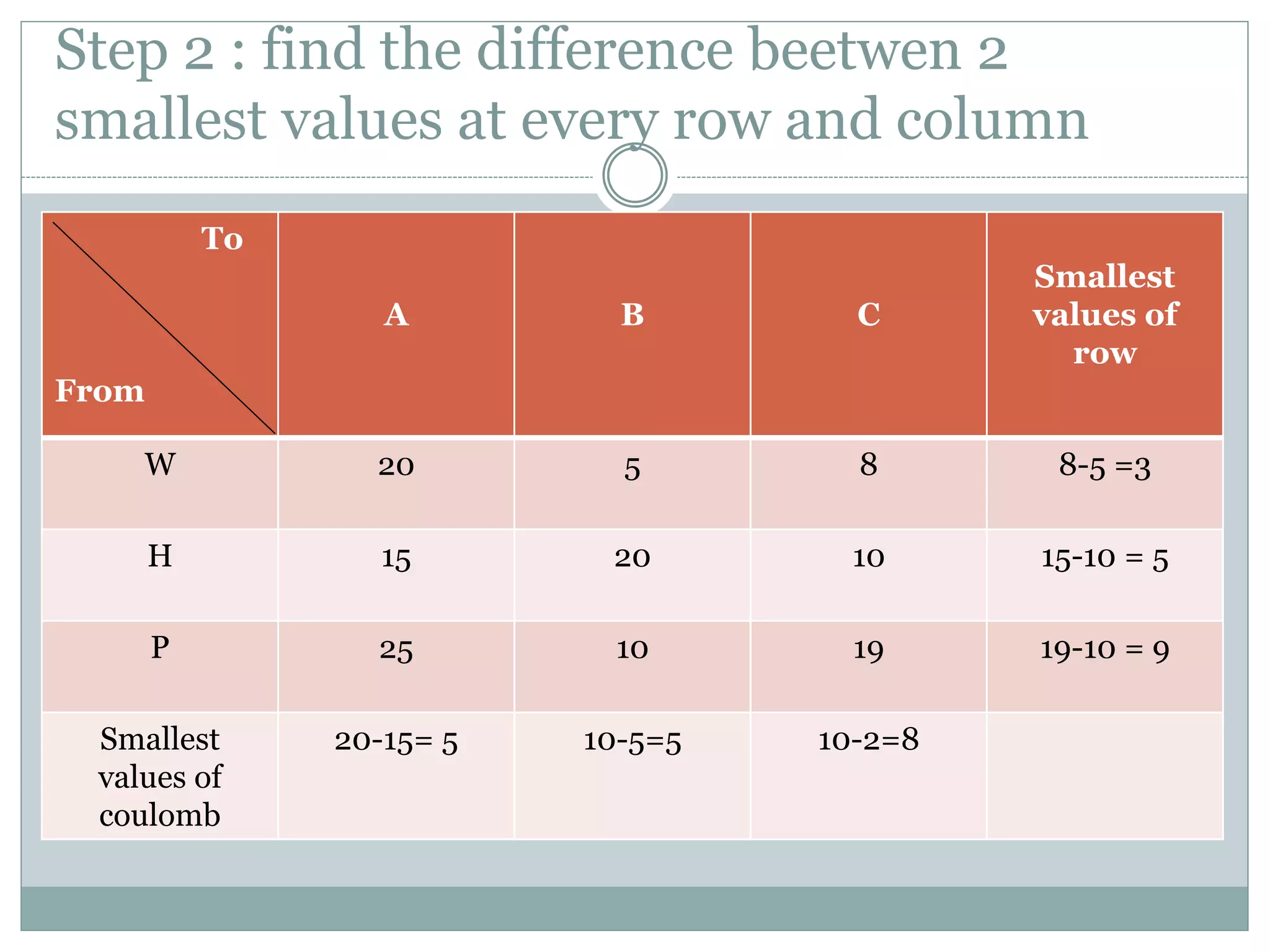
VAM (Vogel's Approximation Method) is a method for allocating resources from multiple sources to multiple destinations in a way that minimizes costs. It involves constructing a matrix of supply, demand, and transportation costs, then iteratively allocating quantities based on the lowest cost options until all supply and demand are balanced. The method is demonstrated on an example of transporting fertilizer from 3 factories to 3 markets, with the transportation costs minimized to a total of 1890 units.