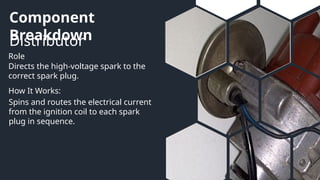
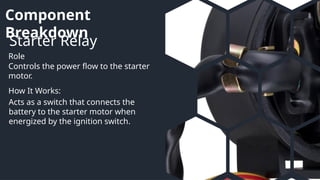
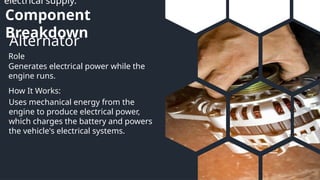
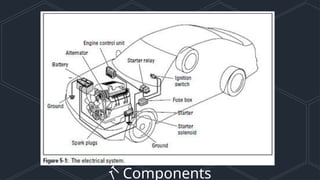
This presentation covers the essential components of automotive and small engine systems, focusing on ignition, starting, charging, and the engine control unit (ECU). It details how each component functions and interacts, emphasizing the ignition process, starting mechanisms, charging system, and the ECU's role in managing engine performance. Diagrams are included to illustrate the connections and workings of these systems.