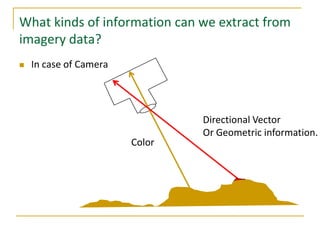
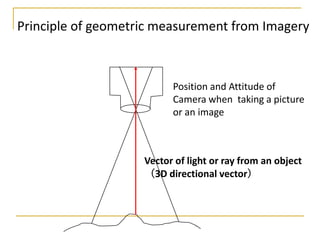
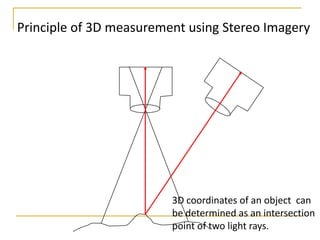
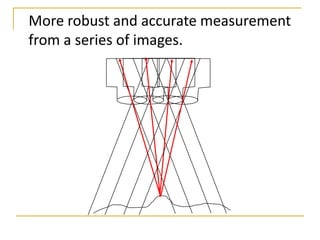
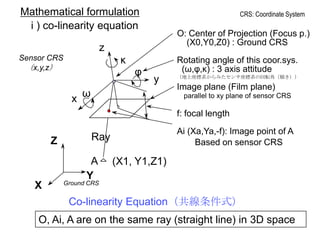
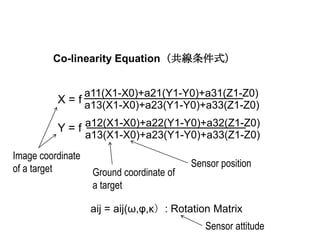
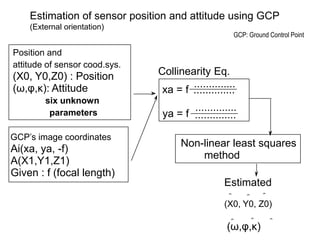
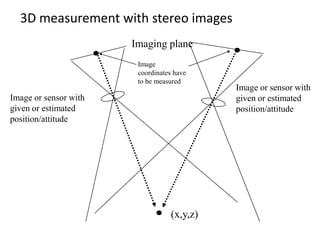
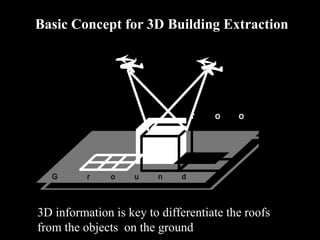
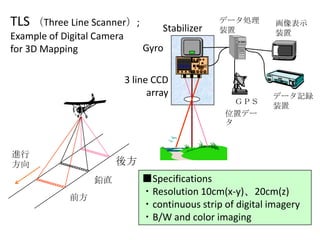
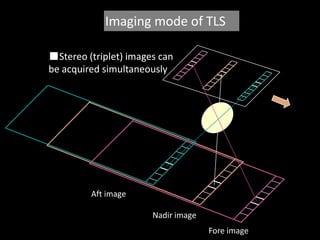
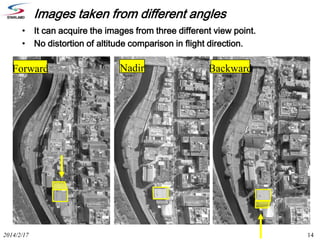
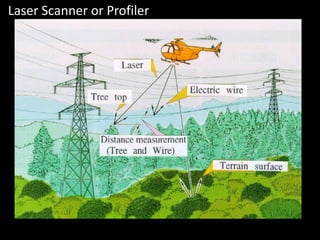
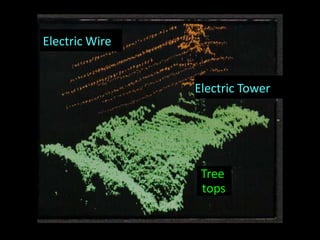
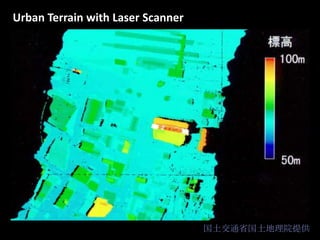
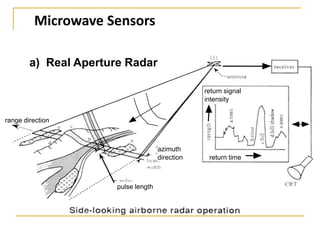
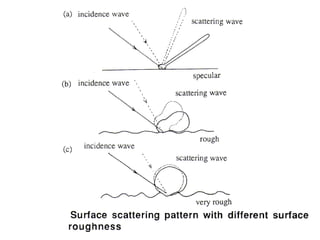
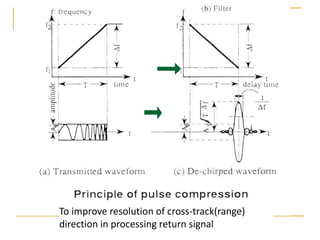
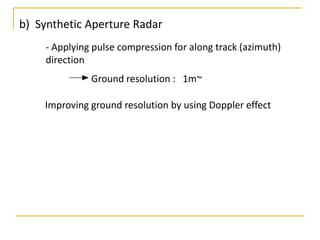
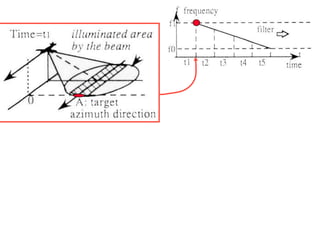
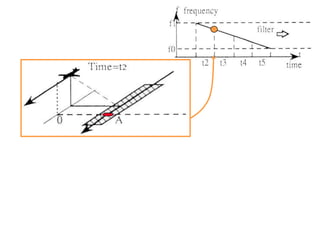
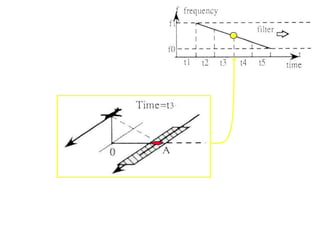
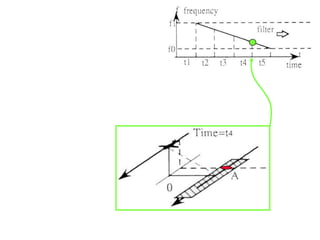
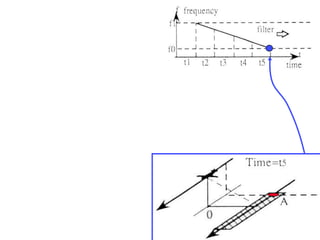
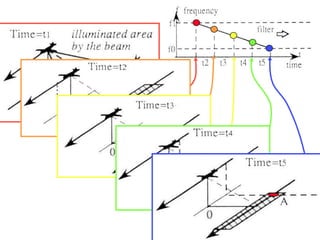
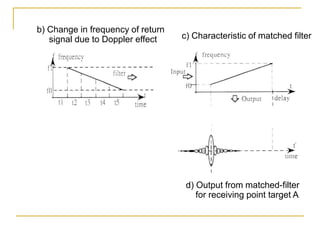
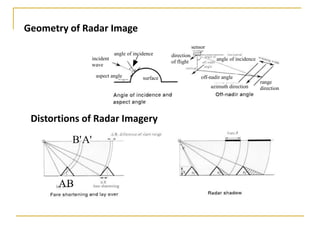
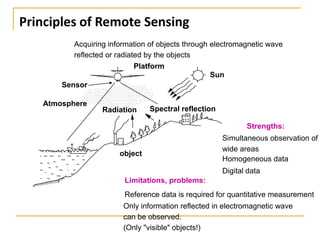
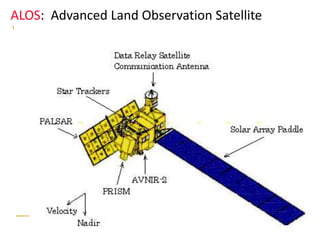
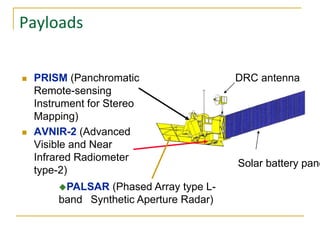
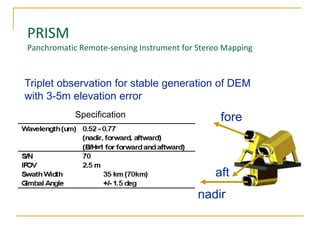
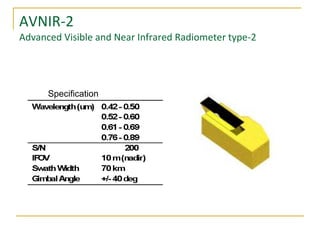
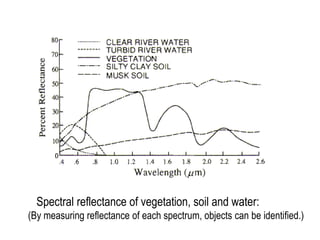
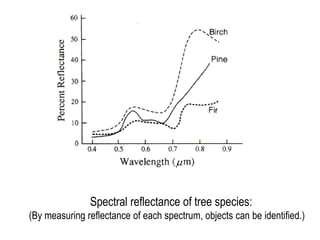
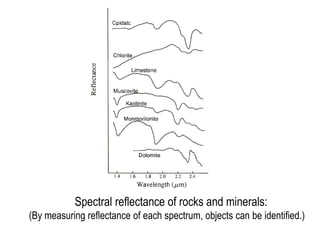
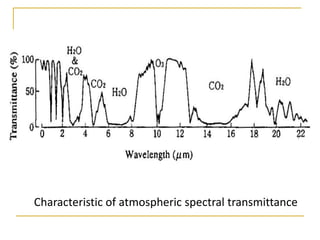
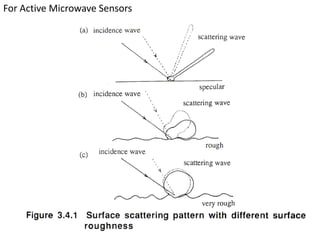
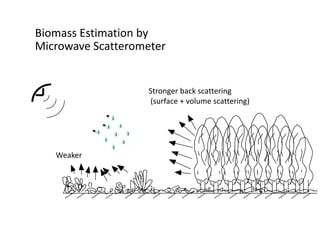
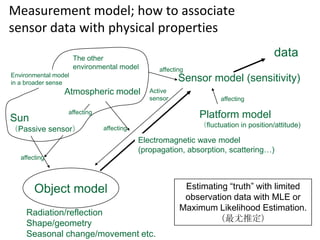
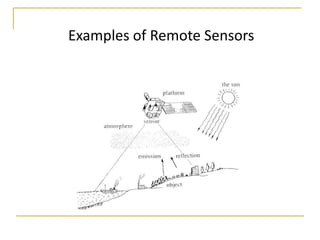
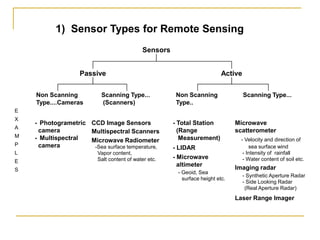
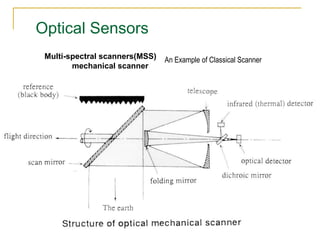
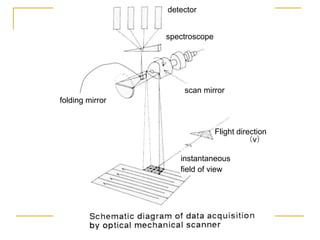
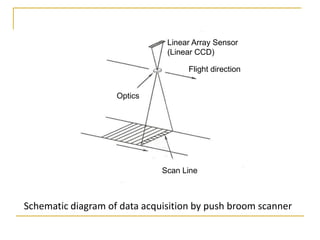
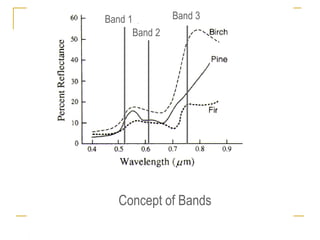
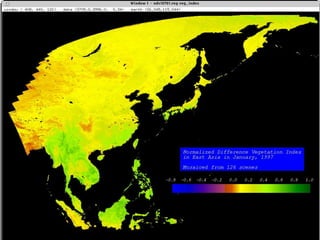
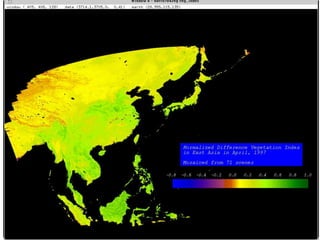
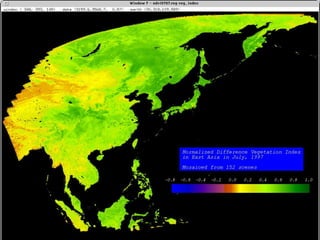
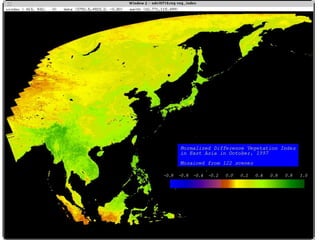
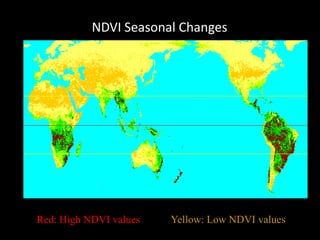
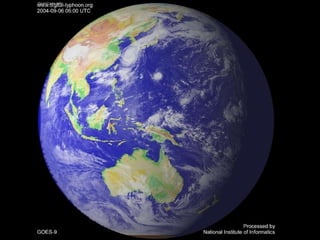
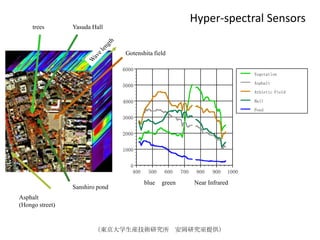
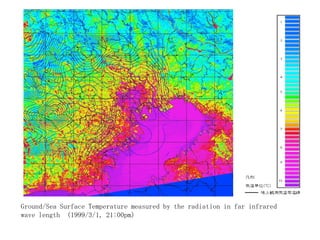
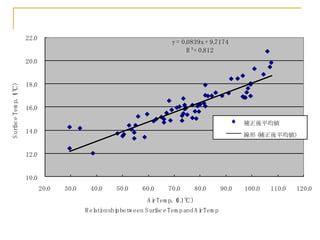
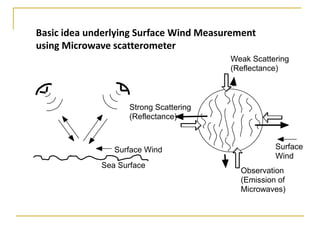
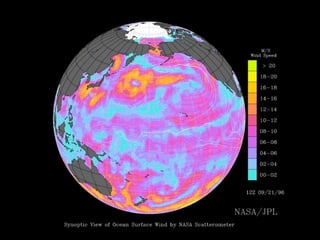
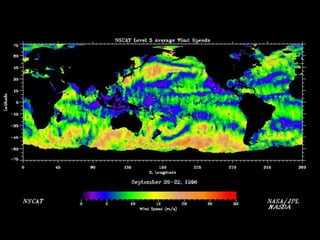
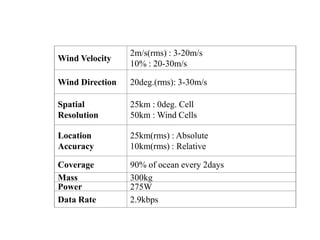
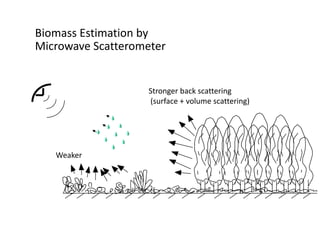
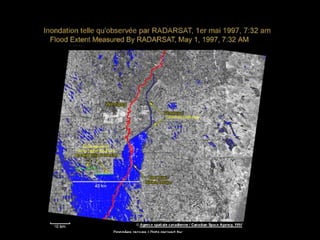
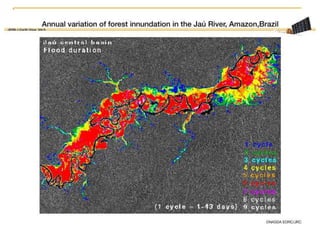
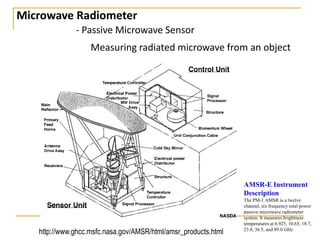
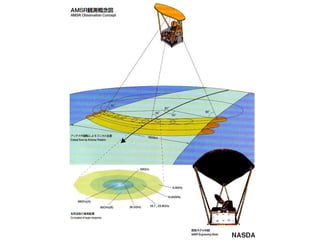
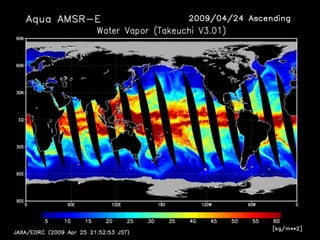
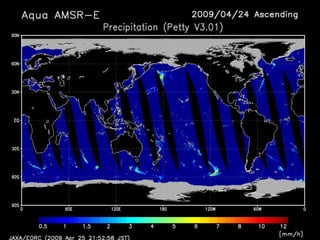
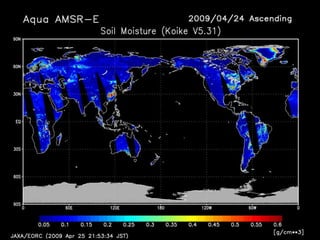
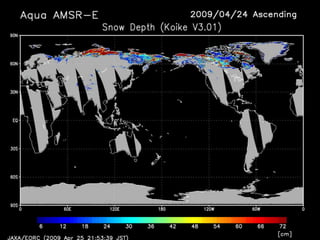
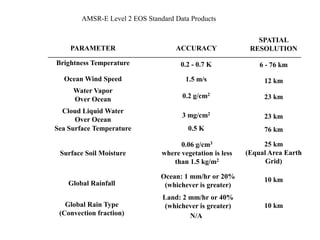
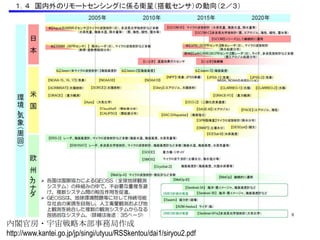
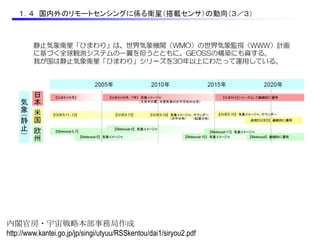
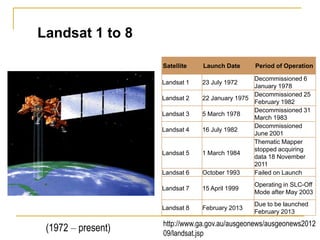
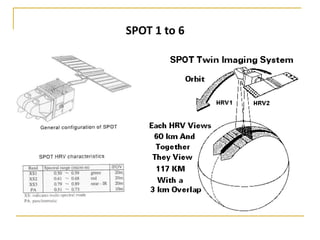
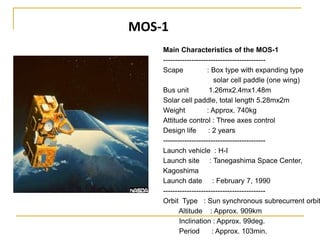
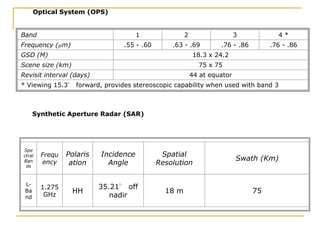
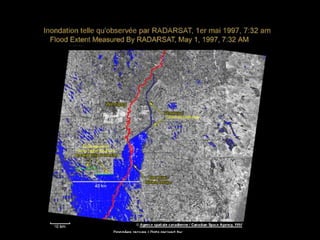
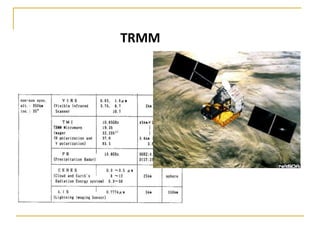
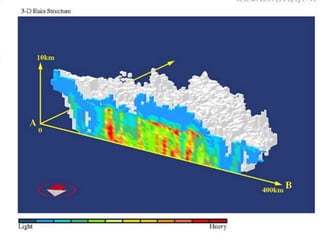
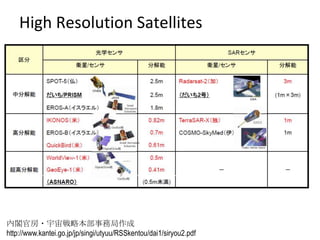
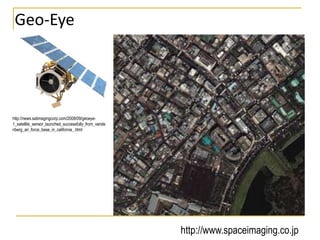
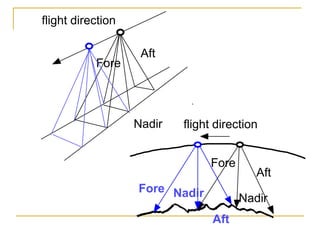
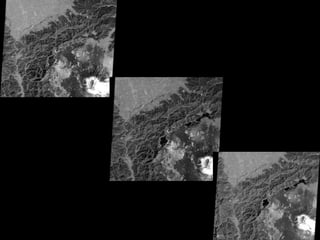
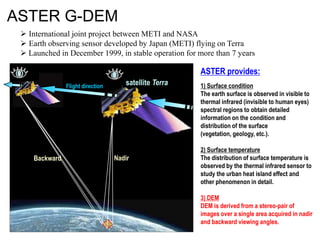
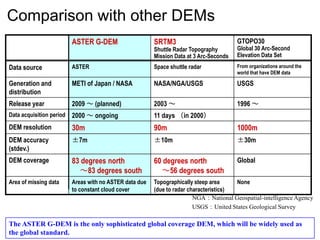
Remote sensing uses sensors on platforms like satellites or aircraft to collect imagery and geospatial data of the Earth. Various sensors can extract different types of information like color, geometry, or 3D coordinates using principles like stereo imagery. Mathematical models like collinearity equations relate image coordinates to ground coordinates. Sensor position and attitude can be estimated using ground control points. 3D measurements are possible with stereo imagery. Different sensor types exist for applications like vegetation monitoring, land use mapping, and disaster monitoring.