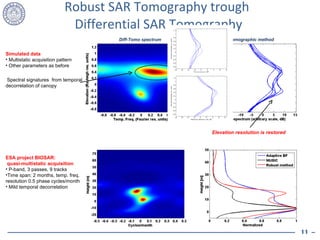
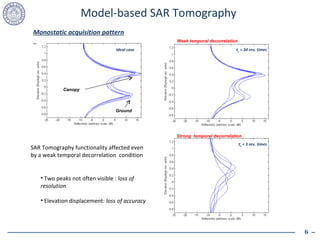
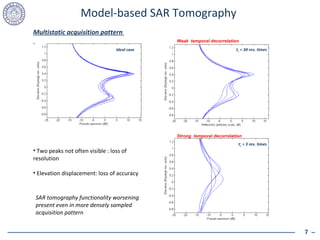
1. Temporal decorrelation effects from scatterer motion can severely degrade the performance of SAR tomography by causing loss of elevation resolution and accuracy.
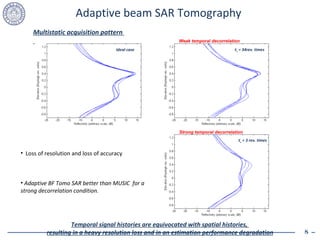
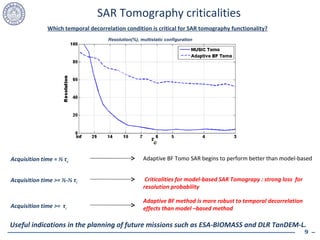
2. Model-based SAR tomography is more strongly affected by temporal decorrelation compared to adaptive beamforming tomography. Acquisition time spans greater than half the decorrelation time can critically impact performance.
3. Differential tomography is proposed as a new approach that accounts for temporal changes and can extract elevation information more robustly even in temporally decorrelating scenes. It shows potential to improve SAR tomography for future spaceborne missions.

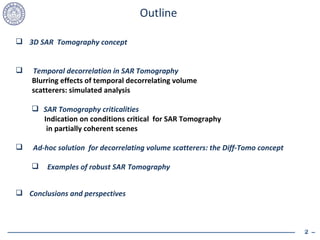
![3D SAR Tomography concept flight direction b N b n b 1 s, elevation z y ( b 1 ) y ( b n ) y ( b N ) Range-azimuth cell Azimuth Ground range Signal spatial sample at baseline b n : Define an elevation-dependent spatial frequency: 1-D Fourier relation Tomo-SAR can localize the multiple scatterers through spatial spectral estimation (i.e. elevation beamforming) Applications: solving InSAR layover heights and reflectivity misinterpretation in urban areas estimation of forest biomass and height sub-canopy topography soil humidity and ice thickness monitoring [Reigber-Moreira, IEEE-TGARS ’00] Complex amplitude elevation distribution However… Limited and sparse baseline distribution, poor Fourier imaging quality Proposed solutions: adaptive beamforming, SVD, spatial interpolators (compressed sensing)… [Lombardini-Reigber, IGARSS ‘03] [Fornaro-Serafino-Soldovieri, IEEE-TGARS ’03] [Lombardini-Pardini, IEEE-GRSL ‘08] Elevation blurring problems from scatterers motion and temporal decorrelation ! NASA-JPL and ESA recognized this as a major limiting factor (forest scatterers and spaceborne acquisitions)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cailomvergold2010-100429092409-phpapp02/85/Cai-lomver-gold2010-3-320.jpg)
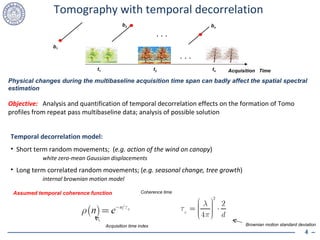
![Tomographic analysis: scenario and methods Temporal decorrelation model from [Lombardini-Griffiths, IEE-EUREL ’98] Baseline-time acquisition pattern Long term temp. dec. c = 3 rev. times Different temporal decorrelation conditions for temporal decorrelating canopy Long term temp. dec. c = 34 rev. times Analysis of a model based and adaptive BF Tomo SAR methods, useful for critical resolutions Simulated analysis: forest scenario Compact scatterer (ground) + volumetric scatterer (canopy) Different baseline-time acquisition pattern: monostatic and multistatic Height distance: 0.7 Rayleigh res. Units g/v = 1/5 (L-band acquisition) Total SNR = 15dB 16 looks Different temporal decorrelation processes Weak Strong Satellite cluster](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cailomvergold2010-100429092409-phpapp02/85/Cai-lomver-gold2010-5-320.jpg)
![A new approach: the Differential SAR Tomography framework Point-like scatterer in height Uniform motion (l.o.s. direction) spatial harmonic temporal harmonic Discrete space-time spectrum Temporal frequencies code velocities Example: subsidence in urban layover areas Extended scatterers in height Range of velocities spatial harmonic distribution temporal harmonic distribution Continuous space-time spectrum Temporal frequencies code velocities Example: a glacier flow (sliding random volume over ground) Temporal decorrelation of a scattering component temporal harmonic distribution Temporal frequencies are signatures of the temporal decorrelation ! [Lombardini-Fornaro, IGARSS’05] [Fornaro-Serafino-Reale, IEEE-TGARS’09] [Lombardini, ESA FRINGE Wrkshp’07] Diff-Tomo exploits the multibaseline-multitemporal information content to enter the SAR pixel and extract separated information on elevation and velocity of multiple superimposed scatterers [Lombardini, TGARS Jan. 2005] “ Diff-Tomo” is a new interferometric mode, which avoids the misinterpretation of spatial signal histories (scatterers location) and temporal histories in non-stationary scenarios Temporal signal histories from decorrelation can be decoupled from the spatial spectral estimation . D-InSAR and Tomo-SAR crossed in an unified framework Joint elevation-velocity resolution of multiple scatterers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cailomvergold2010-100429092409-phpapp02/85/Cai-lomver-gold2010-10-320.jpg)