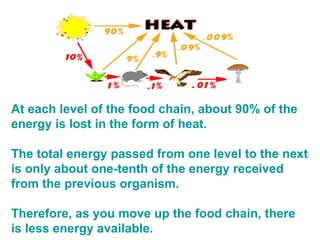
At each level of the food chain, about 90% of the energy from the previous organism is lost as heat. As a result, only about 10% of the energy is transferred to the next level, meaning there is less energy available at higher levels of the food chain. This is illustrated by an example where the sun provides 1000ml of "energy" but by the time it reaches decomposers like mushrooms, only 0.1ml remains.