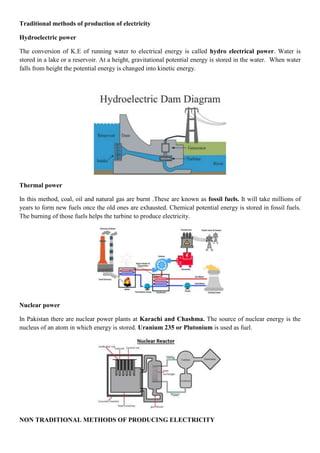
The document discusses various aspects of energy, including its definition, forms, demand, and production methods. Key topics covered include work and energy calculations, the environmental impact of energy consumption, and the measurement of energy in different units. It highlights both traditional and non-traditional methods for generating electricity, emphasizing the need for sustainable energy sources to mitigate environmental degradation.