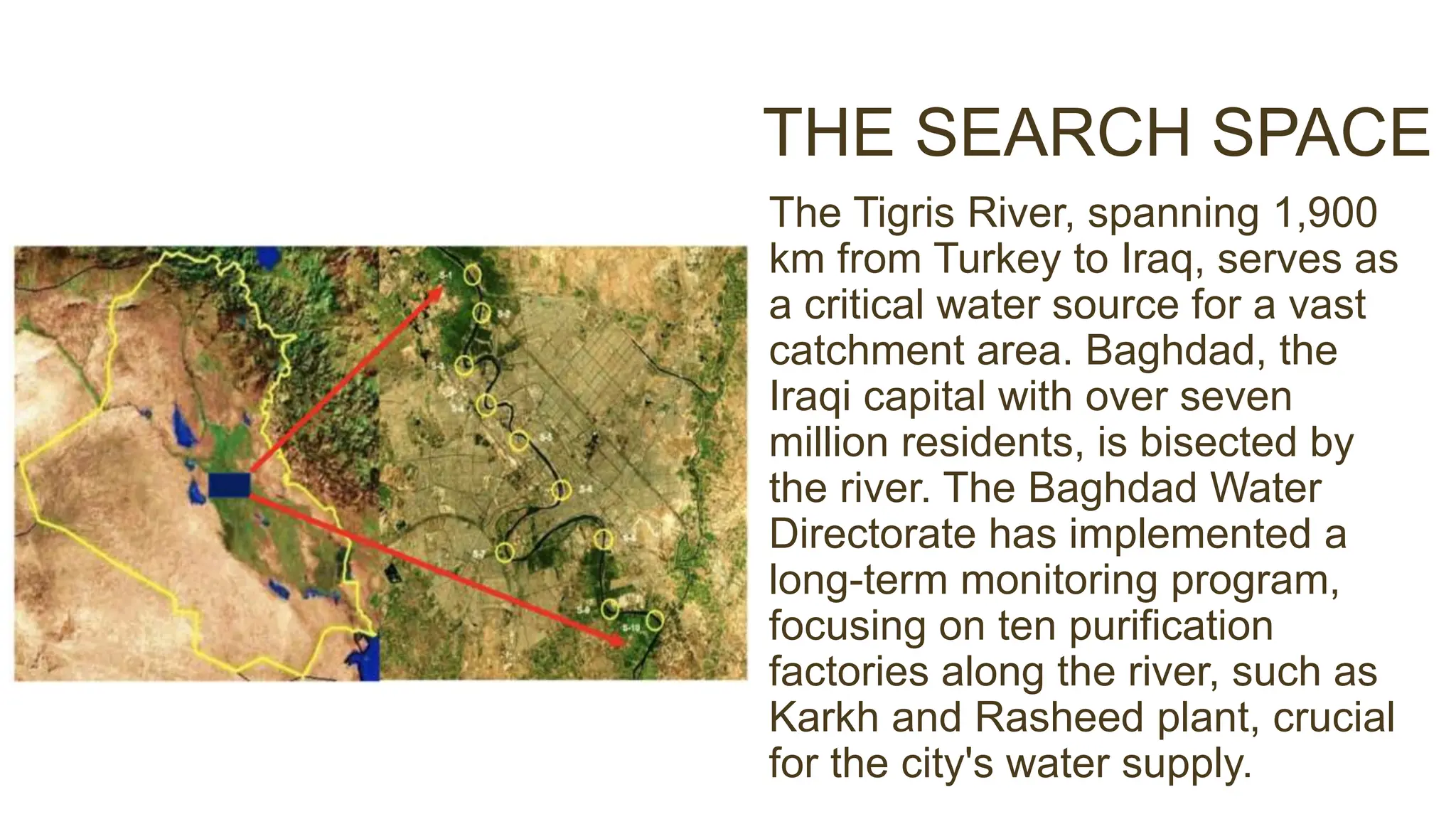
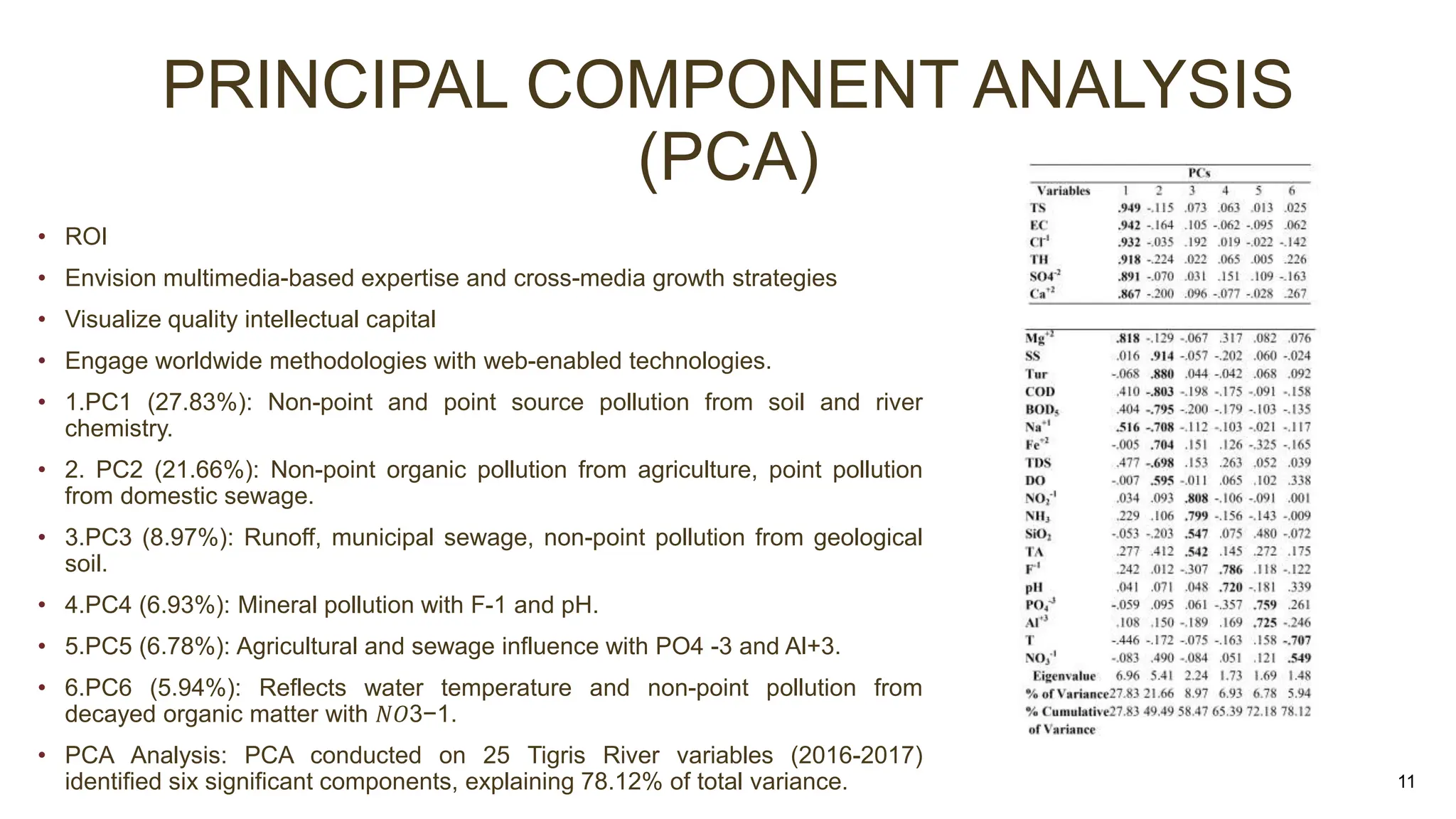
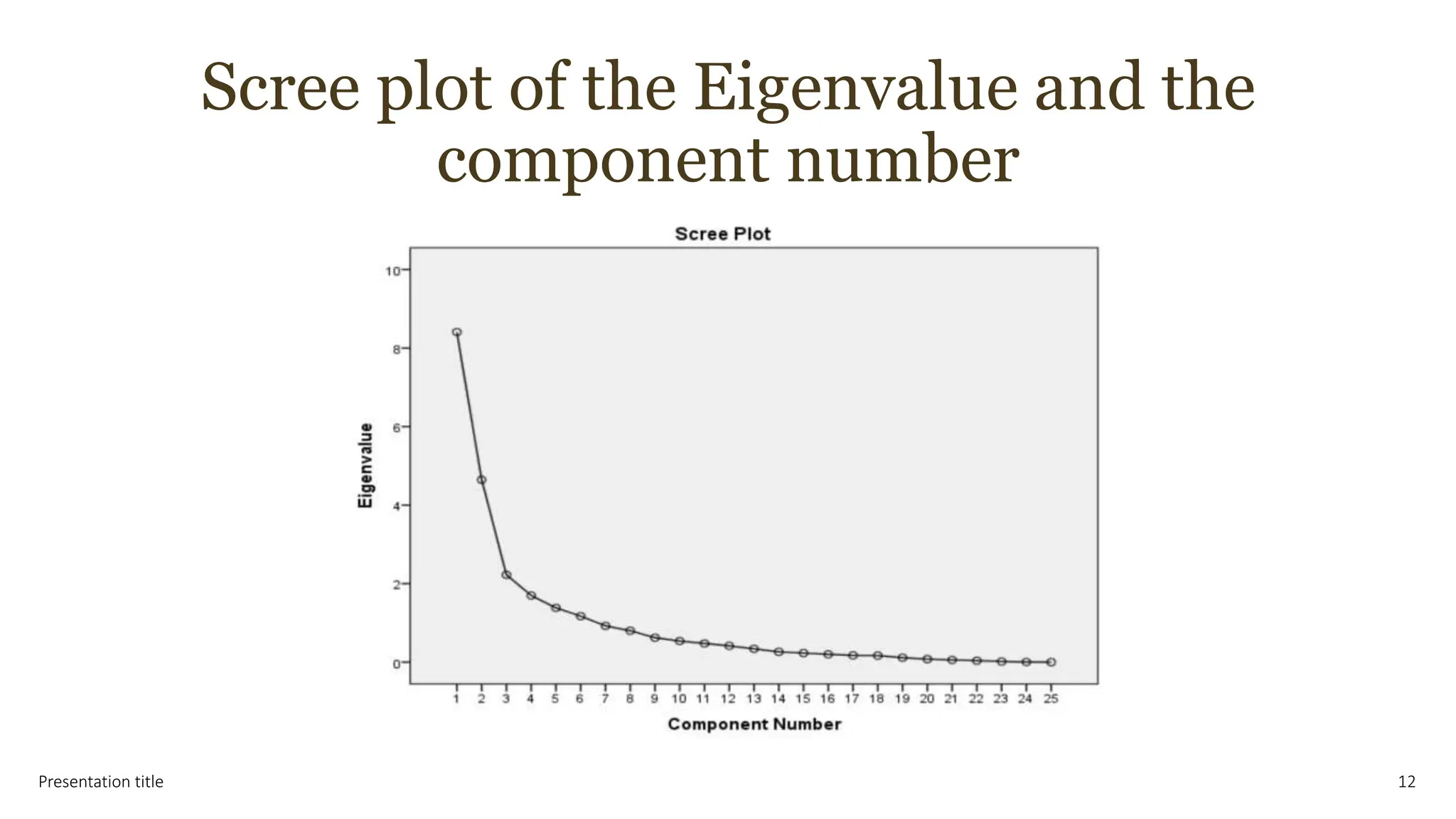
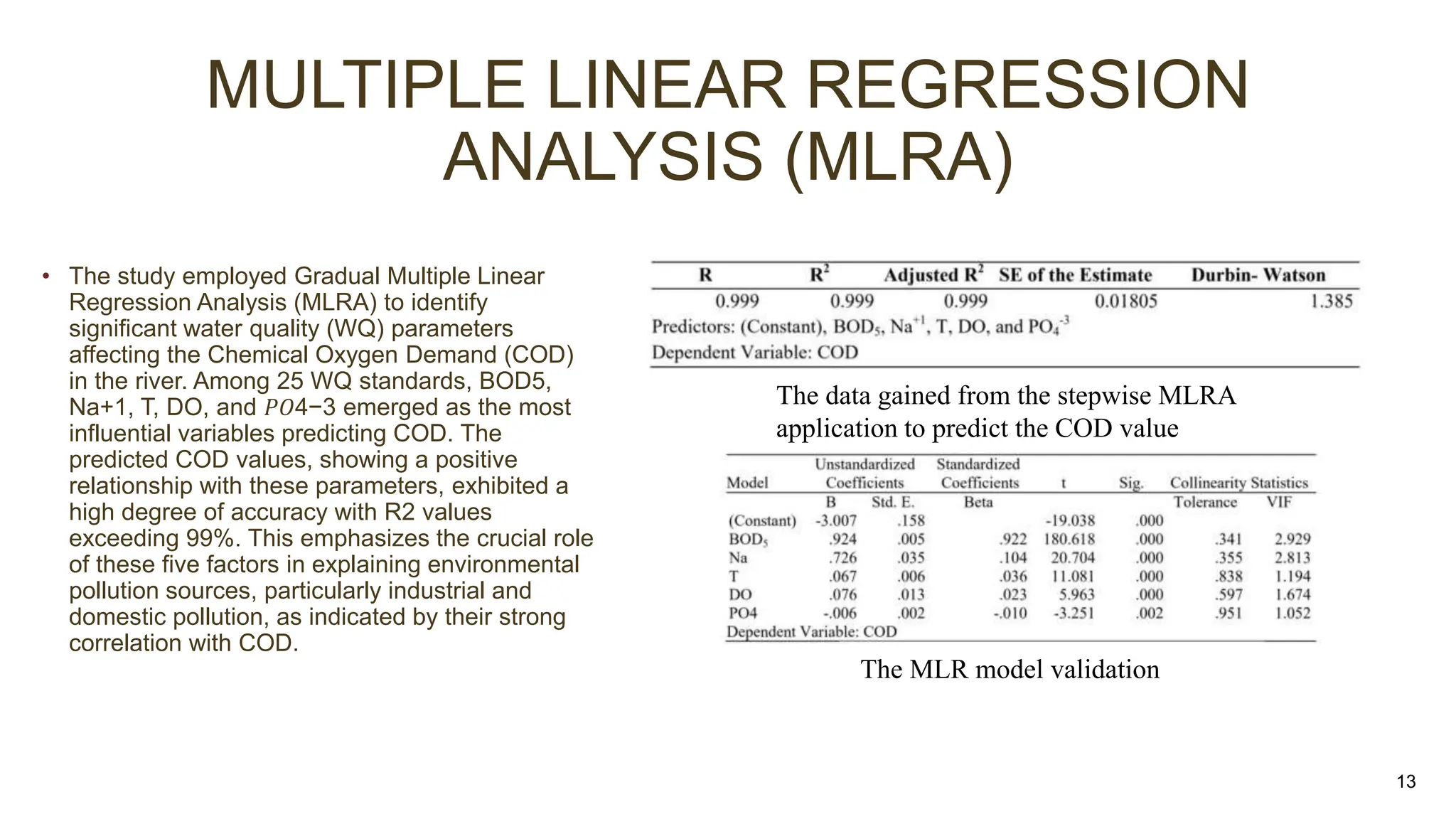
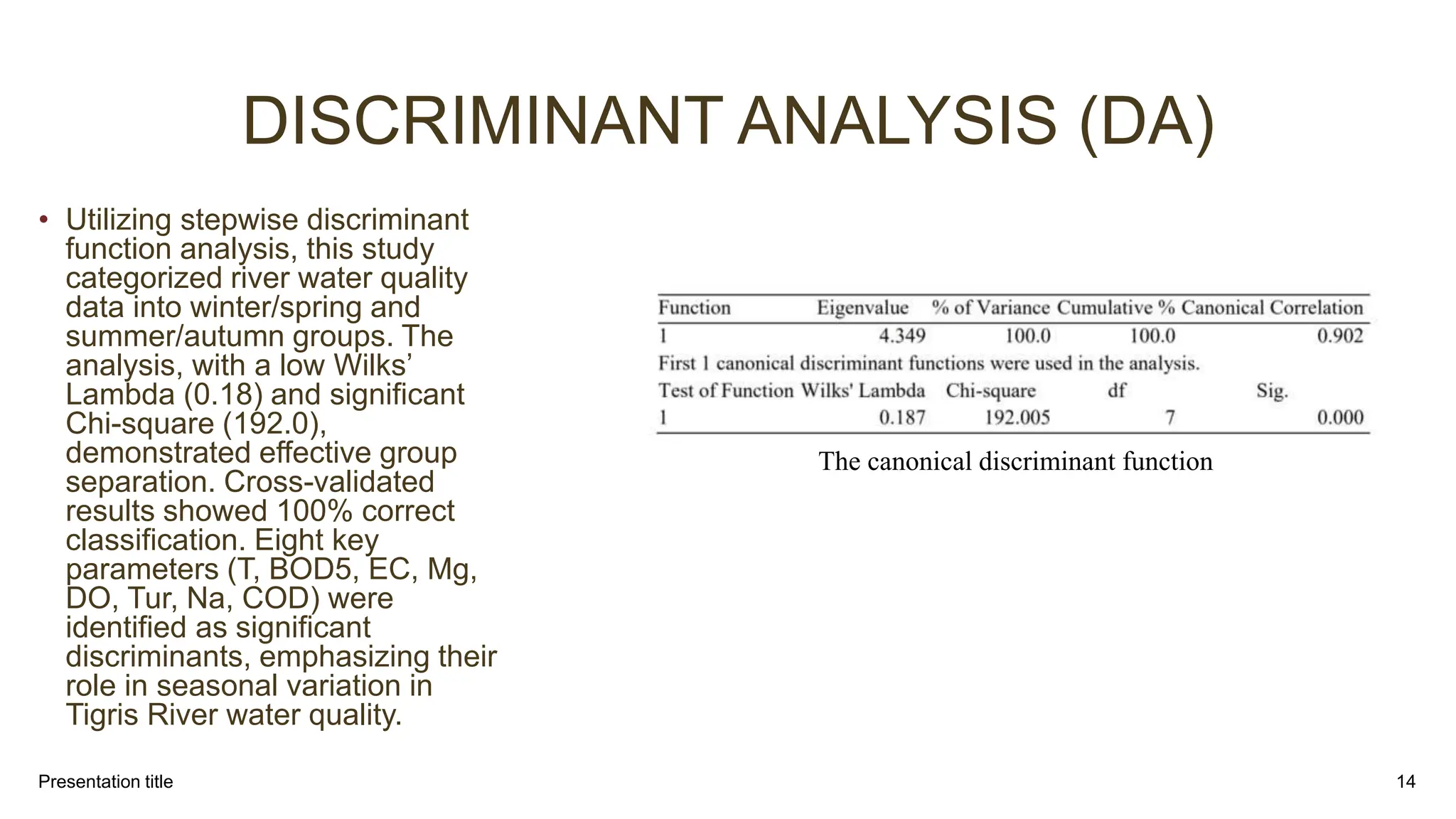
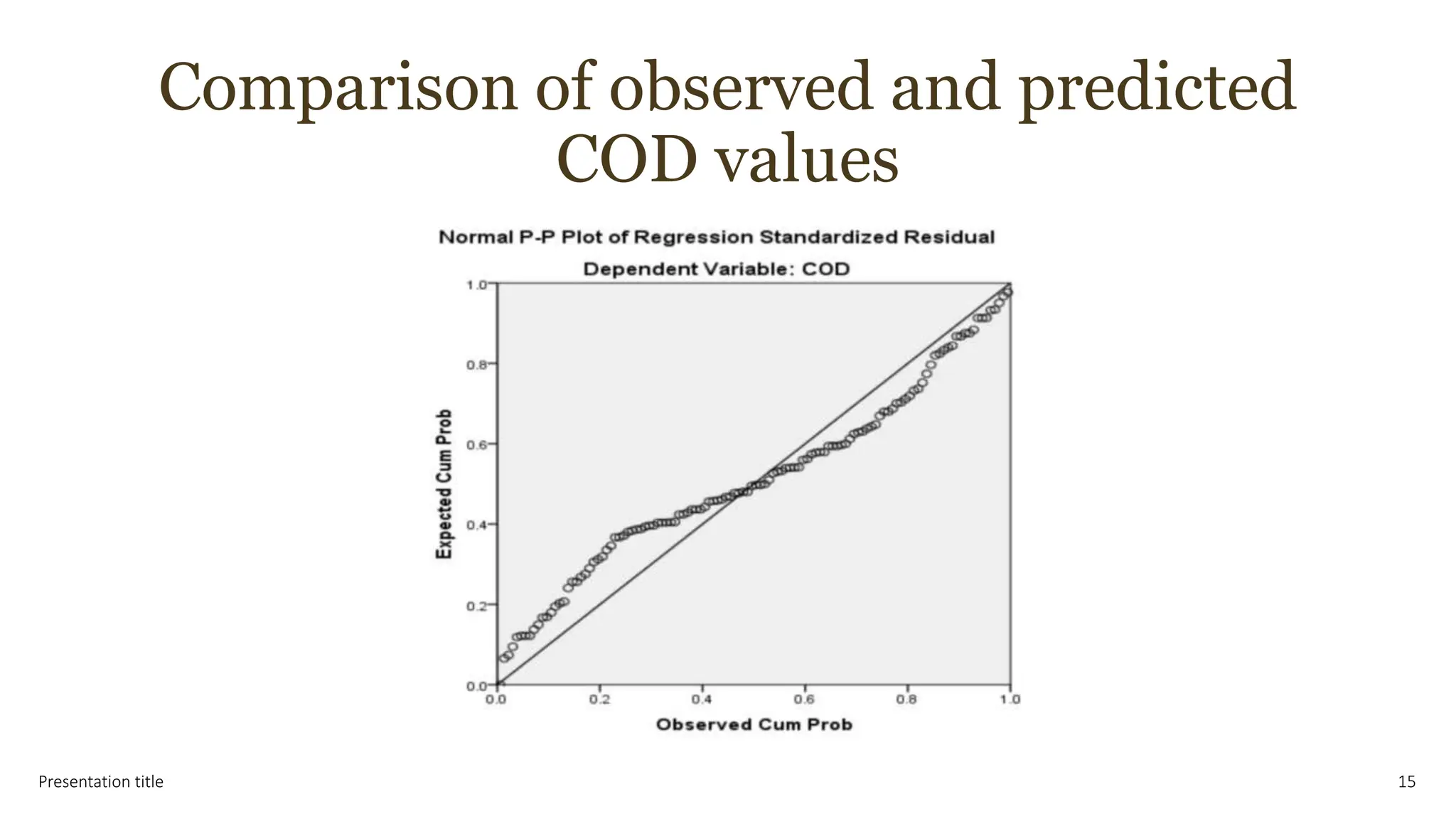
This document presents the results of a study evaluating water quality in the Tigris River in Baghdad, Iraq using multivariate statistical techniques. Principal component analysis identified six significant components explaining 78.12% of variance in water quality parameters. Discriminant analysis effectively classified water quality data into winter/spring and summer/autumn groups and identified eight key parameters influencing seasonal variations. Multiple linear regression analysis revealed five parameters - BOD5, Na+, T, DO, and PO4-3 - as most influential in predicting chemical oxygen demand, emphasizing their role in pollution from industrial and domestic sources. The multivariate statistical analyses provided valuable insights for managing water quality parameters and preserving the river ecosystem.