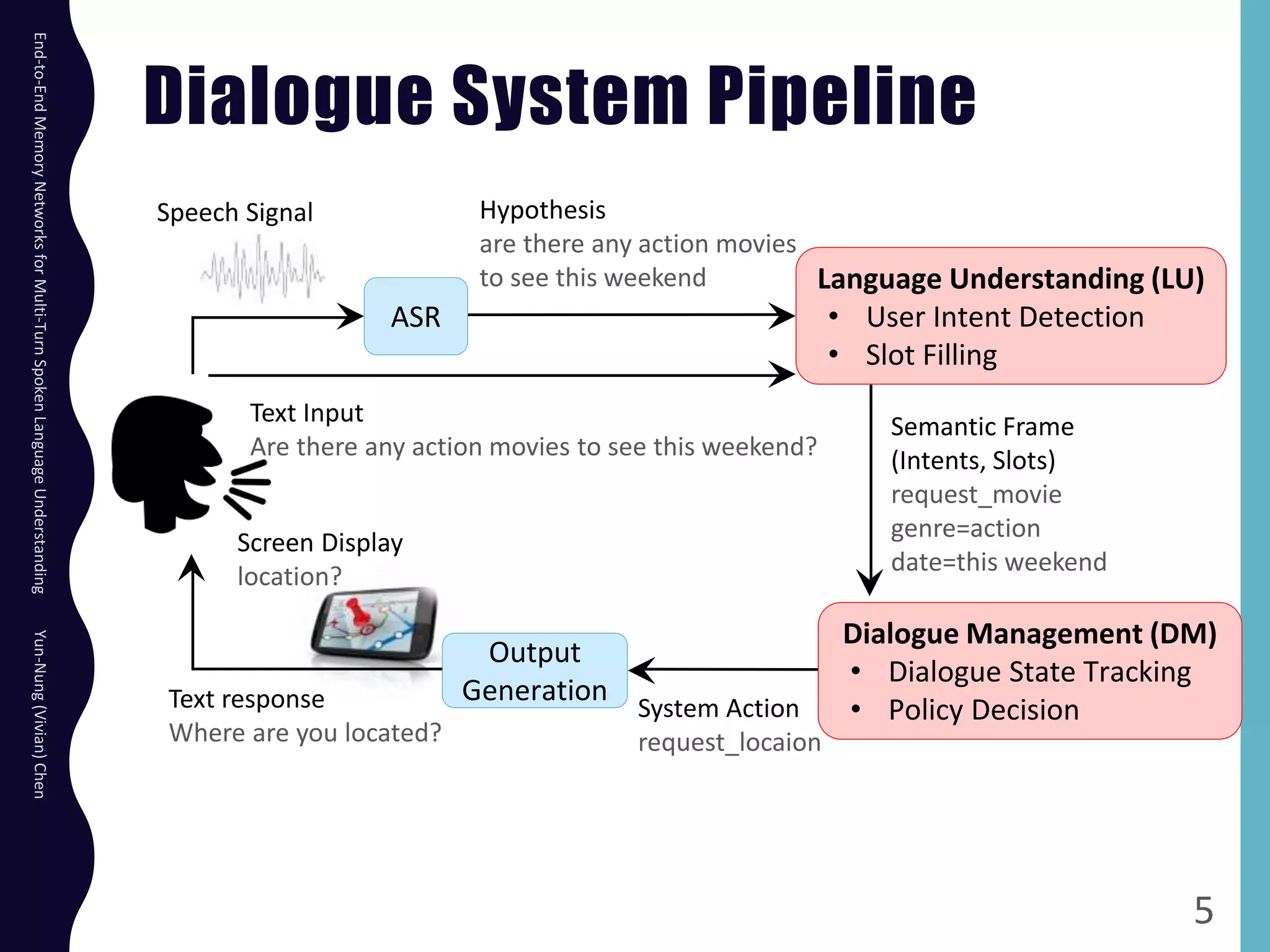
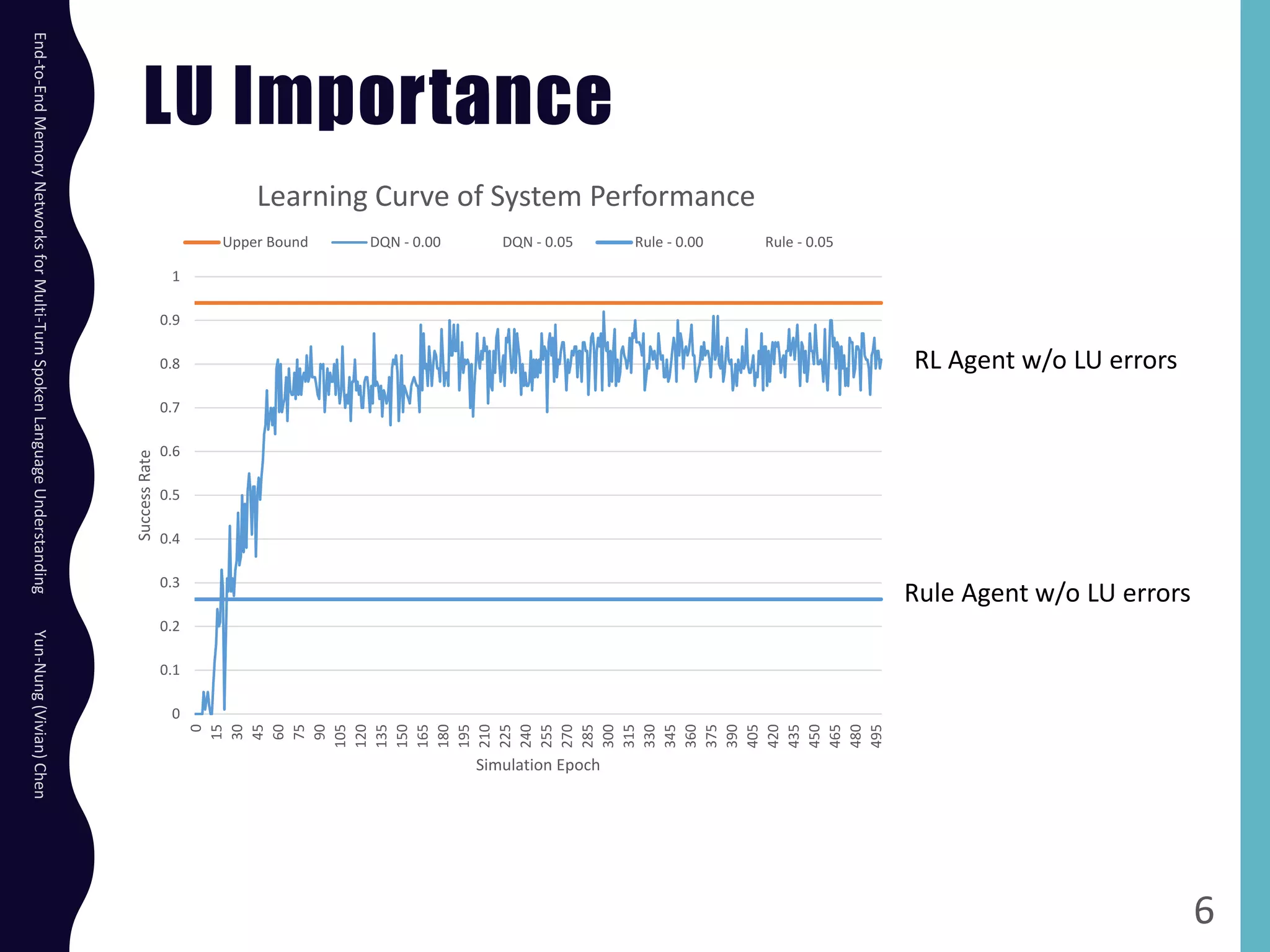
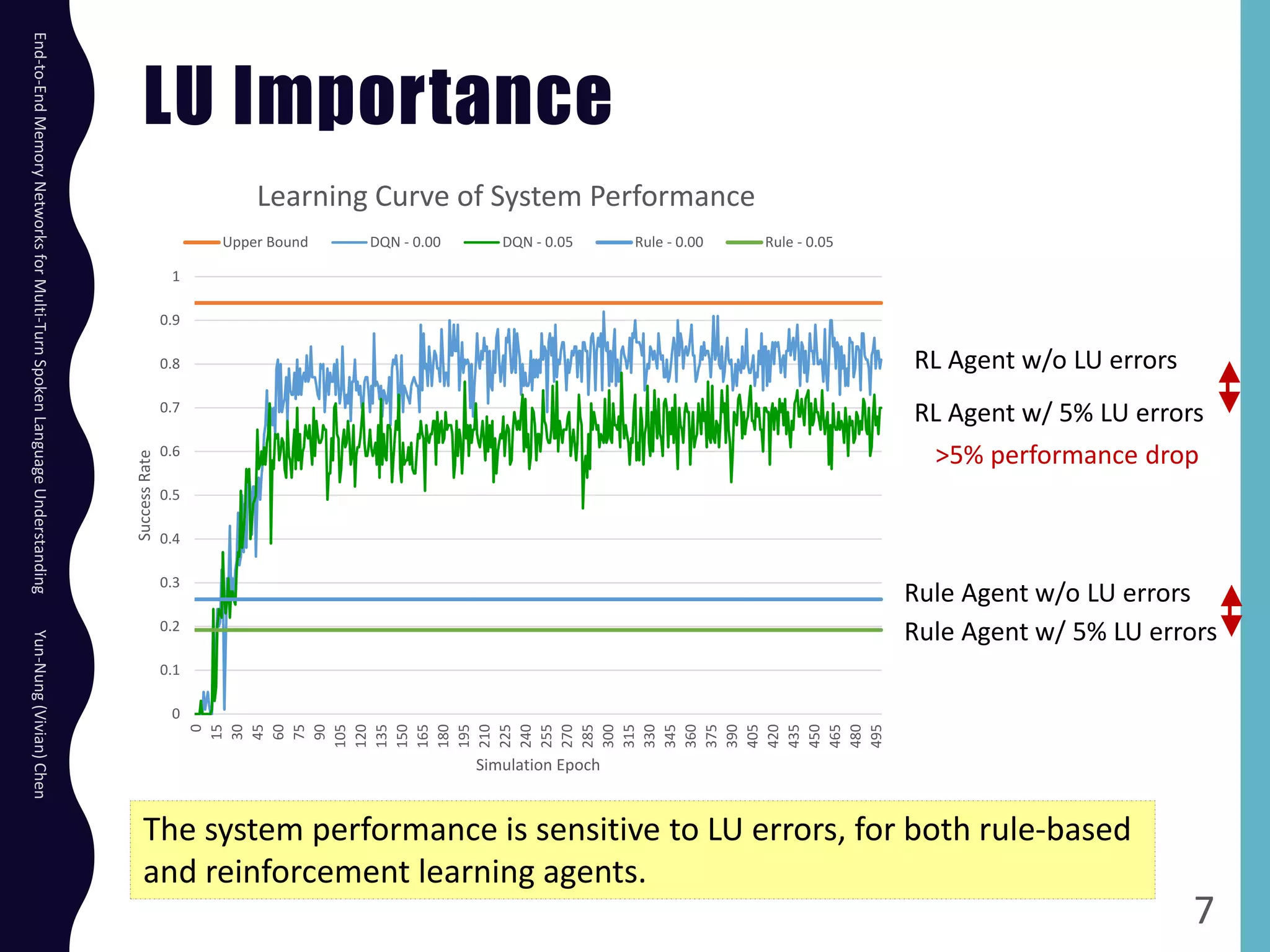
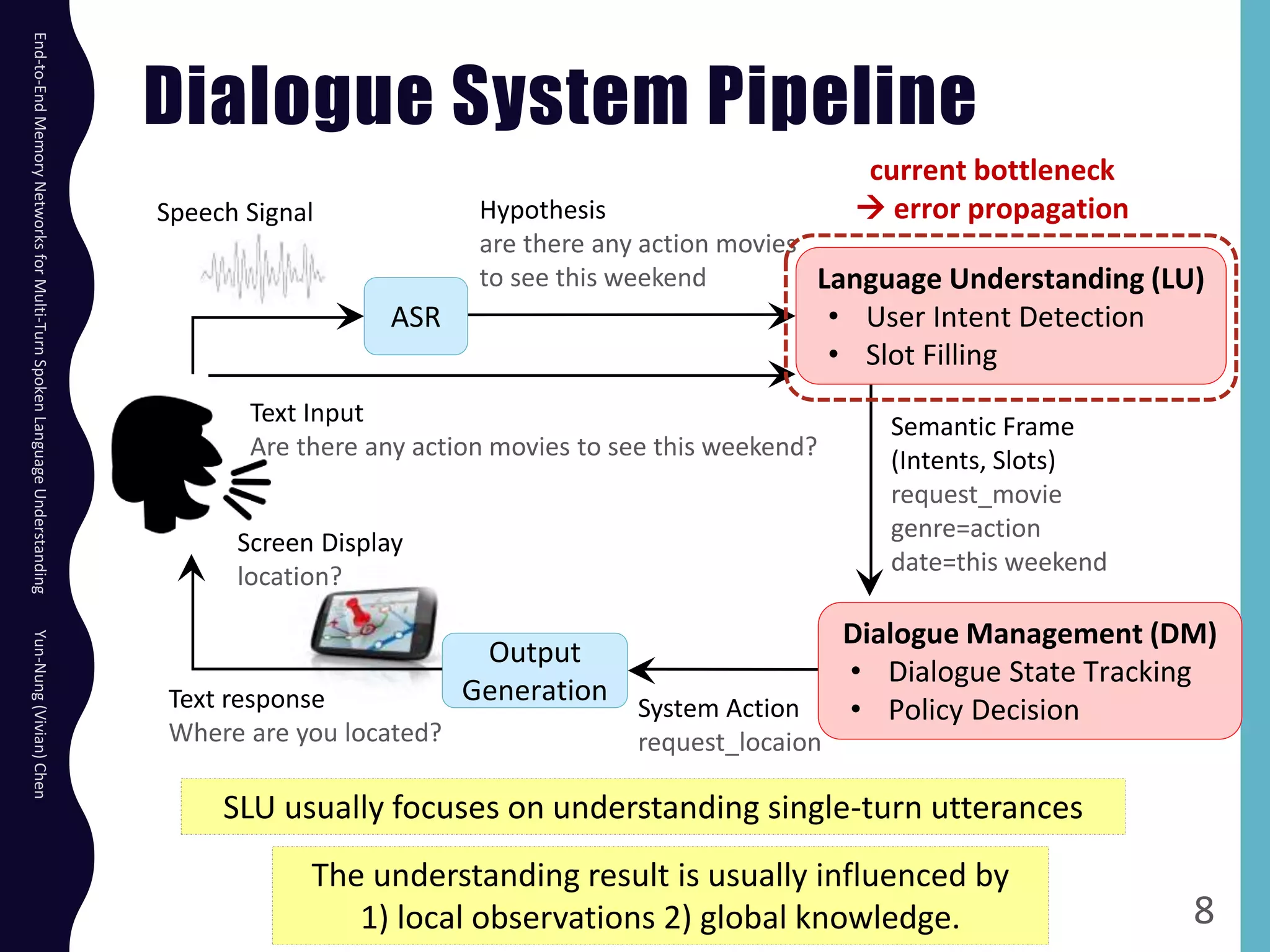
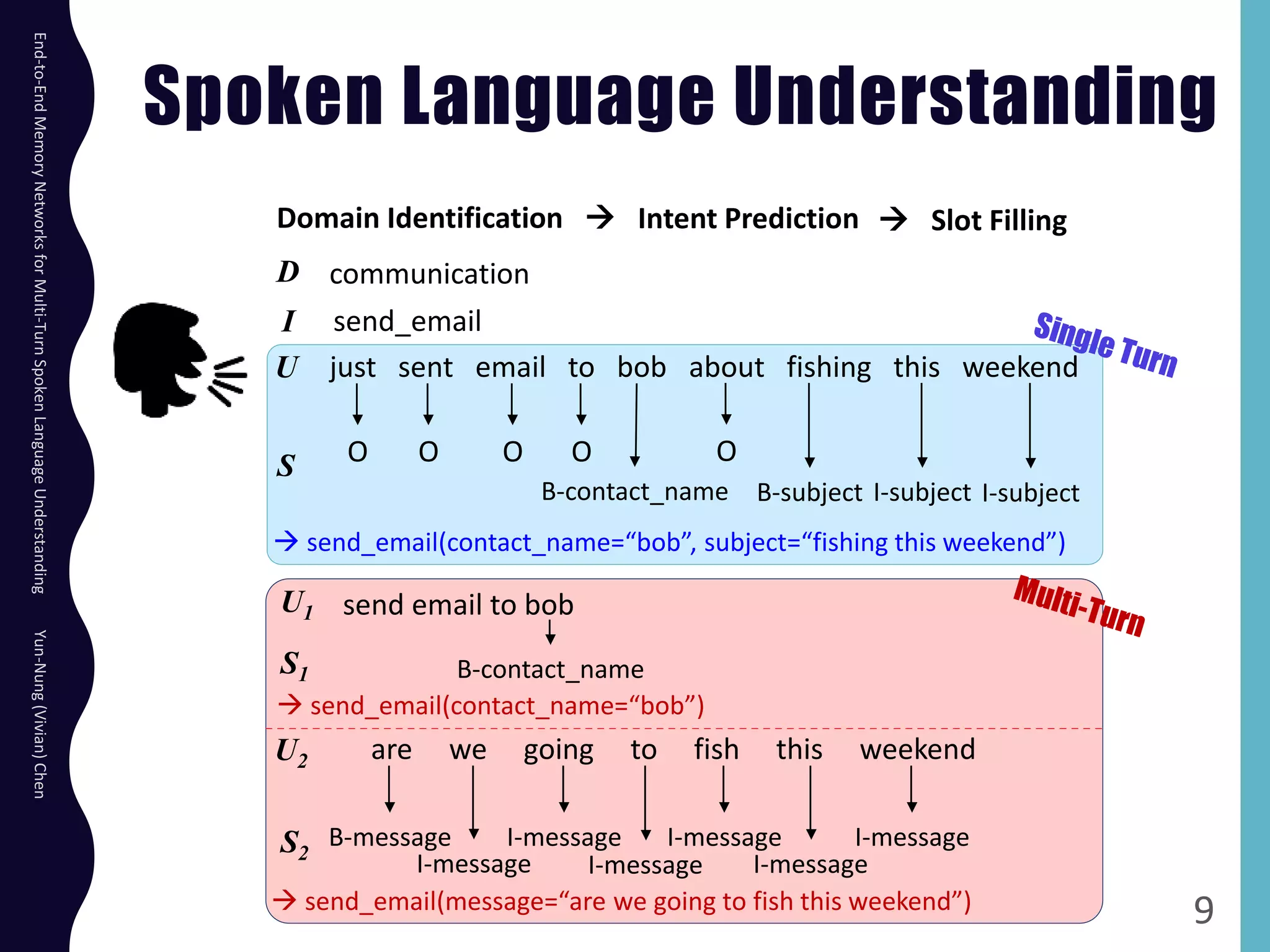
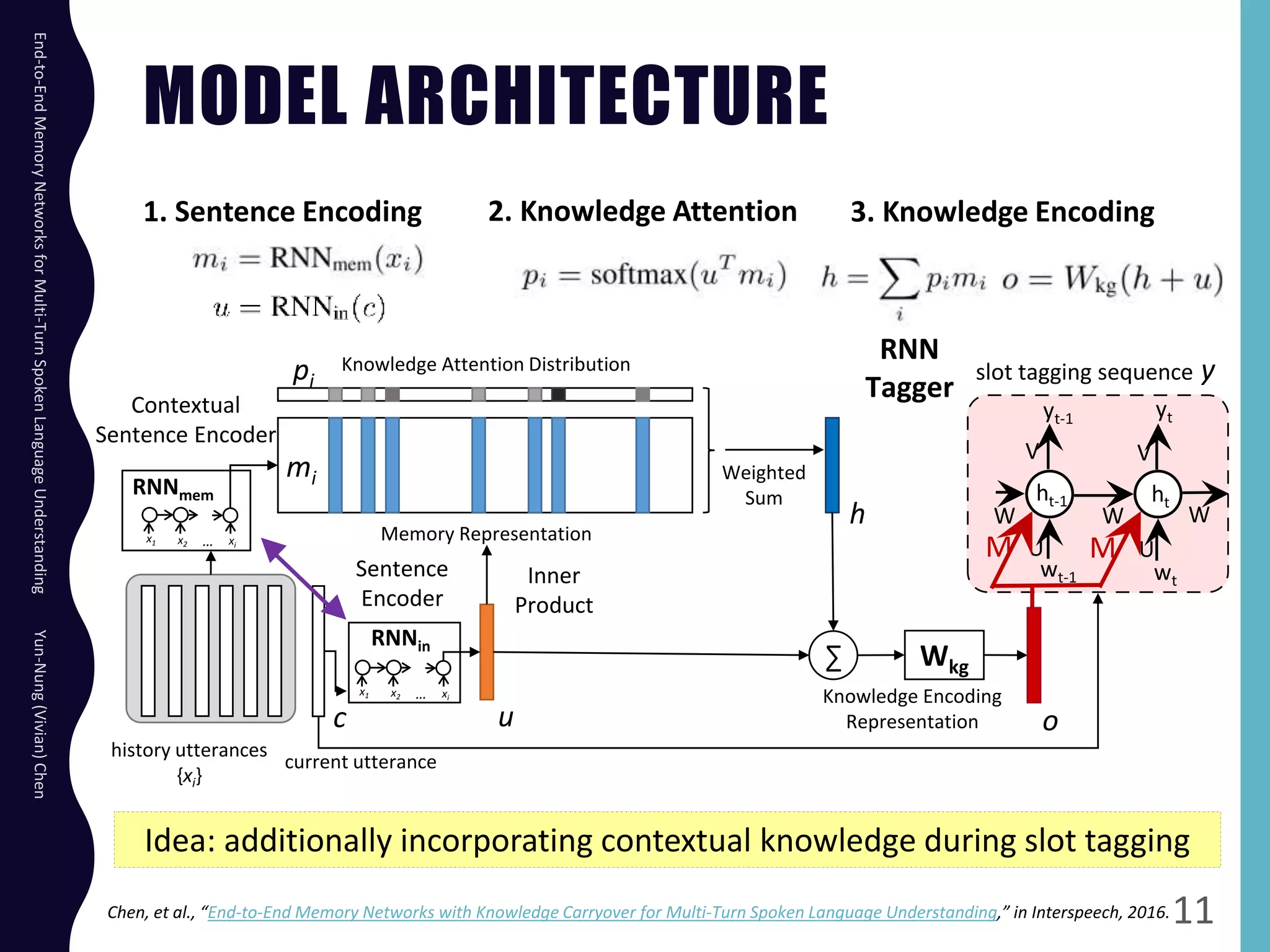
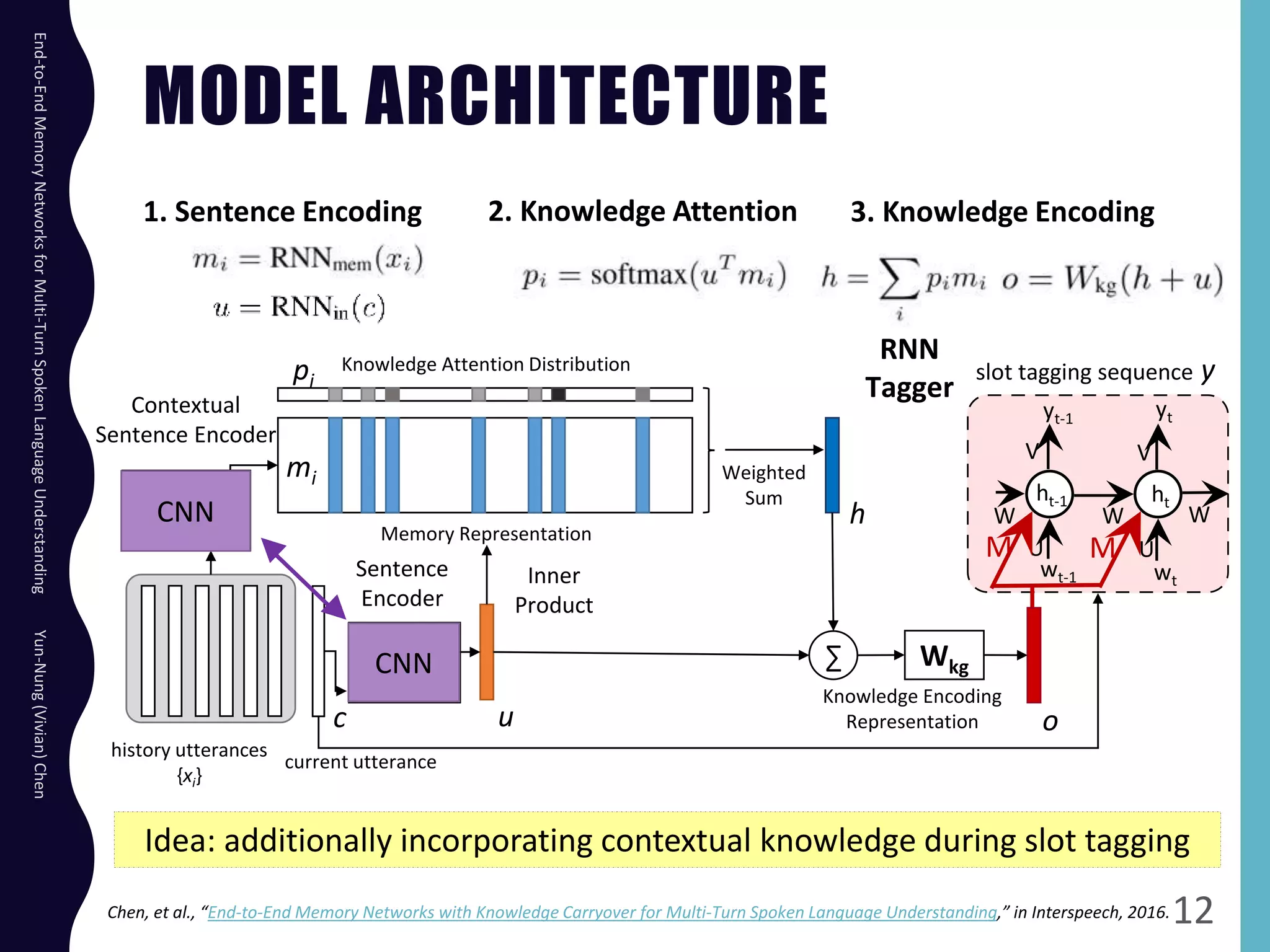
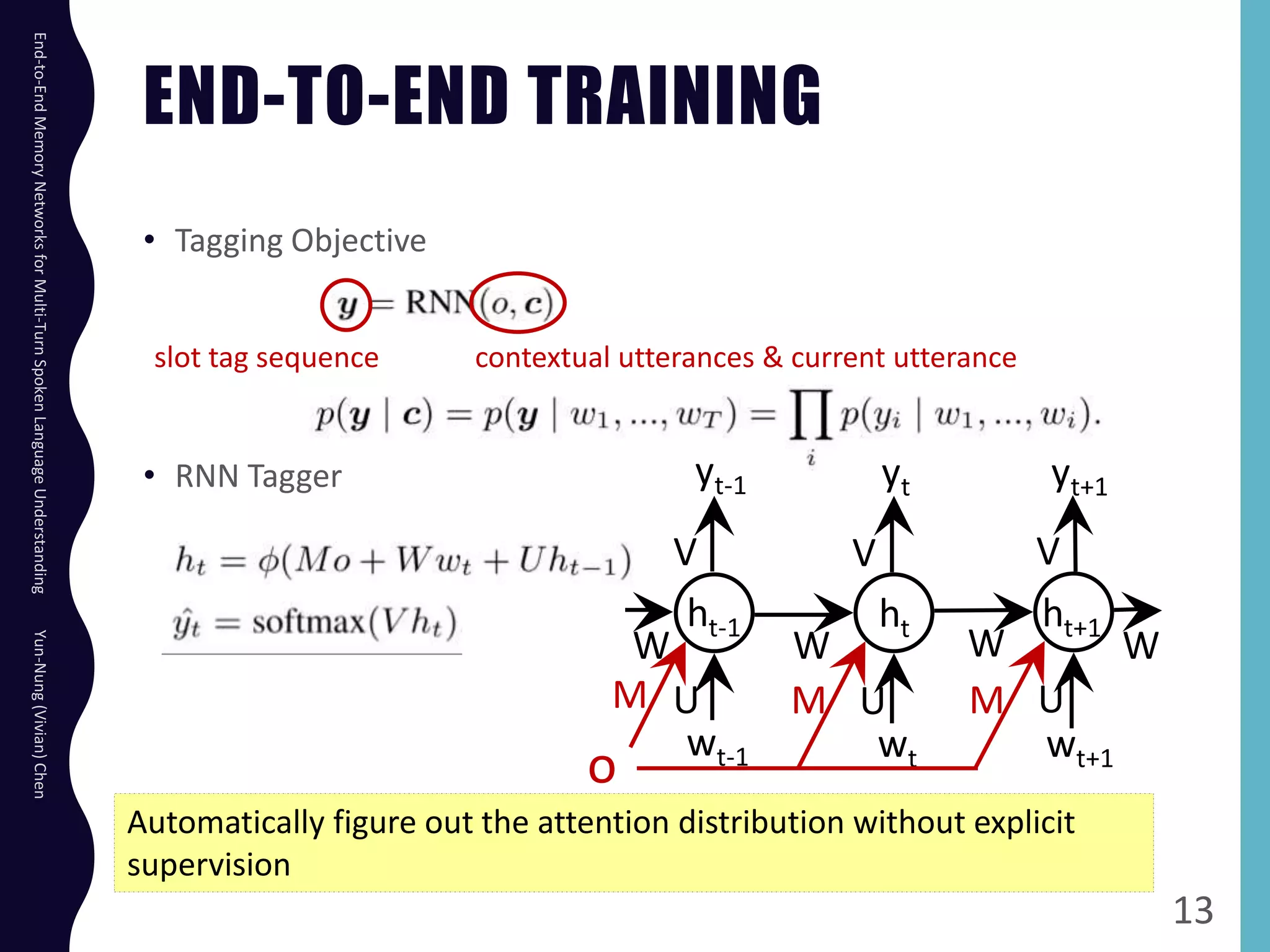
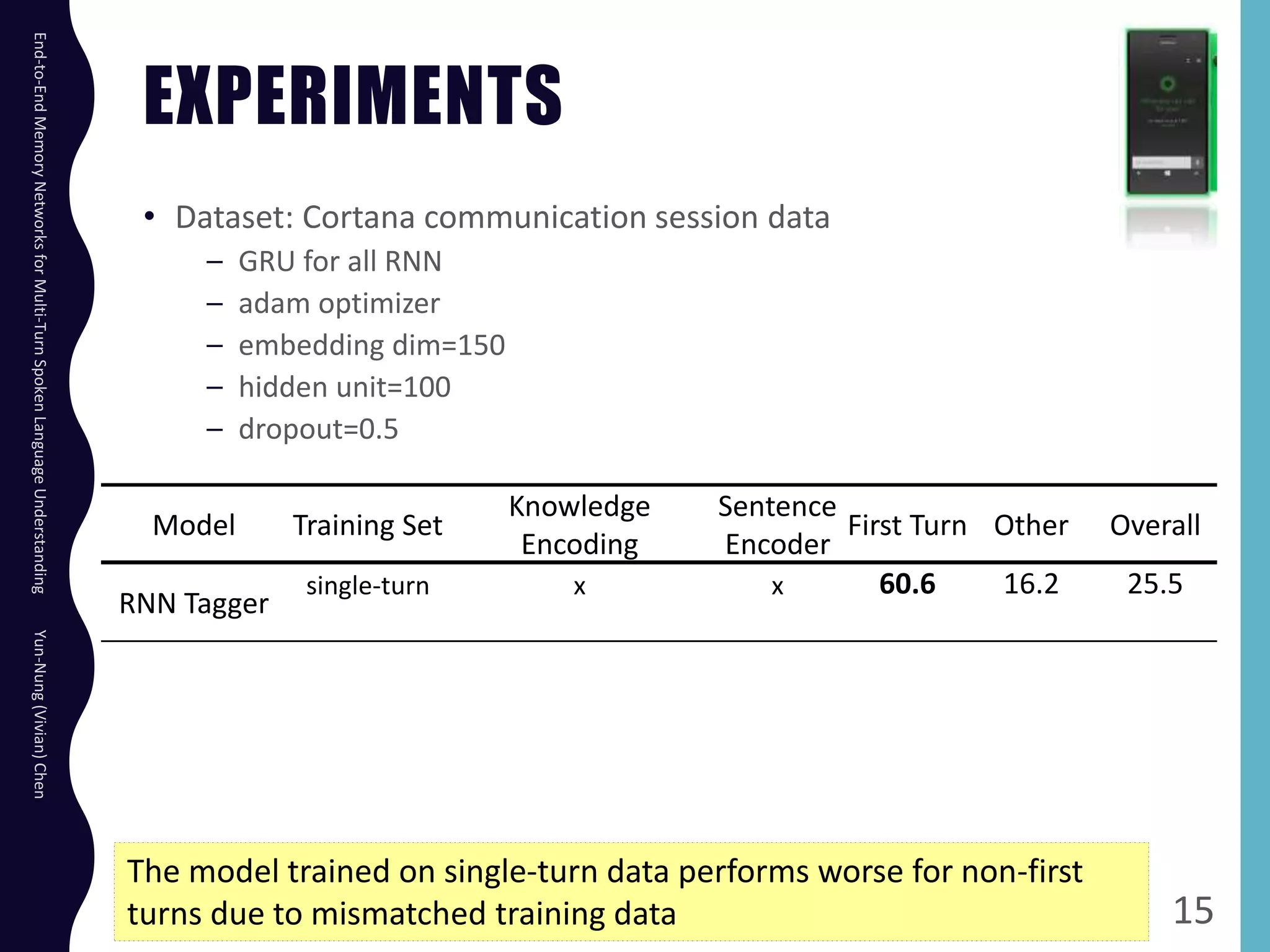
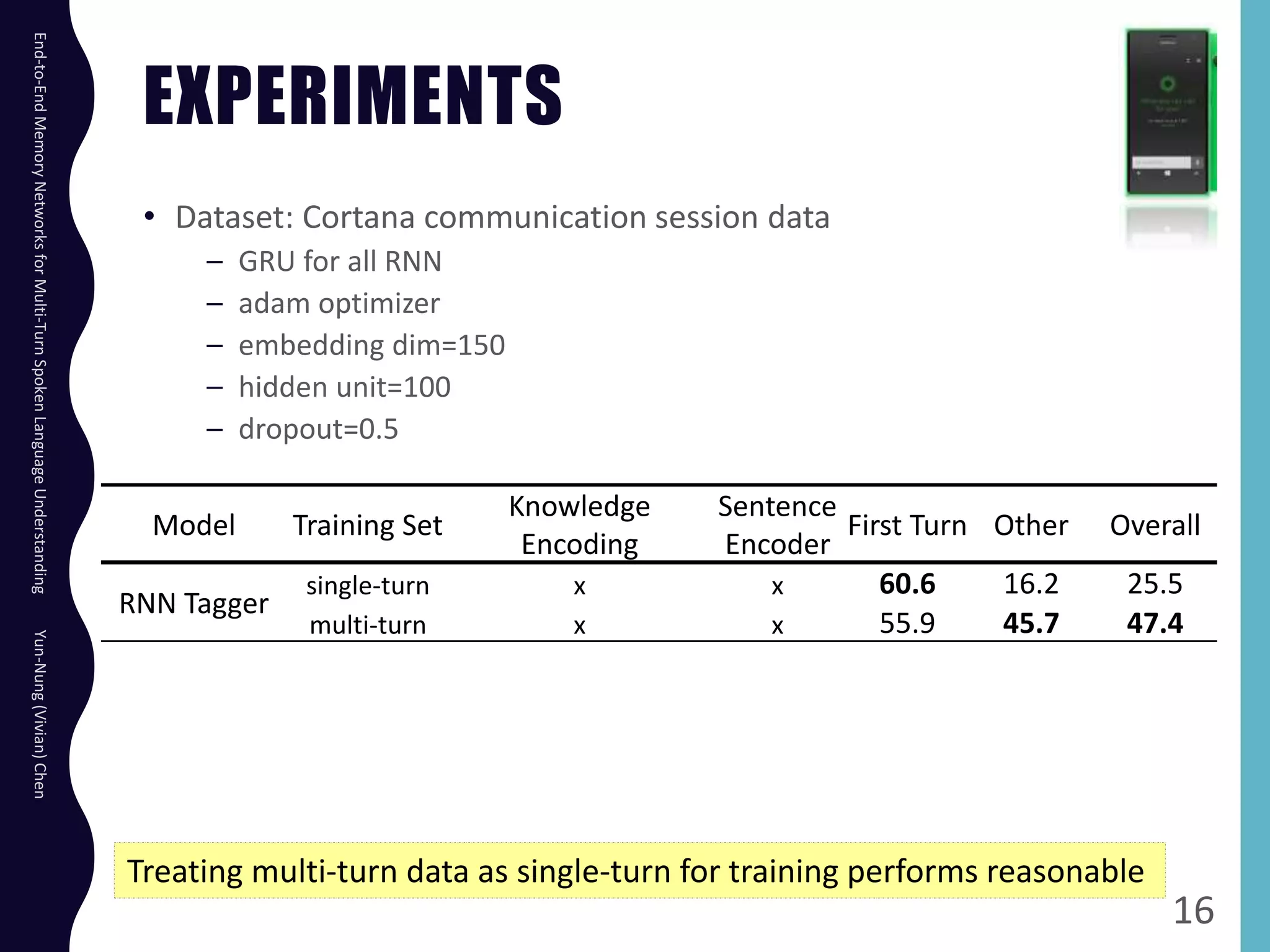
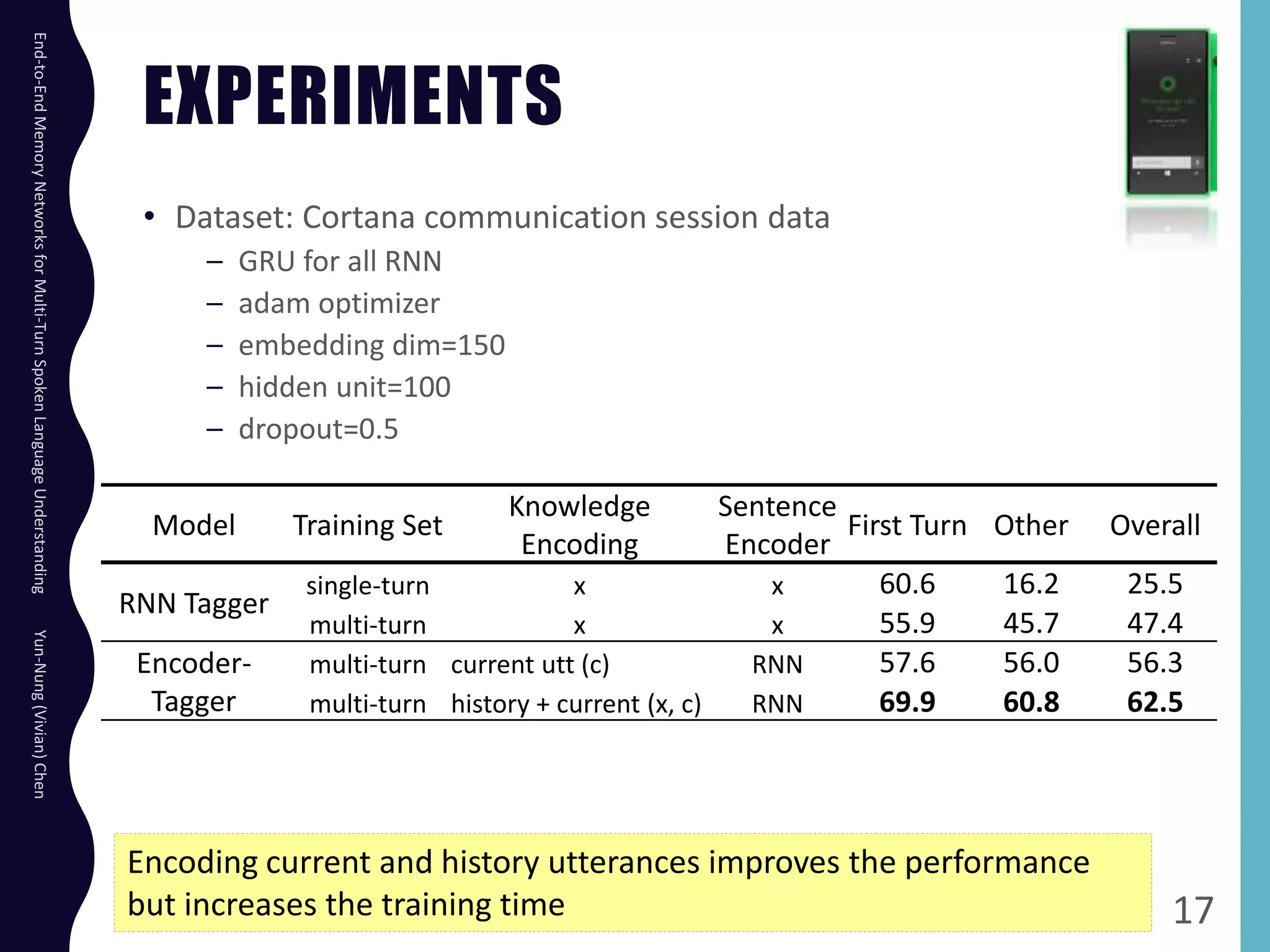
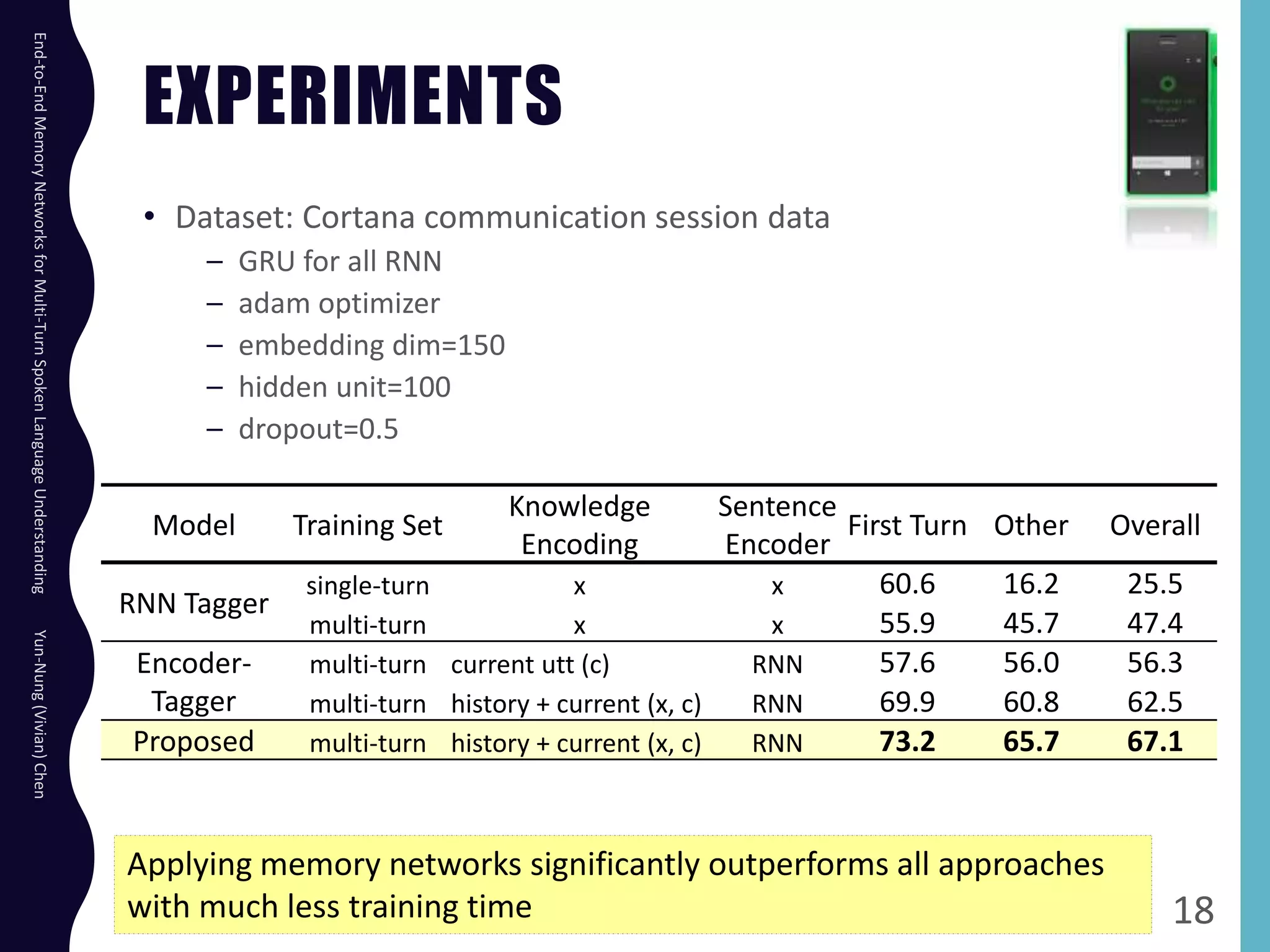
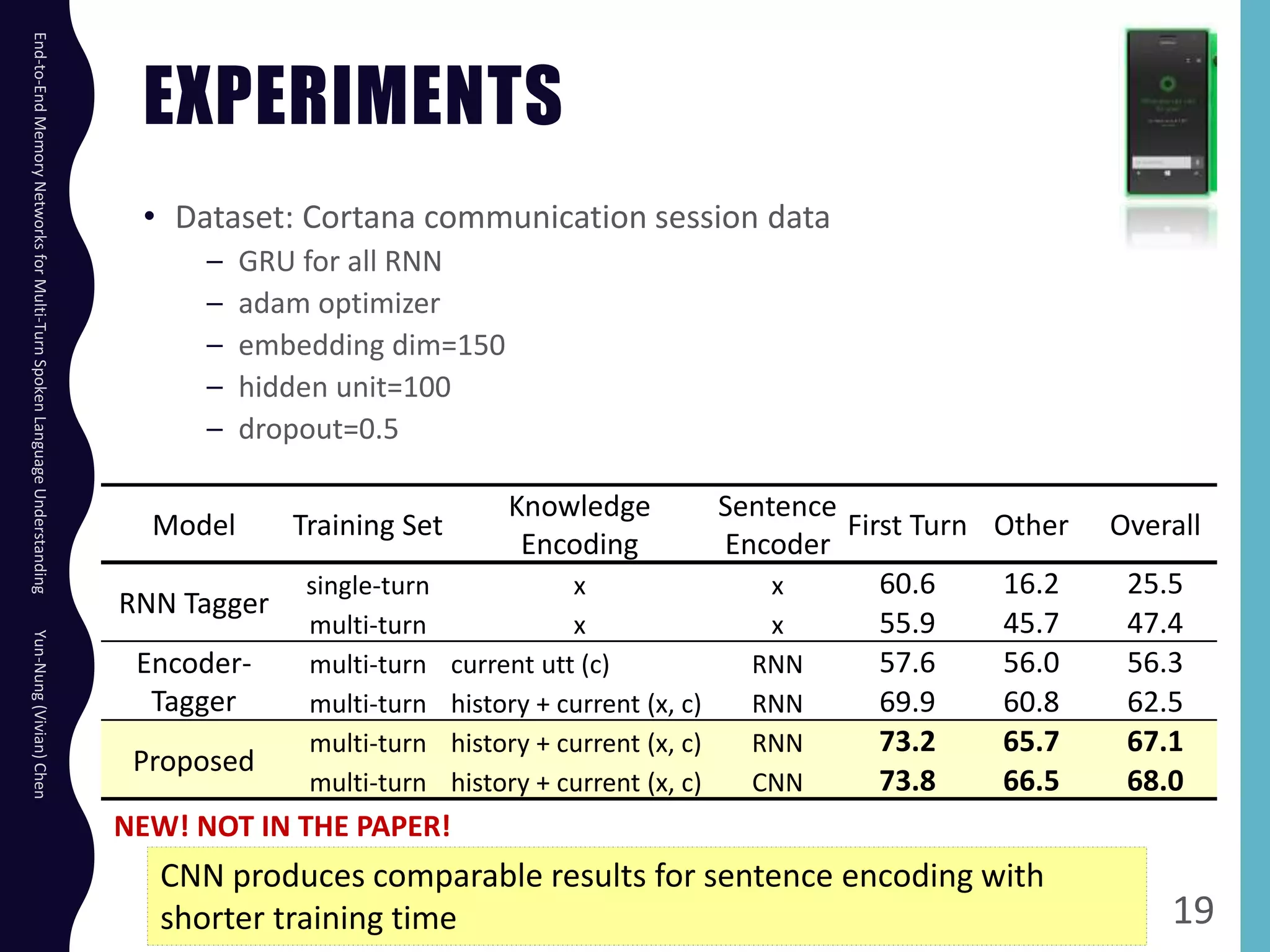
The document describes an end-to-end memory network model for multi-turn spoken language understanding. The model encodes context from previous utterances using an attention mechanism over the memory of past utterances. It then performs slot tagging on the current utterance incorporating the contextual knowledge. Experiments on a Cortana dataset show the model outperforms alternatives, achieving 67.1% accuracy by encoding both history and current utterances with the memory network.