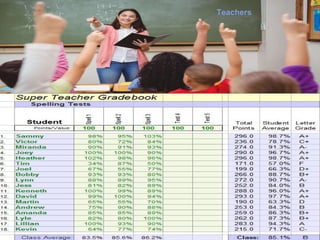
End user development (EUD) refers to activities that allow non-professional computer users like managers, teachers, and homemakers to program computers to perform tasks specific to their needs. EUD tools like spreadsheets allow users to create complex data models without formal programming knowledge. While EUD provides benefits like rapid development and innovation, disadvantages include limited user knowledge, loss of data and program quality control, and solutions that may not scale well as needs change.