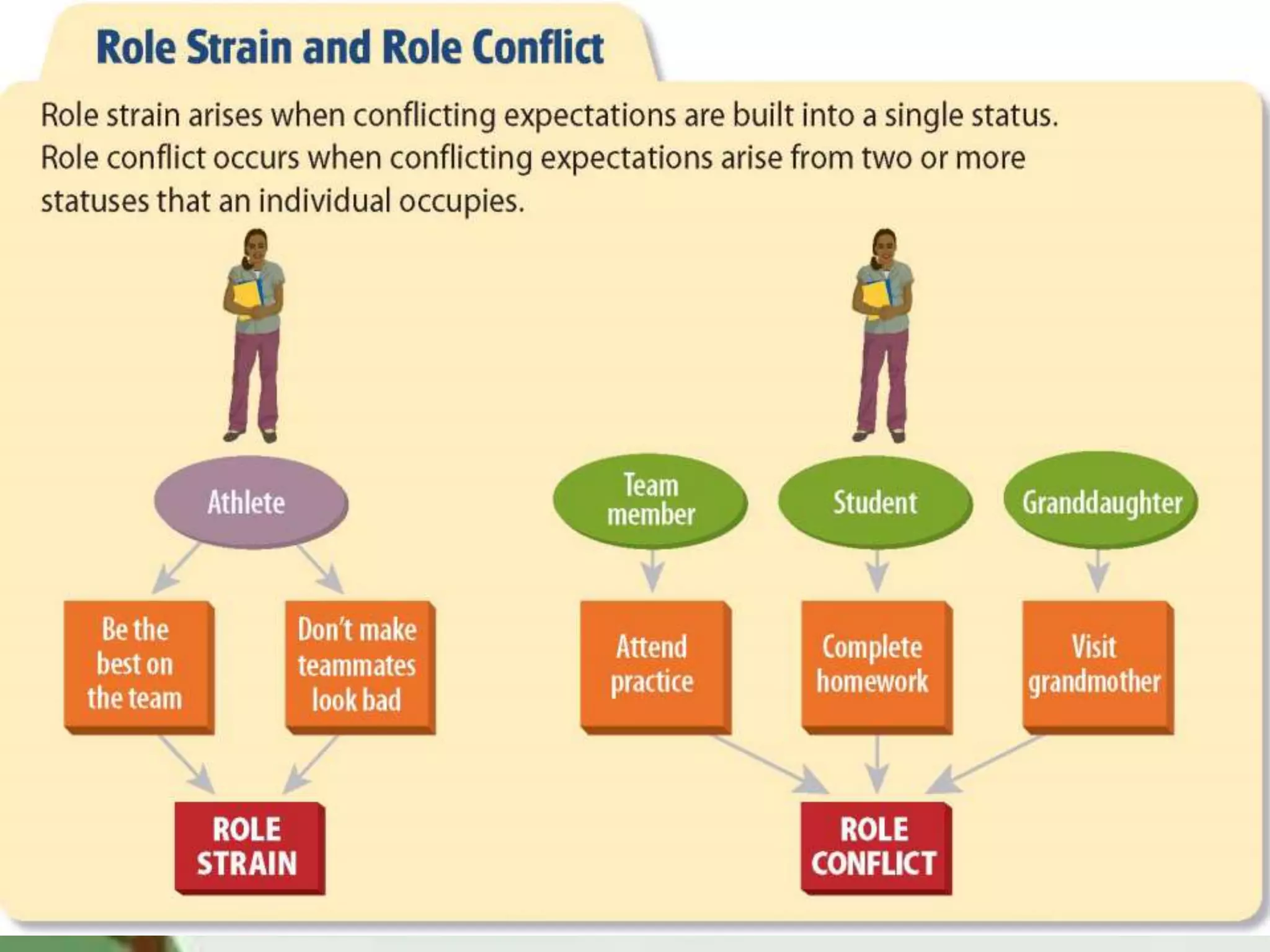
The document discusses key concepts related to socialization and identity formation. It describes enculturation as the process by which people learn the values and behaviors of their surrounding culture. Socialization teaches individuals to control impulses, prepare for social roles, and develop shared meanings. George Herbert Mead contributed to understanding the development of self through a four-stage process from imitation to understanding generalized social expectations. Identity is shaped by cultural, ethnic, national, and religious affiliations as well as by social statuses and roles which are guided by norms, values, and expectations for behavior.