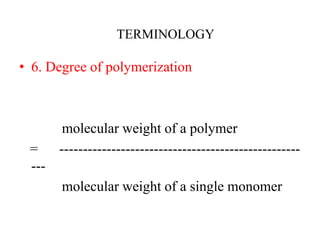
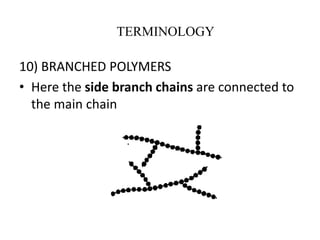
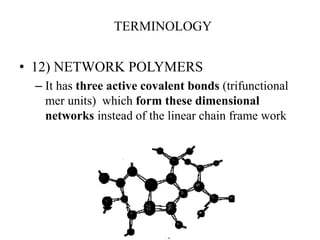
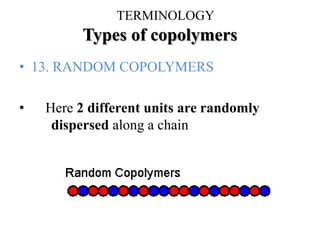
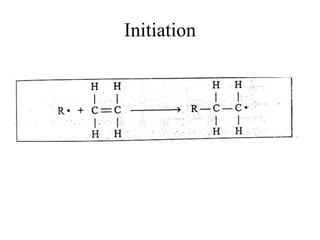
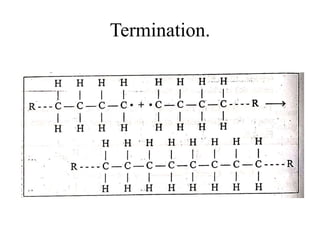
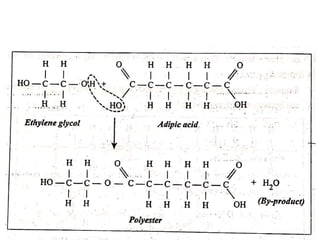
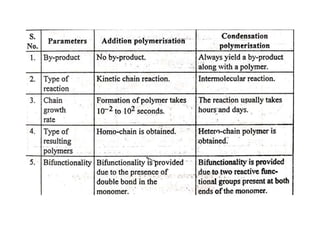
This document defines key terminology related to polymers, including:
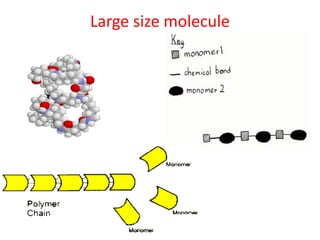
- Monomers are small molecules that link together to form polymers.
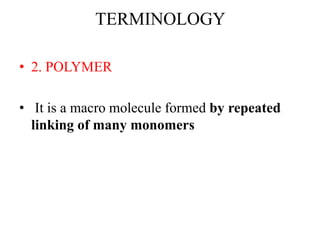
- Polymers are large molecules composed of many repeating monomer units.
- Polymerization is the process of linking monomers together to form polymers.
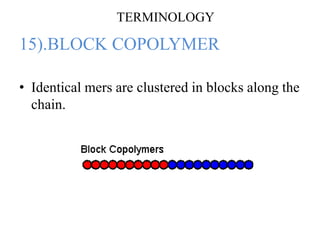
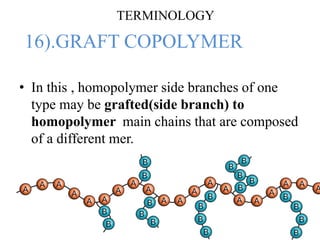
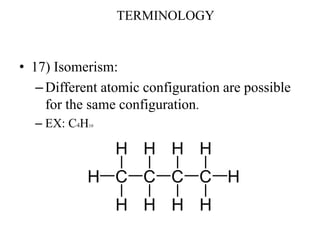
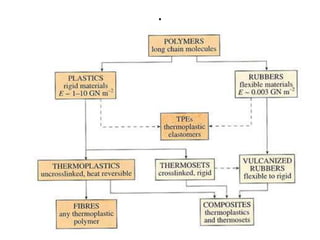
- There are different types of polymers including homopolymers, copolymers, linear polymers, branched polymers, and cross-linked polymers.






![• 4. HOMOPOLYMER
Homopolymers - consist of chains with identical
bonding linkages to each monomer unit. This
usually implies that the polymer is made from all
identical monomer molecules.
These may be represented as : -[A-A-A-A-A-A]-
TERMINOLOGY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1nonmetallicmaterials-polymers-211108121315/85/EM-UNIT-III-non-metallic-materials-polymers-11-320.jpg)
![• 5. COPOLYMER
Copolymers - consist of chains with two or
more linkages usually implying two or more
different types of monomer units.
These may be represented as : -[A-B-A-B-
A-B]-
TERMINOLOGY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1nonmetallicmaterials-polymers-211108121315/85/EM-UNIT-III-non-metallic-materials-polymers-12-320.jpg)