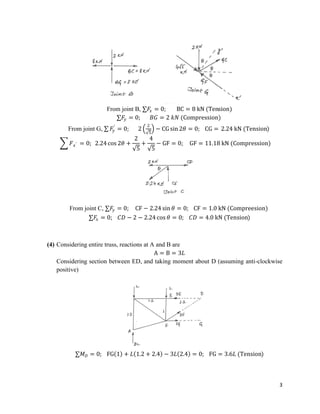
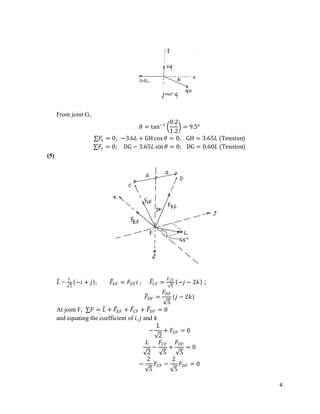
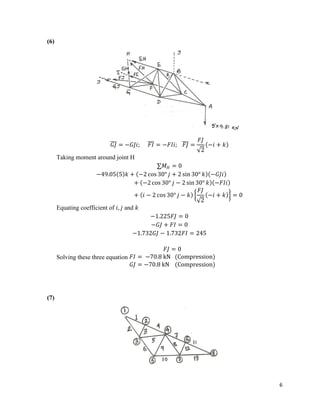
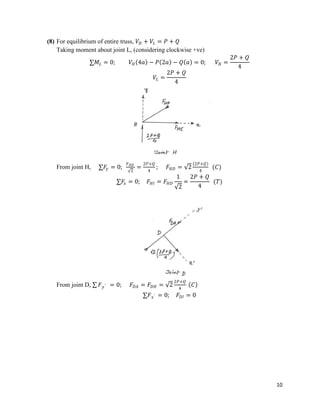
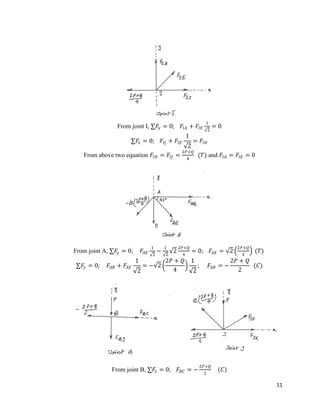
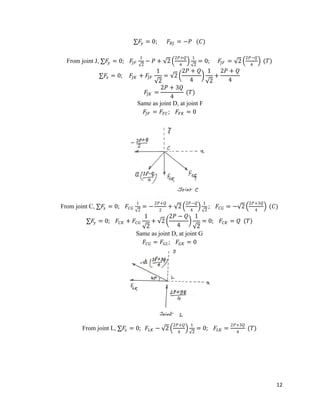
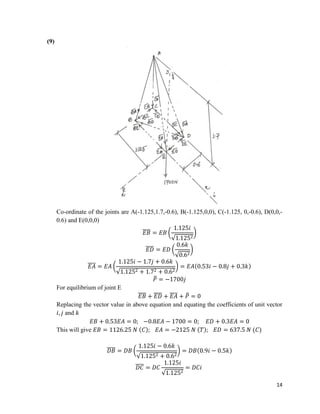
The document provides calculations for analyzing the forces in several truss structures. It analyzes trusses by taking moments of forces at joints, applying equilibrium equations, and solving the resulting systems of equations. Force diagrams are drawn to indicate tensions and compressions. Key steps include (1) taking moments at joints to set up equations, (2) applying force equilibrium conditions to create additional equations, and (3) solving the systems of equations to determine member forces.