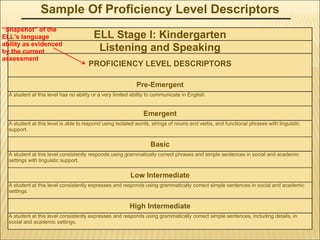
The document provides guidance on planning and implementing English language development (ELD) instruction according to the Arizona English Language Proficiency Standards. It includes information on how to structure ELD time allocations based on students' proficiency levels, determine language objectives, and code lessons to target specific standards. Sample language objectives and examples of coding ELD lessons are also provided.







































![ELD [ELP standard/Language Objective] is the driver and ACADEMIC CONTENT is the vehicle. (What does this mean?)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9130165/85/ELPS_Train_The_Trainer_COPY-41-320.jpg)





















