Embed presentation
Downloaded 28 times



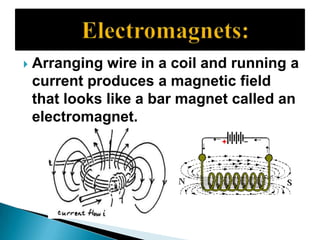
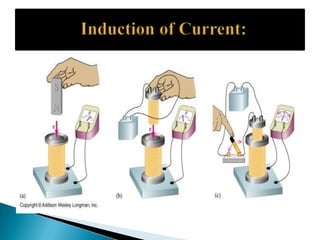

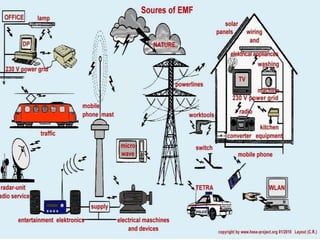
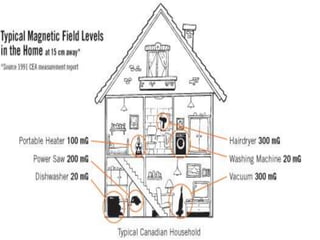

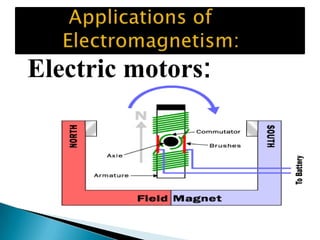
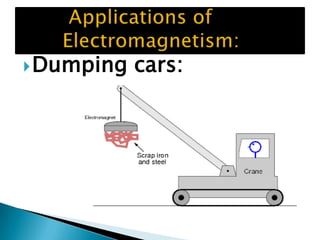
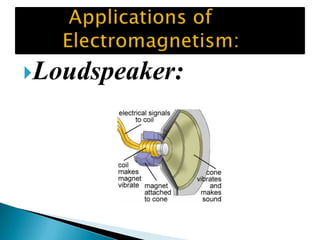
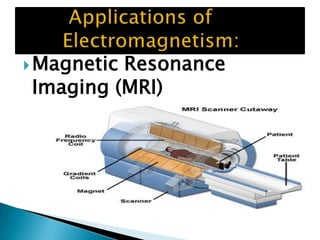

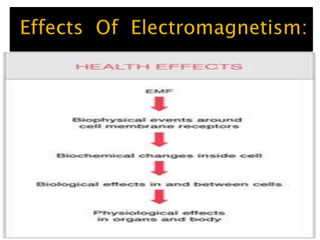


This document discusses electromagnetism and its applications. It explains that a moving electric charge creates magnetic fields and changing magnetic fields create electric charges. It describes how coils of wire and electric currents are used to create electromagnets. It also discusses how changing magnetic fields produce electric fields and vice versa. Finally, it provides some examples of applications of electromagnetism like electric motors, dumping cars, loudspeakers, MRI, communication systems, radar, and medical imaging.


















