1) Electromagnetic flow meters measure flow rate without being impacted by fluid properties like density, temperature, pressure, or viscosity. They work by generating a voltage proportional to flow rate when a conductive fluid flows through a magnetic field perpendicular to electrodes.
2) Electromagnetic flow meters have applications in many industrial sectors that involve liquids, including chemical, water, pulp/paper, food/beverage, and pharmaceutical industries.
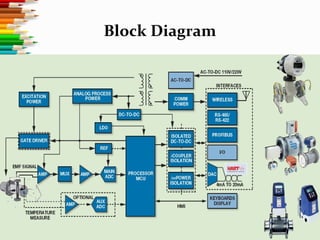
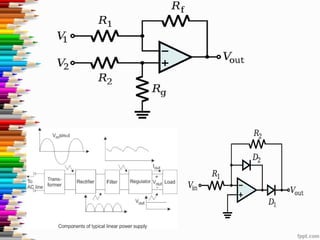
3) The document discusses the technology behind electromagnetic flow meters, including analog and digital components. Digital meters provide advantages like accuracy, quick response, stability, data storage, and wireless communication capabilities.