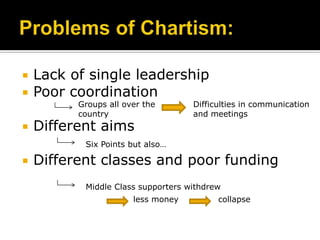
The document discusses the growing calls for electoral reform in Britain during the 1830s. It outlines the unfairness and corruption of the old electoral system, as well as the unequal distribution of political power. Key events that fueled reform efforts included the Peterloo Massacre in 1819 and riots in 1831. This led to the passage of the 1832 Reform Act, though it did not satisfy demands for universal male suffrage. The Chartist movement emerged in the late 1830s calling for working class political rights defined in the People's Charter of 1838. However, divisions over tactics and lack of coordination contributed to the movement's eventual decline.