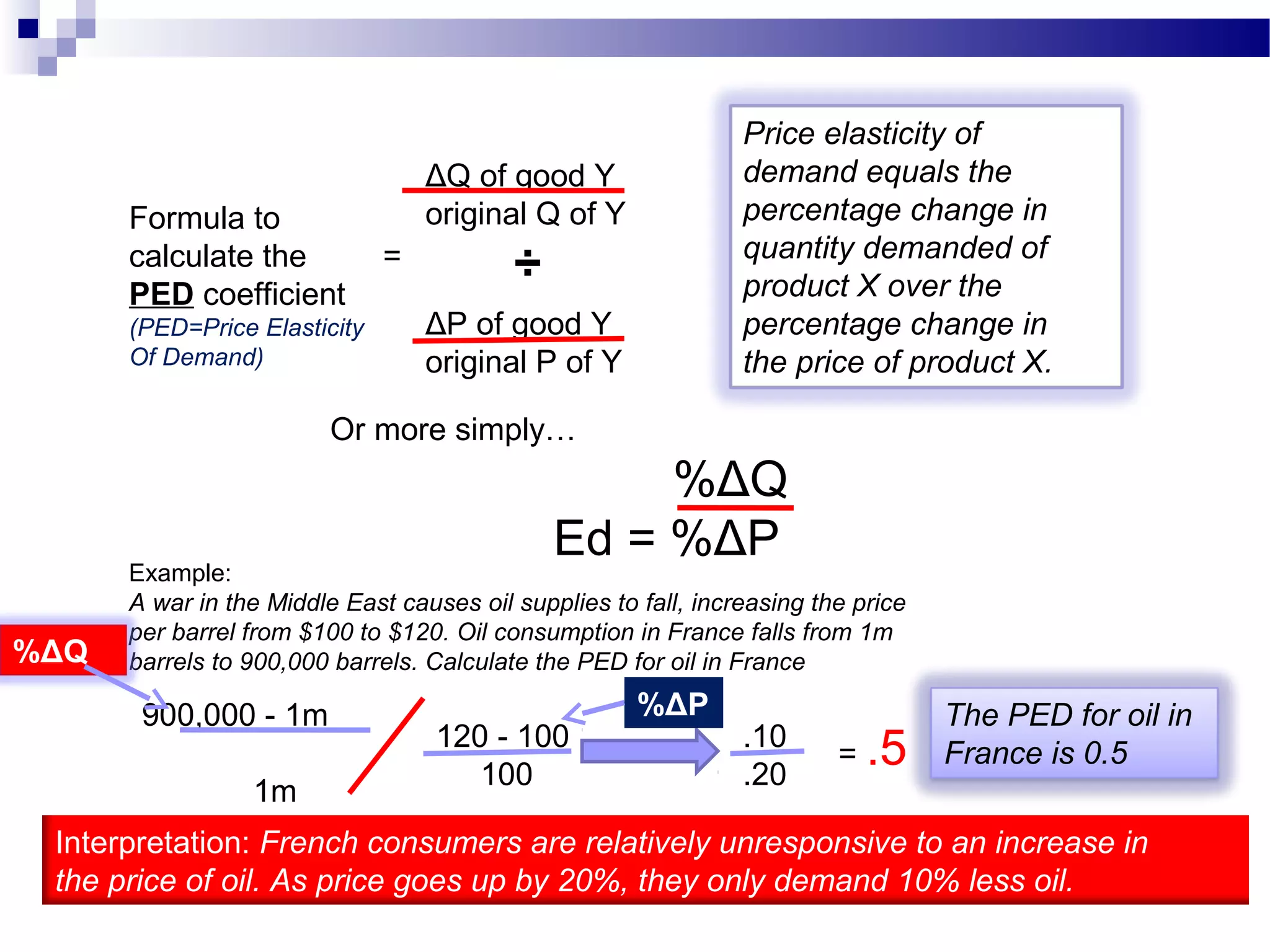
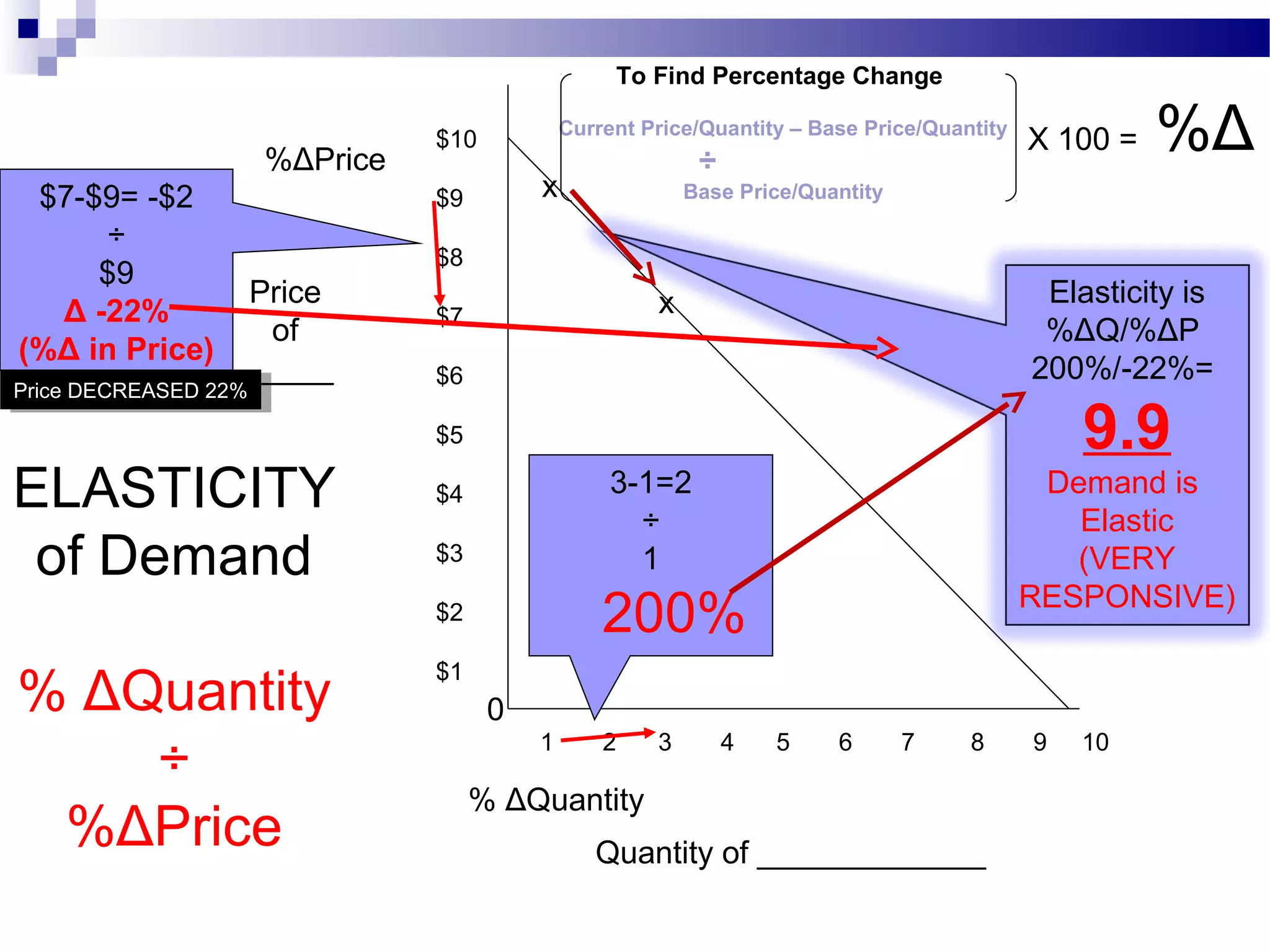
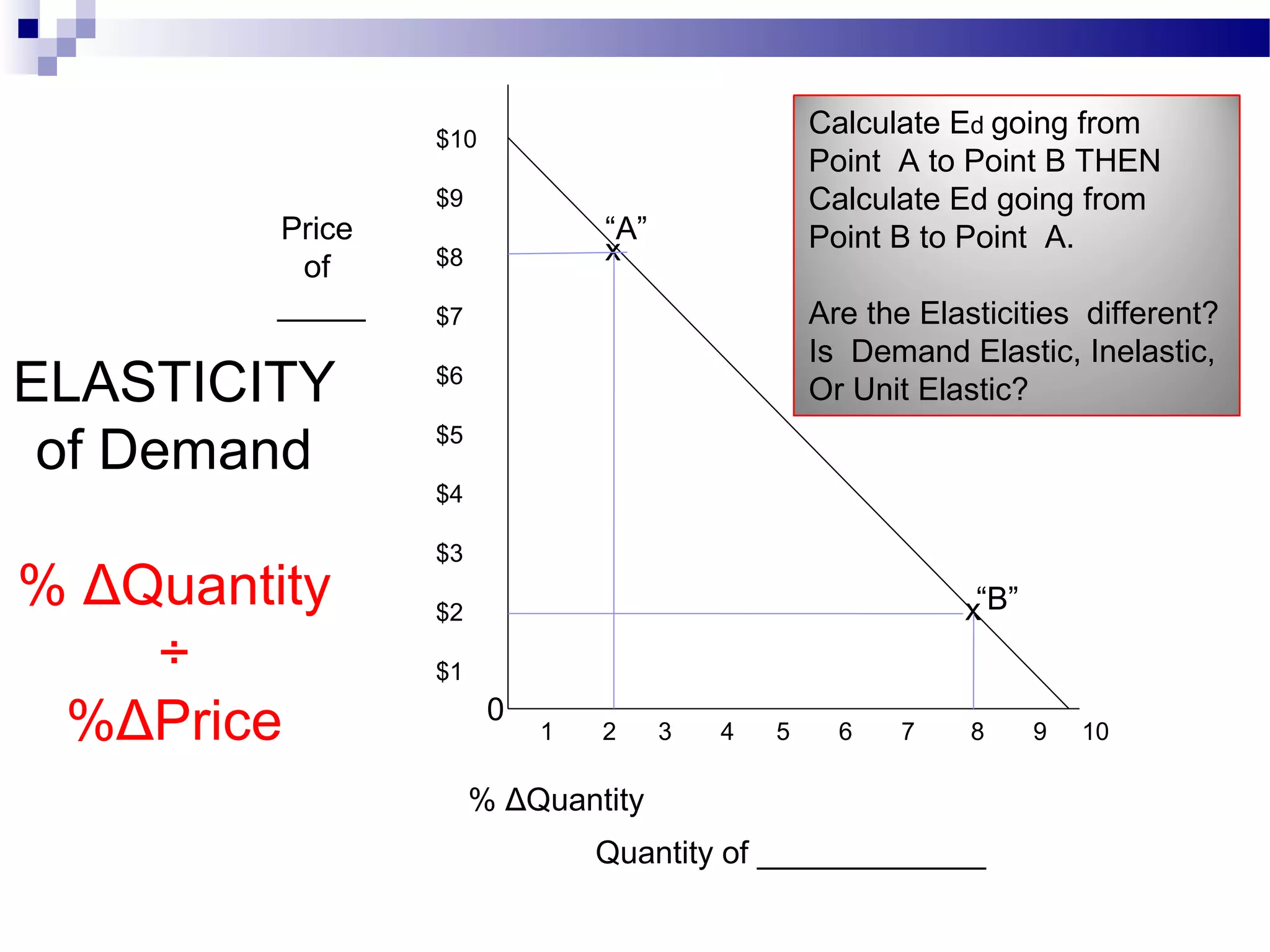
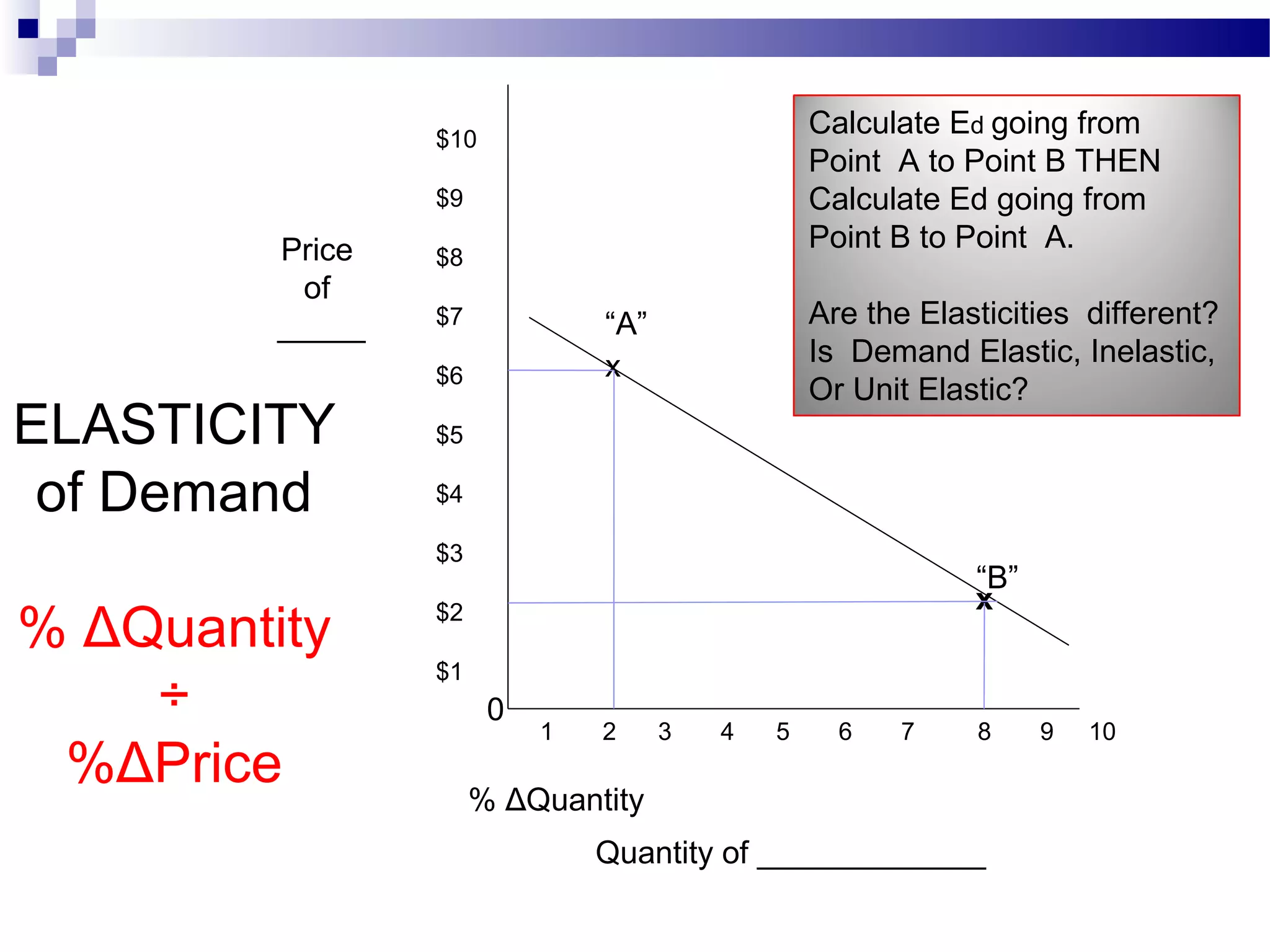
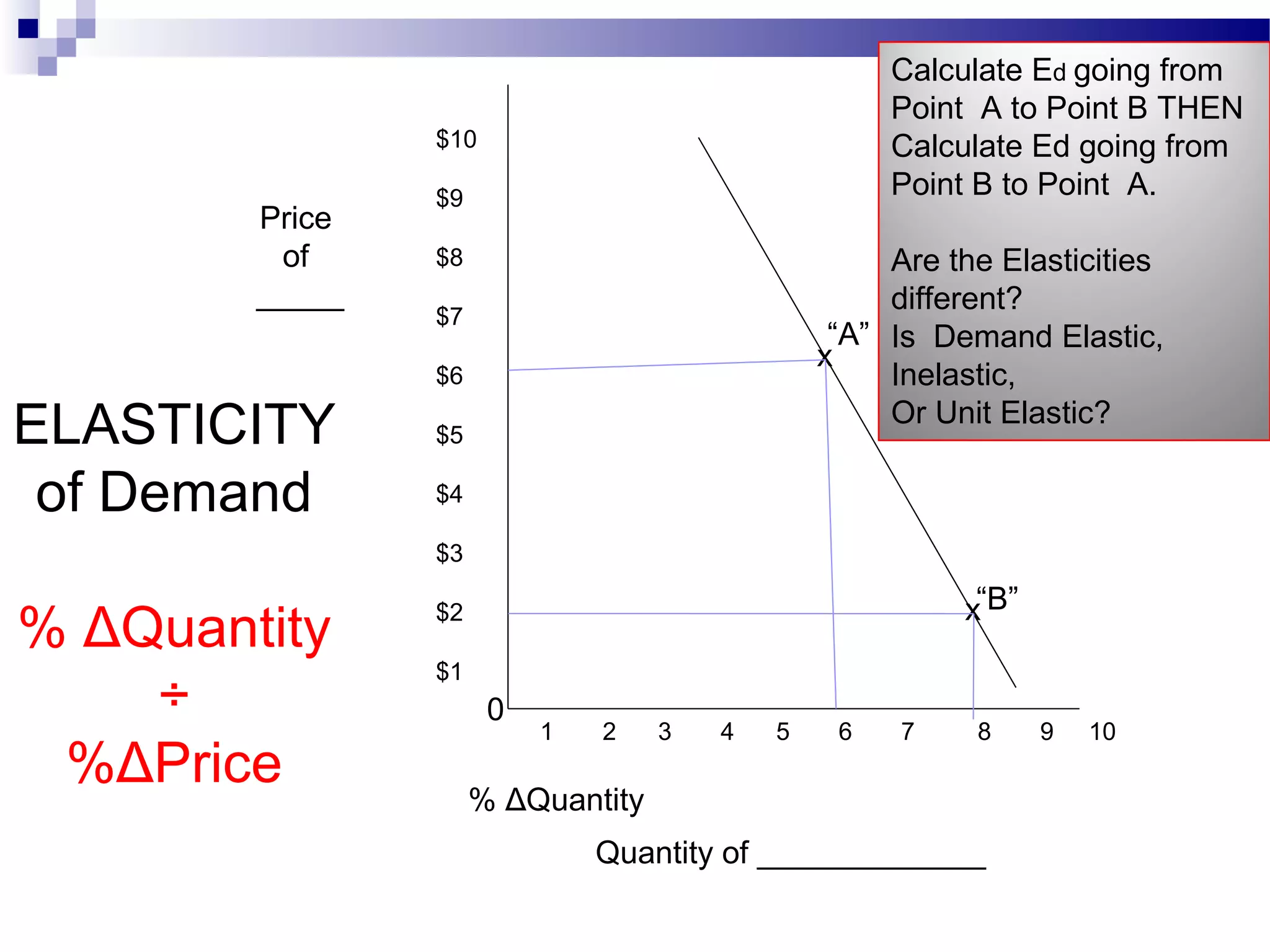
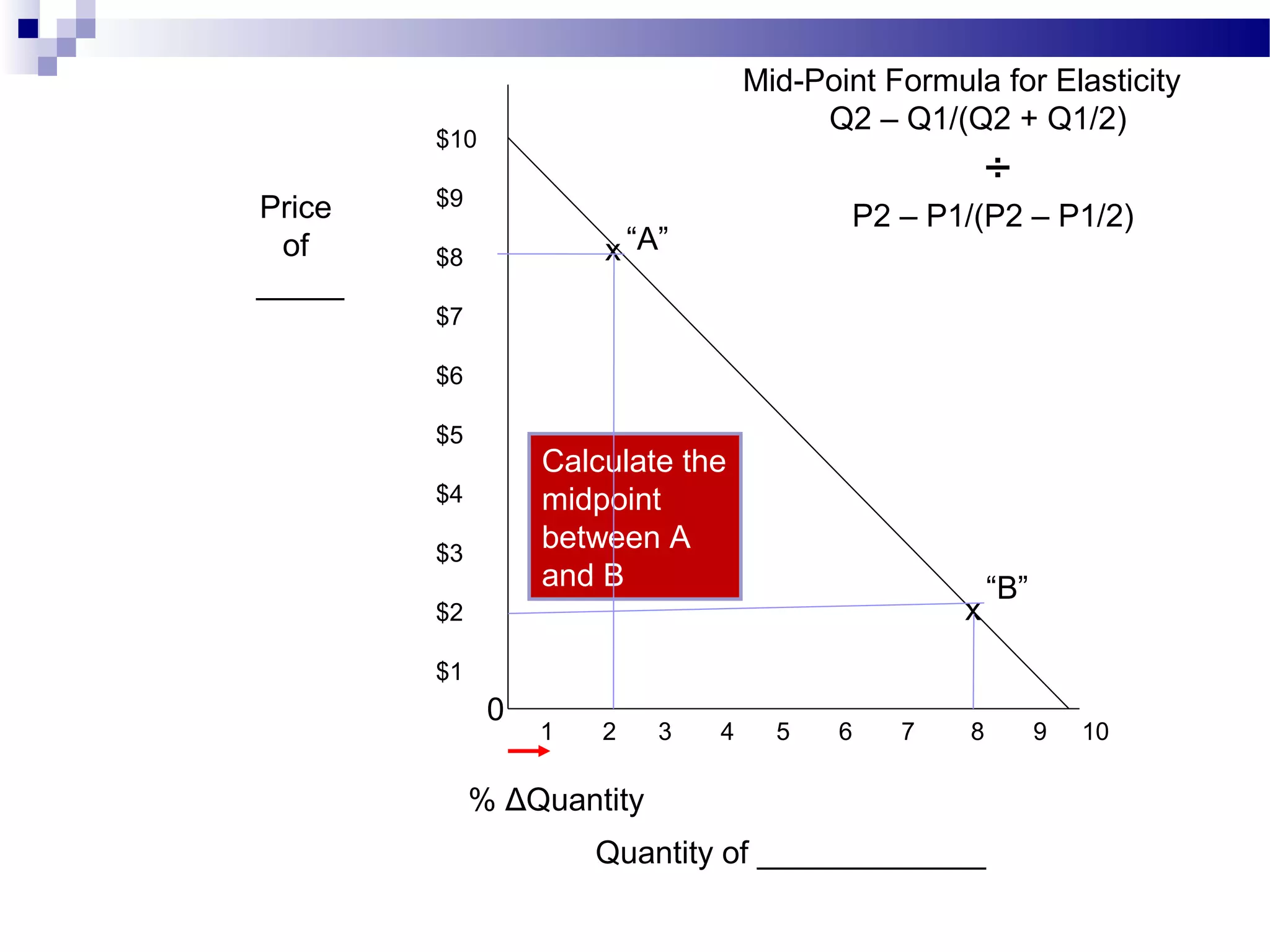
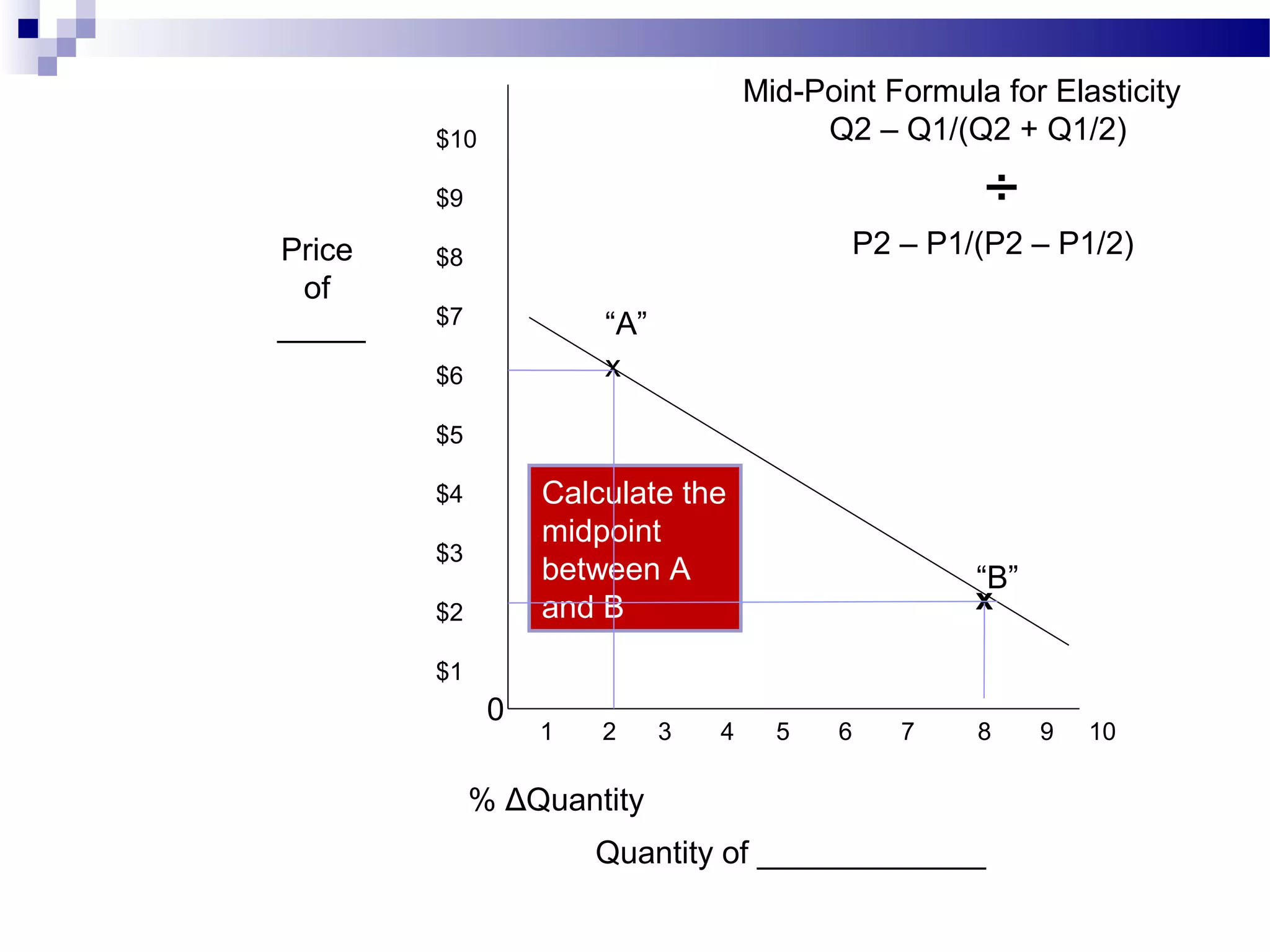
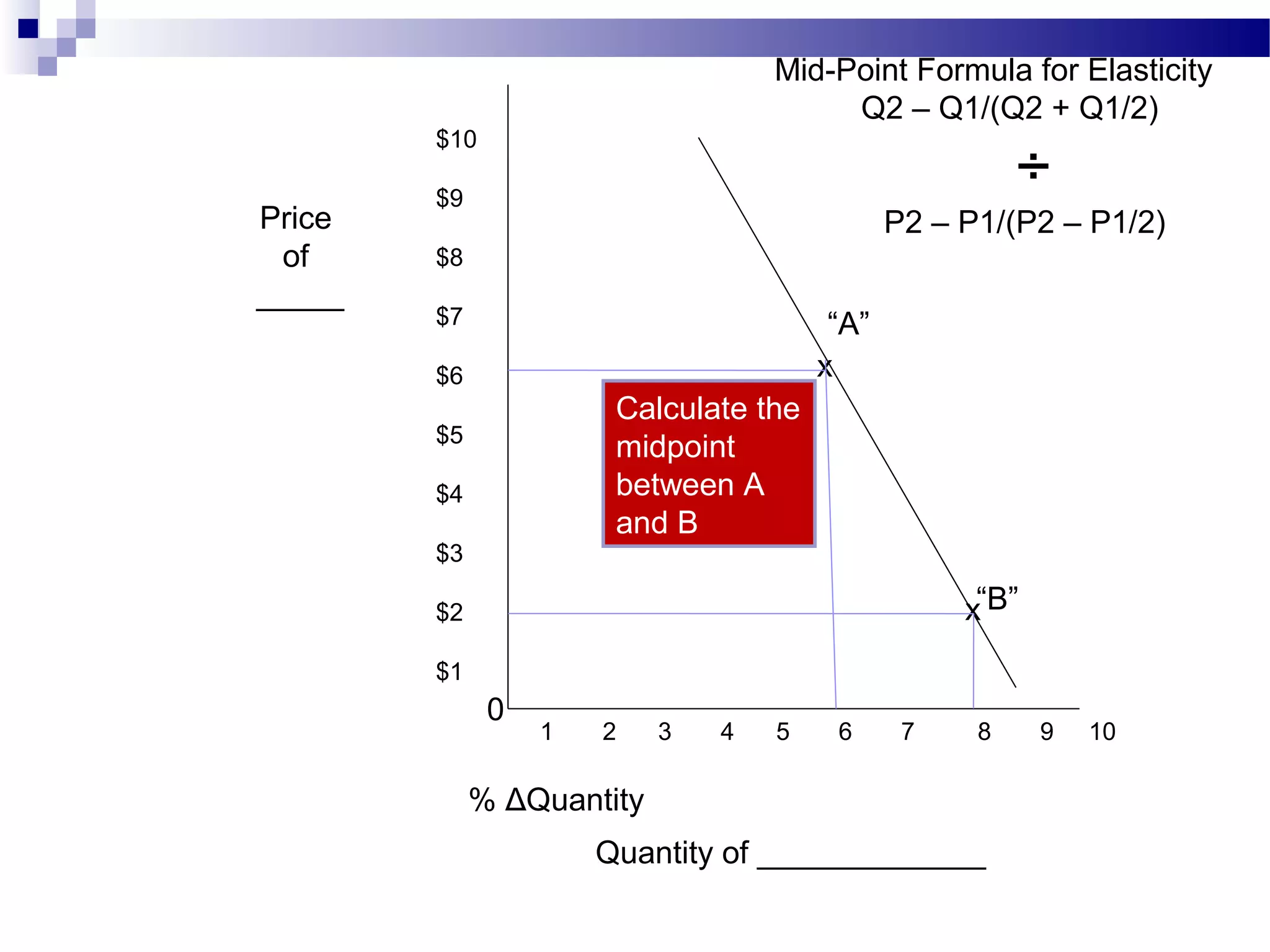
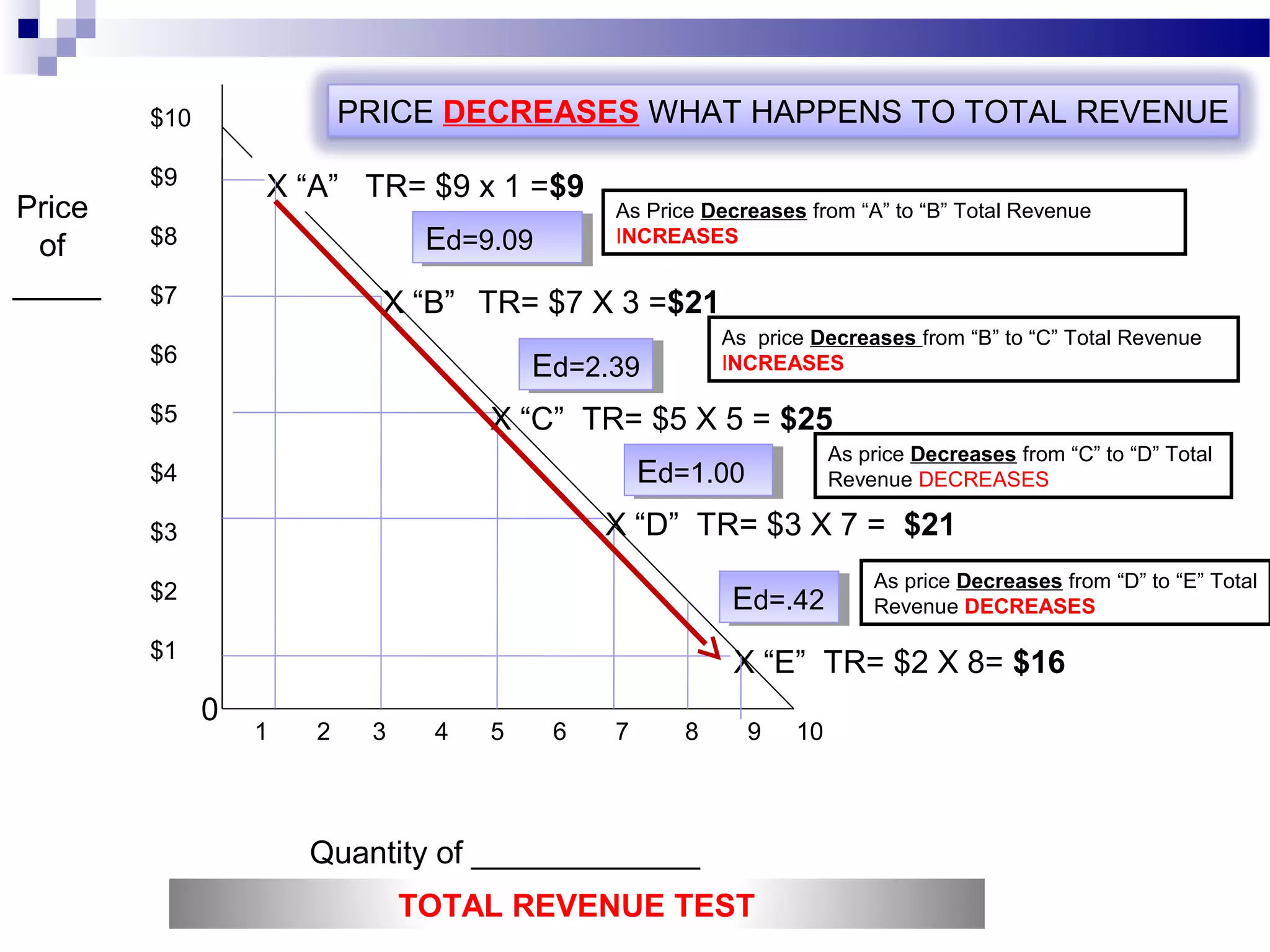
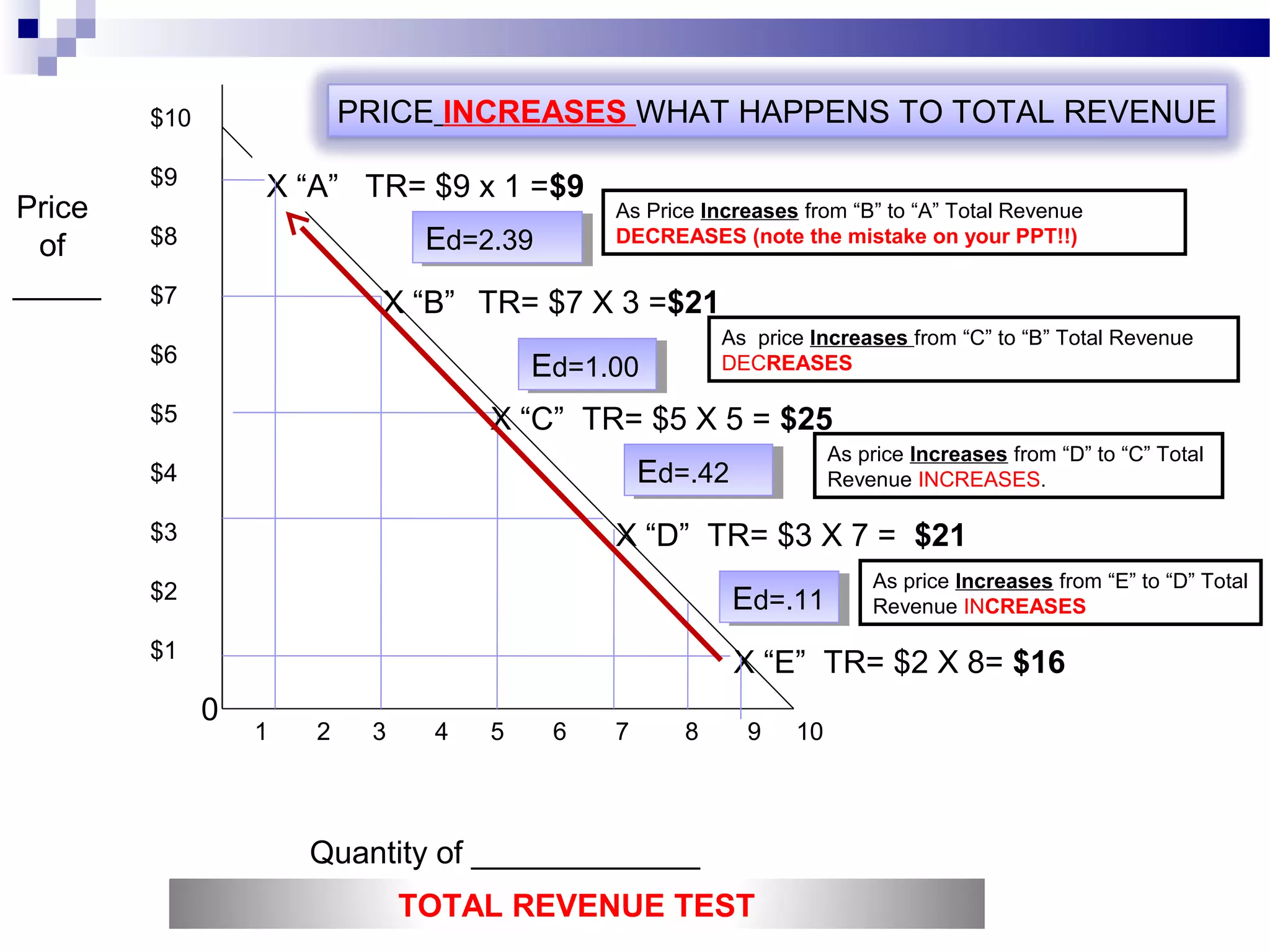
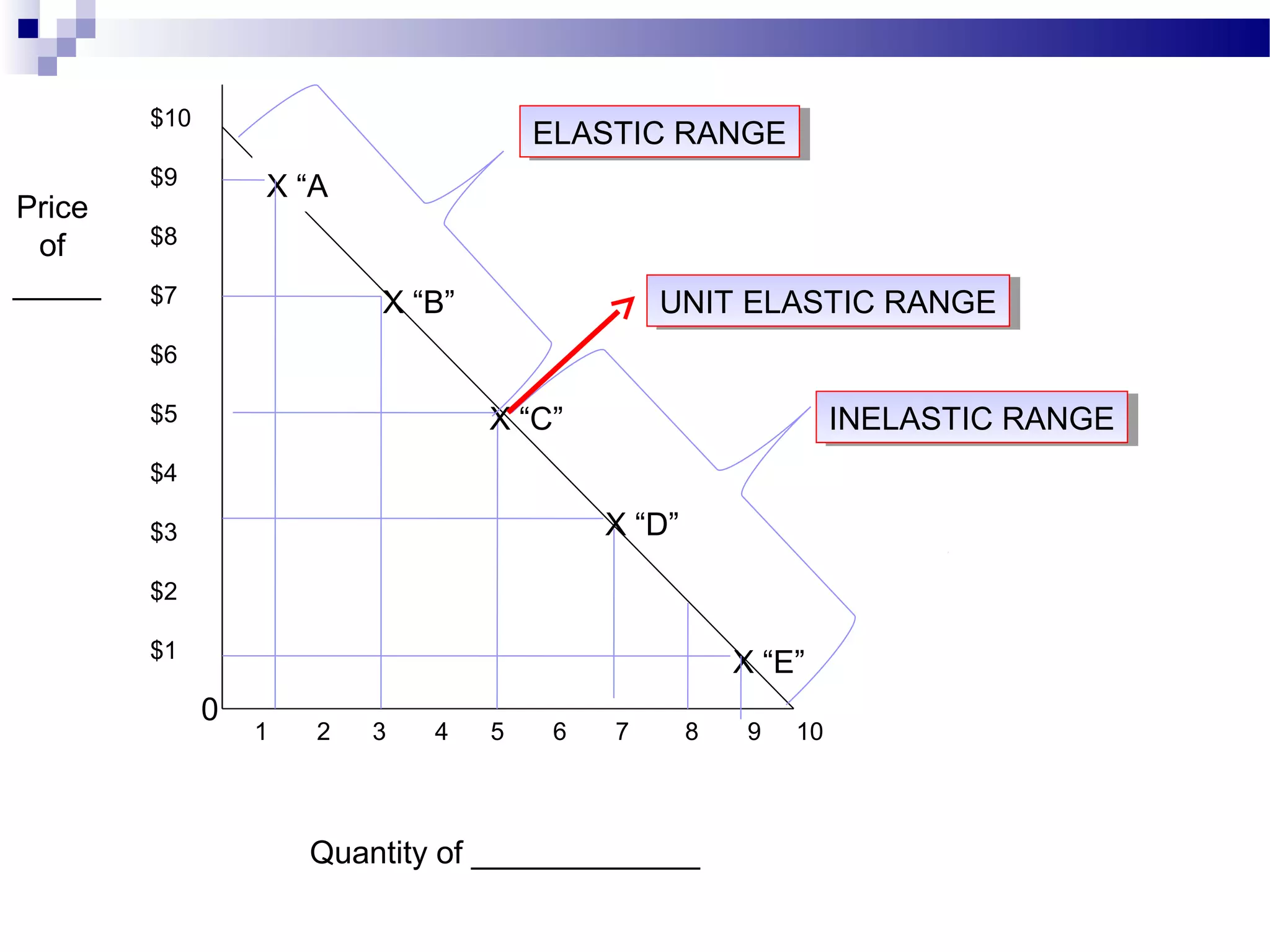
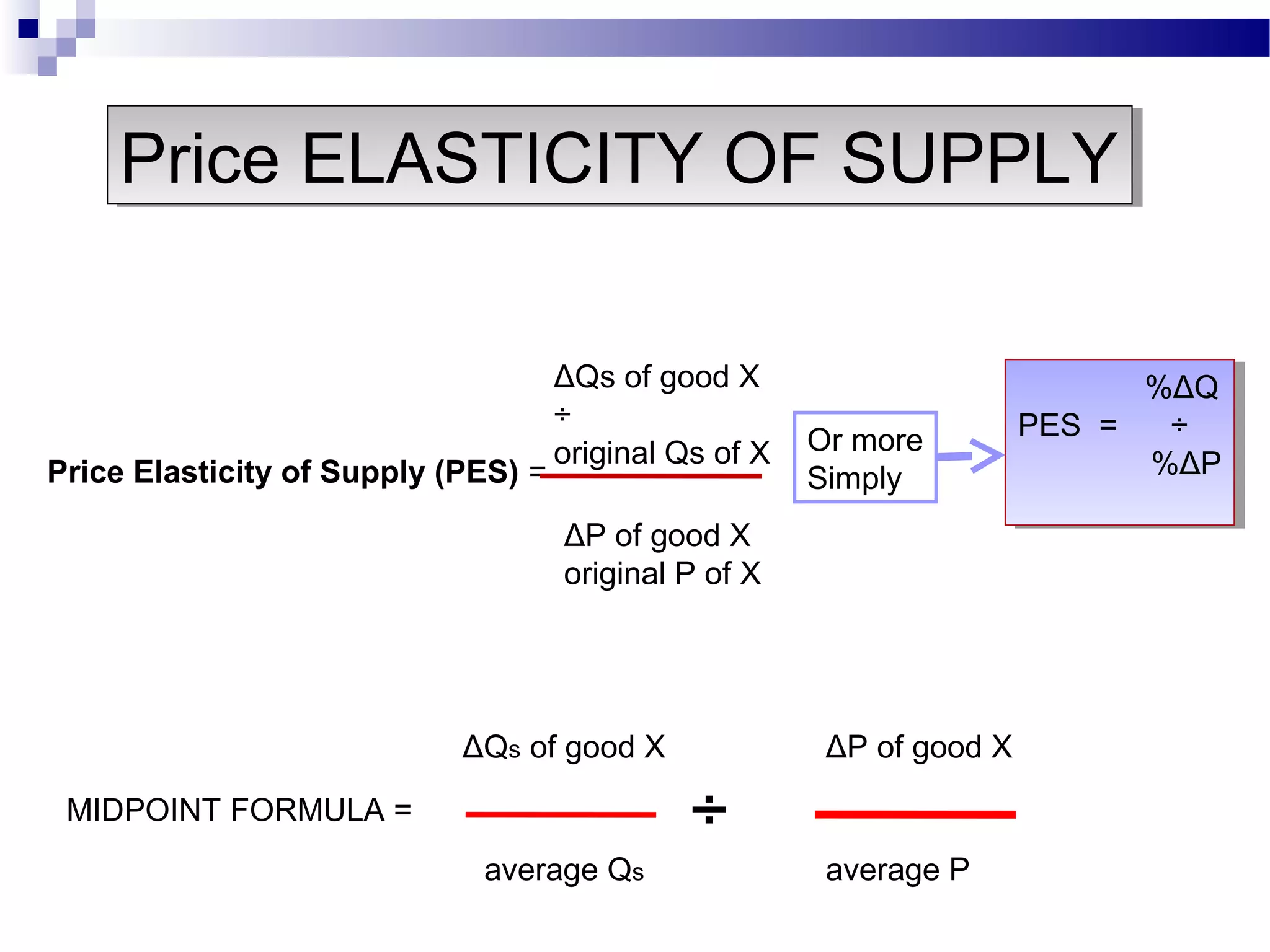
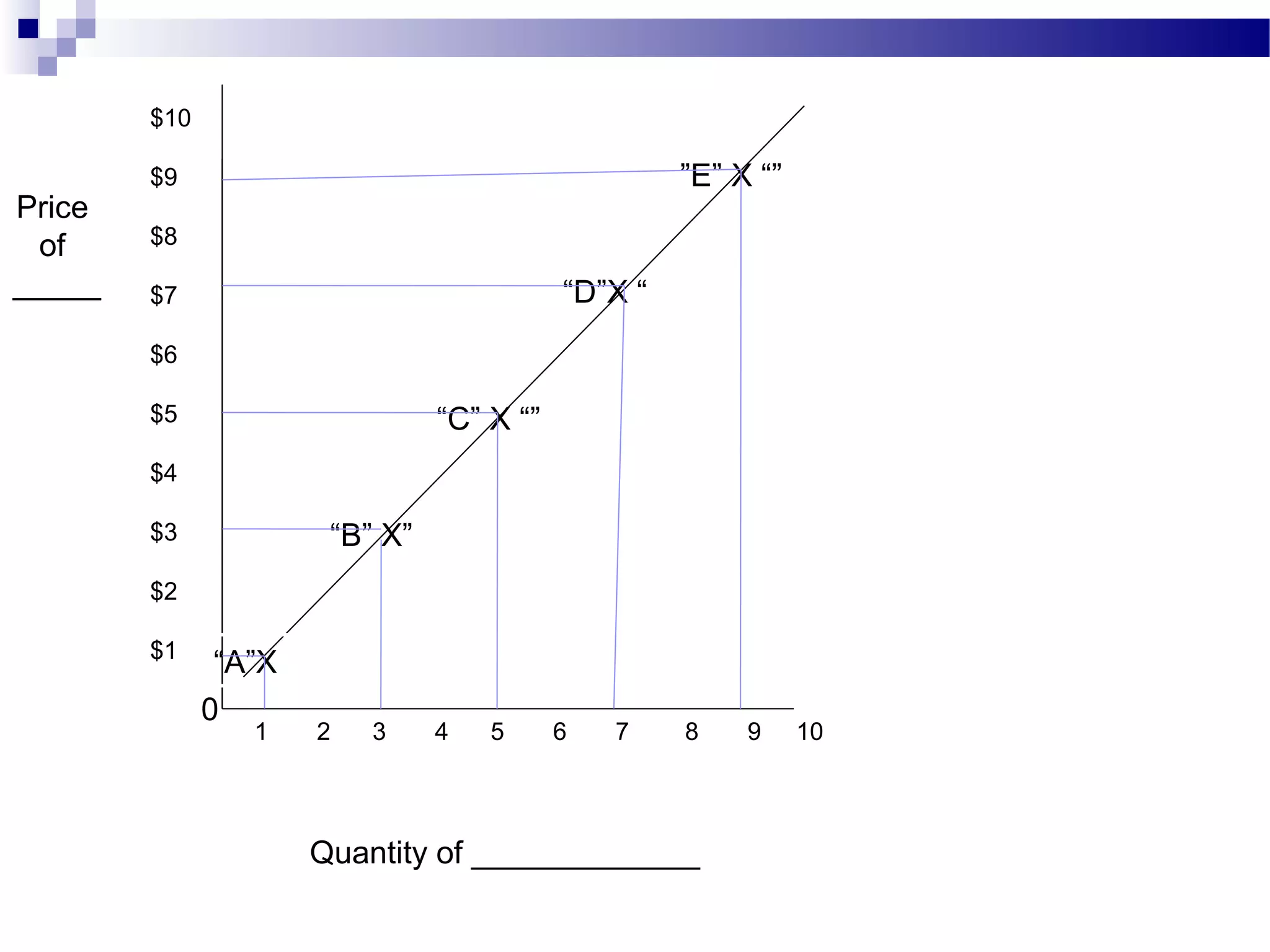
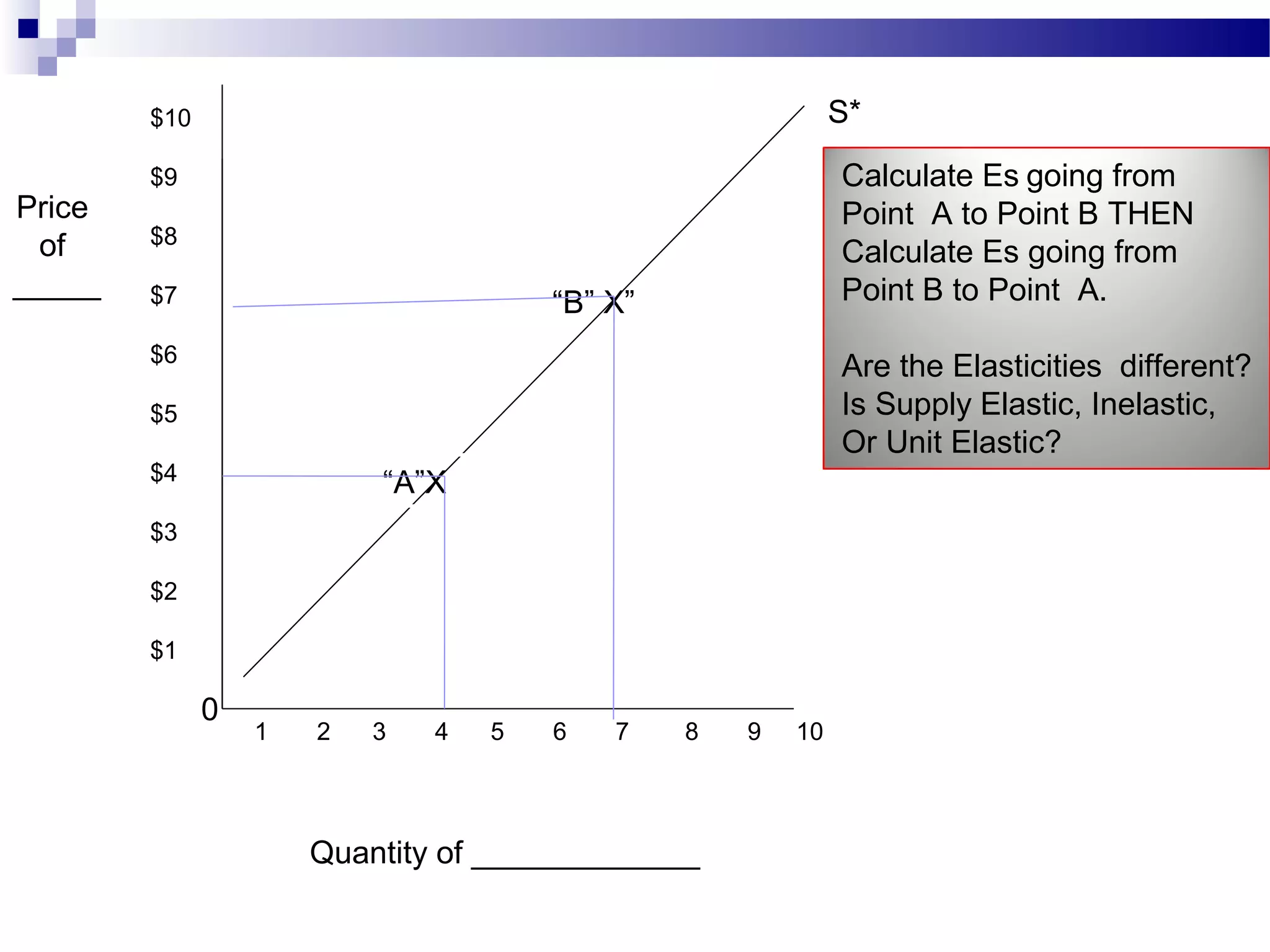
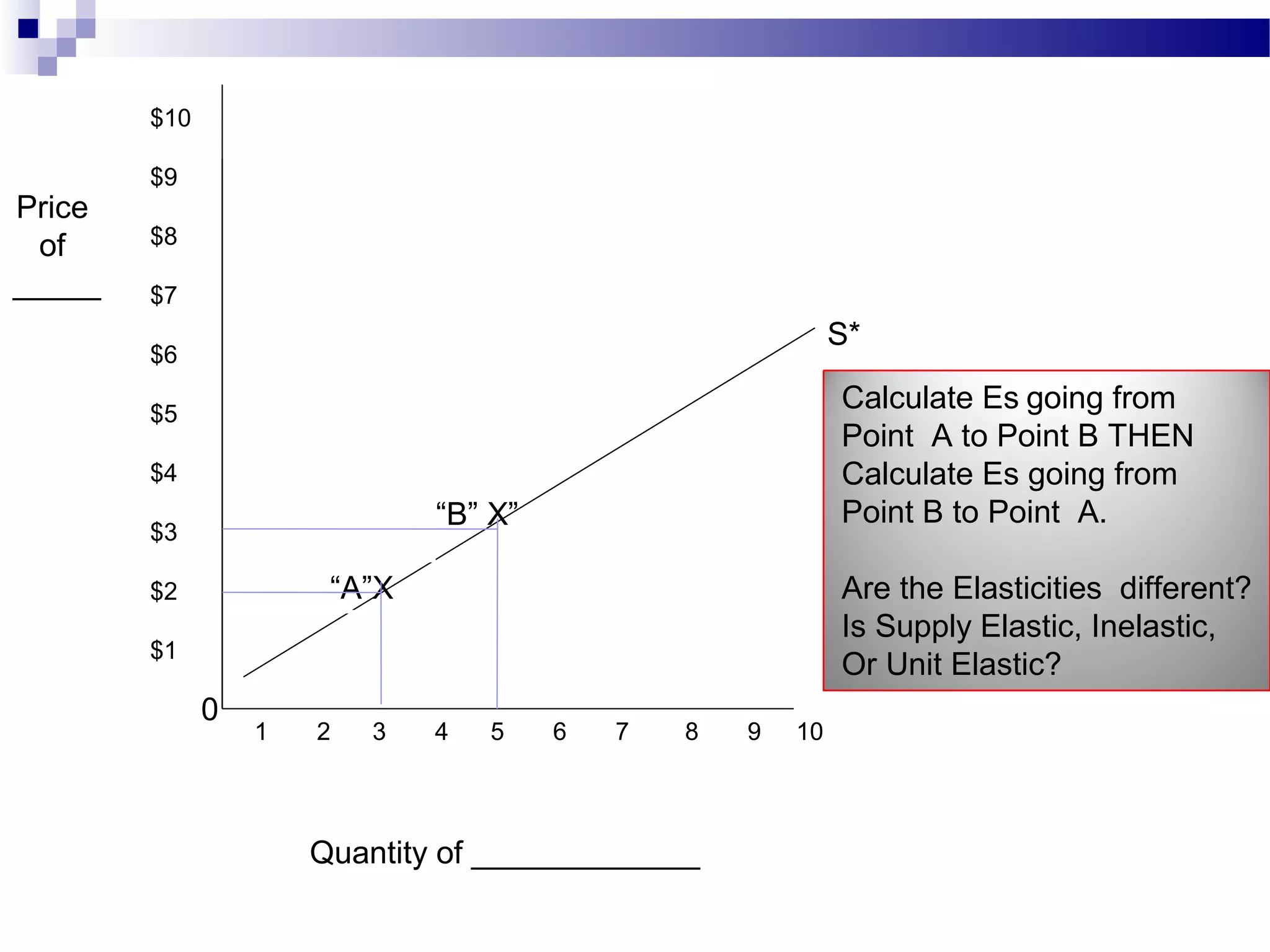
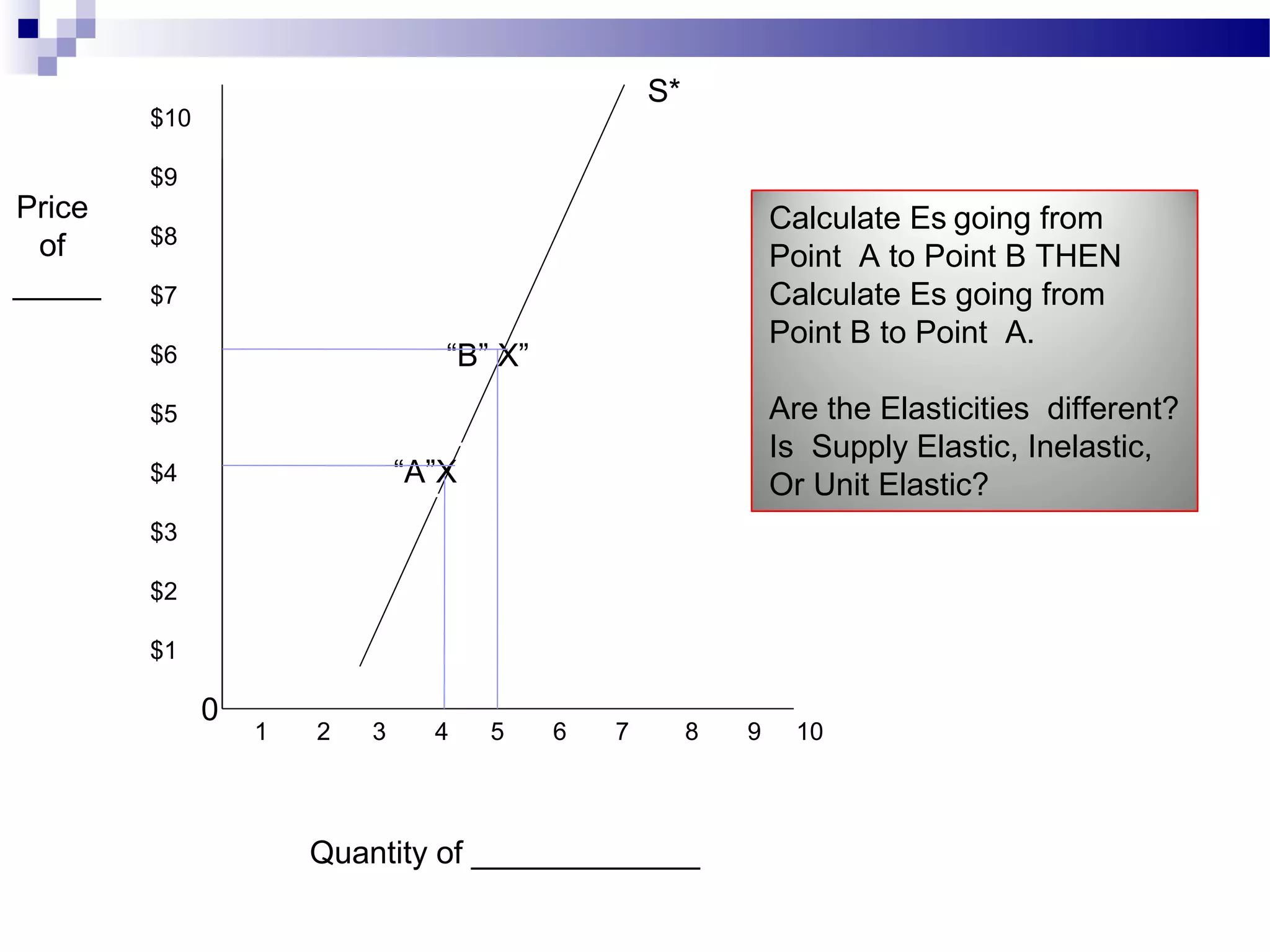
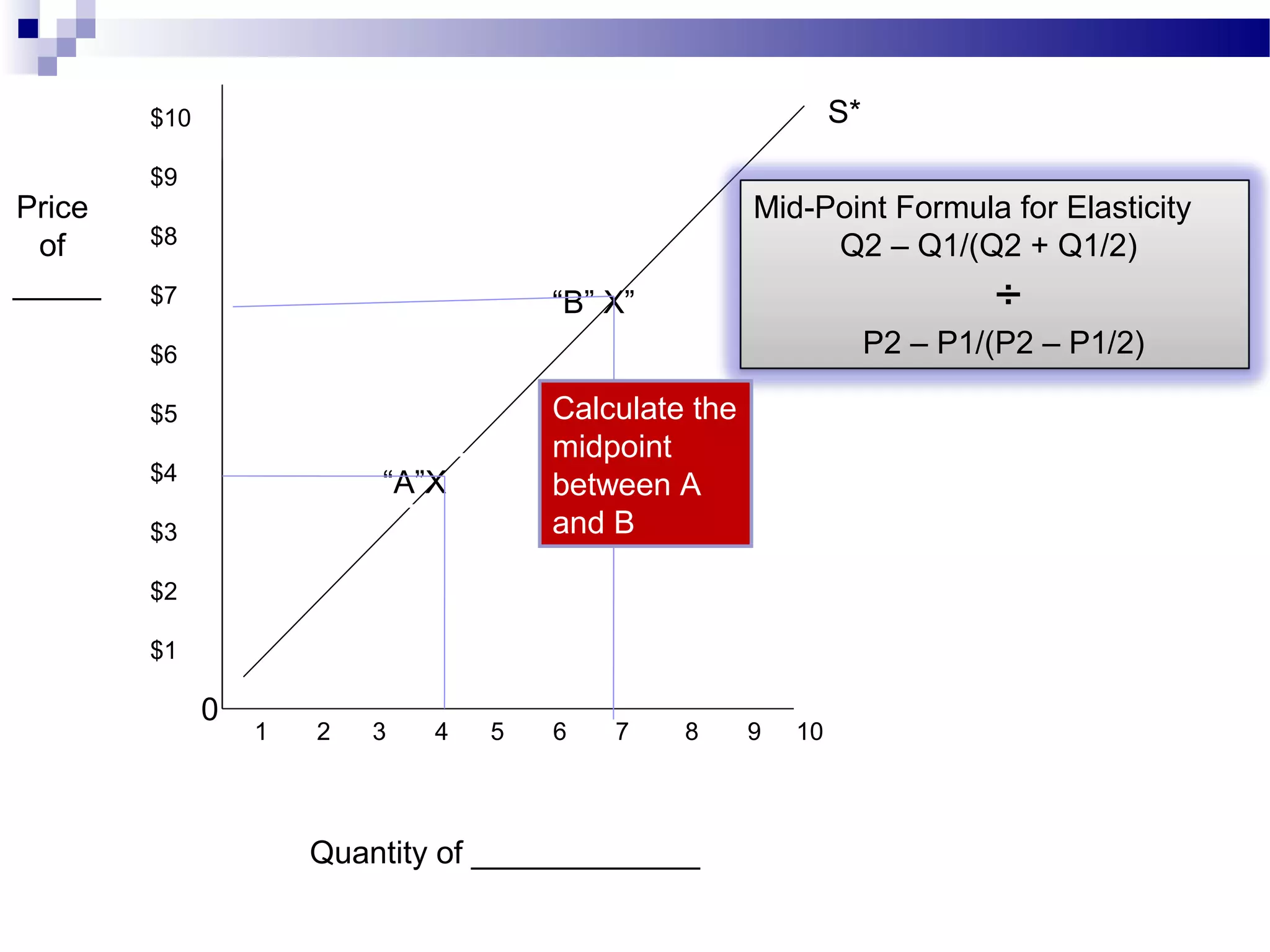
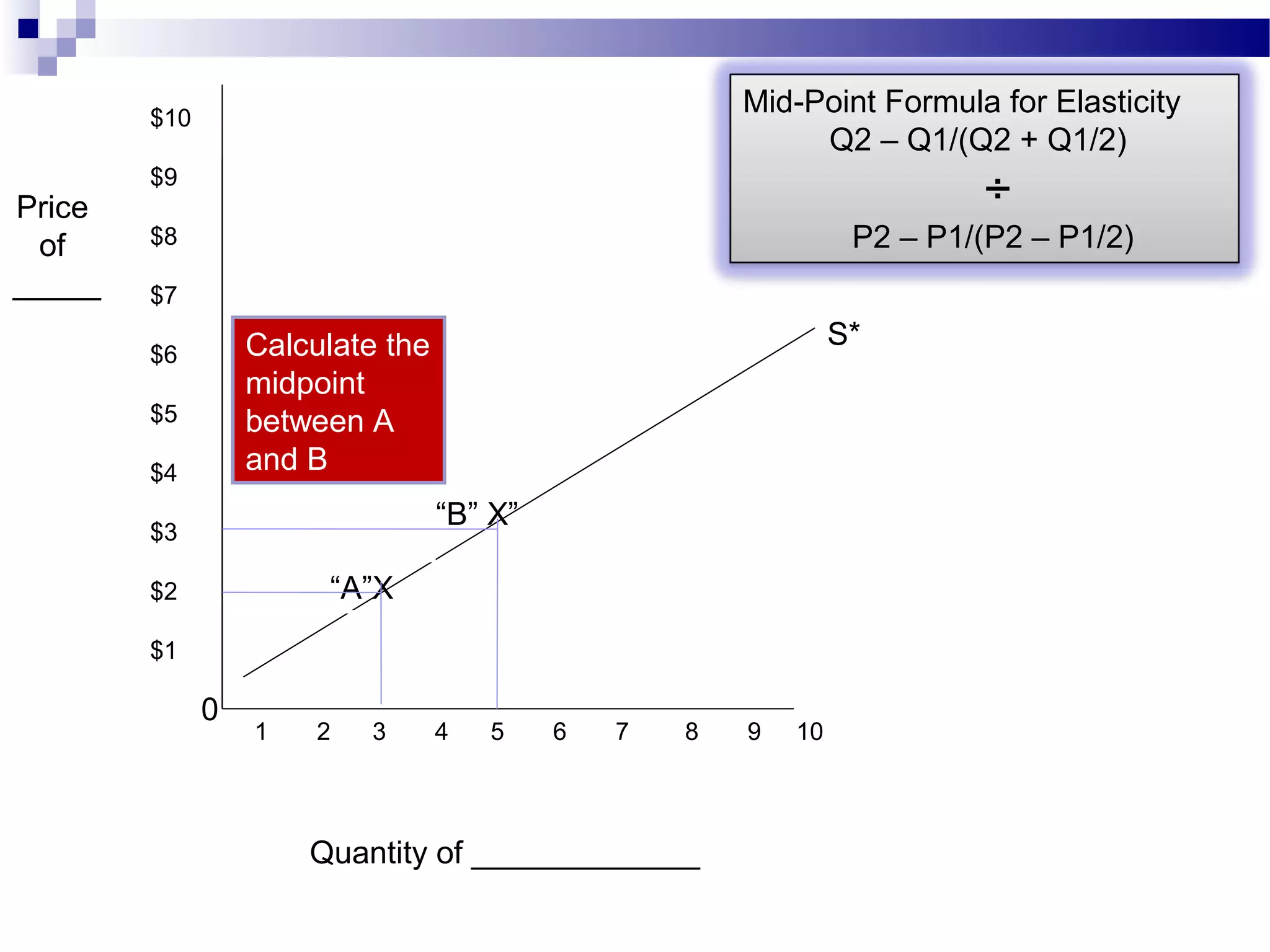
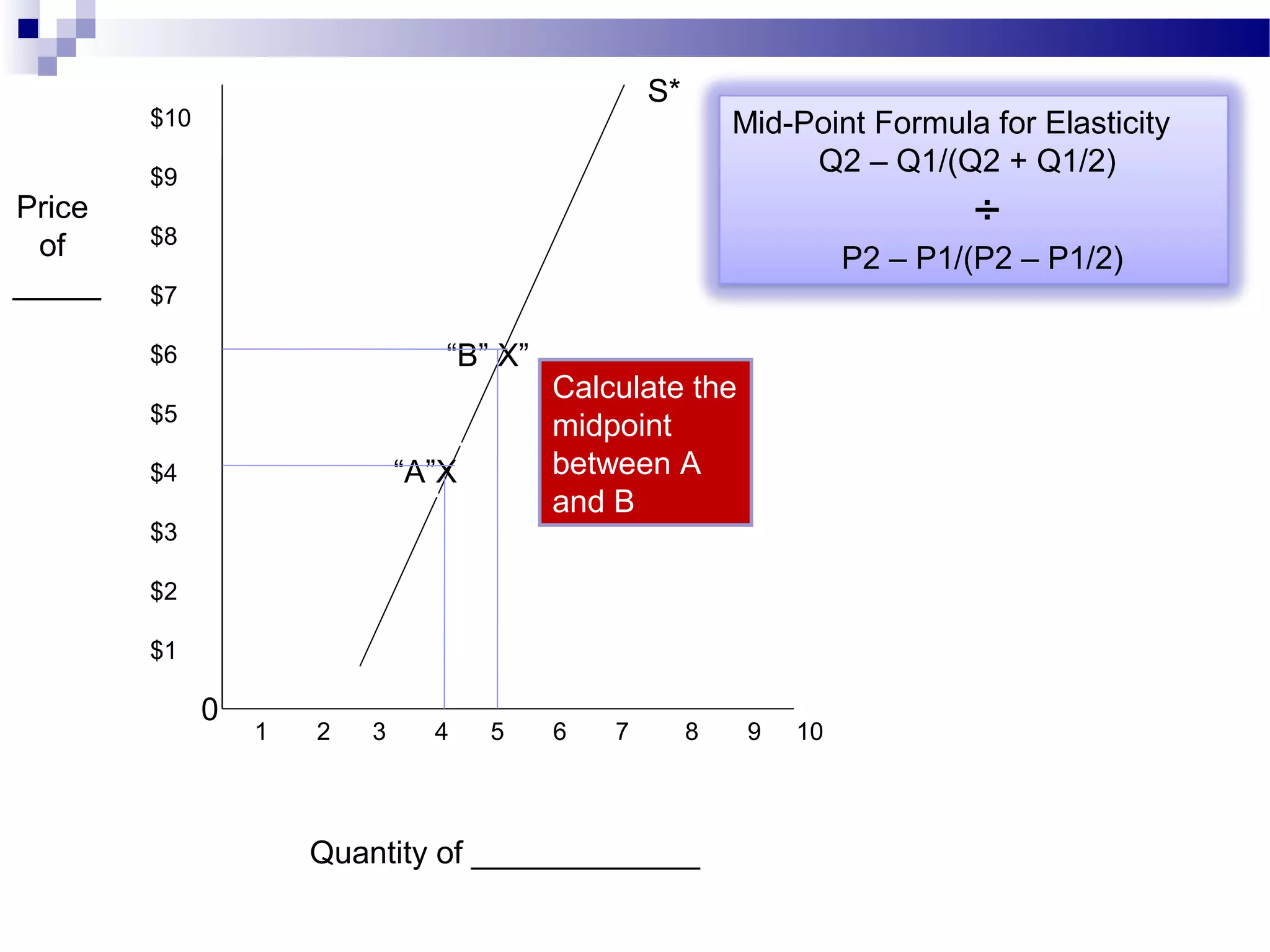
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of consumers or producers to changes in price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity divided by the percentage change in price. Demand is elastic if this value is greater than 1, inelastic if less than 1, and unit elastic if equal to 1. There are several factors that determine the elasticity of demand such as availability of substitutes, proportion of income spent, and whether the good is a necessity or luxury. Elasticity can be calculated between two points on a demand curve using the midpoint formula. The total revenue test also helps determine elasticity based on whether total revenue increases or decreases with a price change.