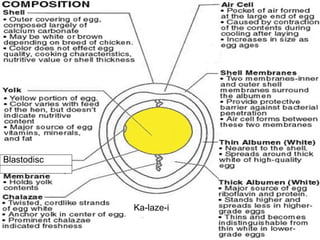
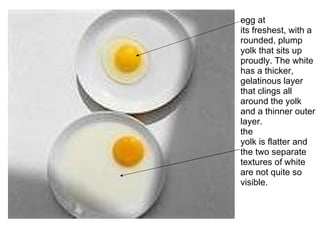
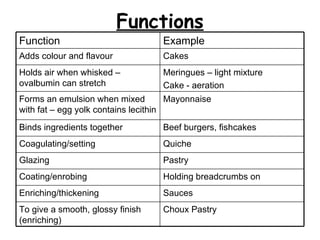
Eggs primarily contain protein and are a cheap, nutritious food in the UK. The main proteins in eggs are ovalbumin, conalbumin, and ovomucoid. An egg has an outer shell, inner egg white divided into thick and thin layers, and a nutrient-rich egg yolk. Eggs are processed into frozen whole eggs or dried eggs through pasteurization and spray or freeze drying. Heat causes egg proteins to coagulate, forming gels or thickening mixtures. Eggs are used in many recipes to bind, emulsify, aerate, and add flavor.