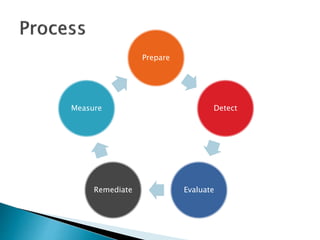
This document outlines the 5 steps of effective vulnerability management: prepare, detect, evaluate, remediate, and measure. It discusses important concepts for each step such as developing security policies and procedures, using vulnerability scanners, establishing evaluation and remediation criteria, implementing patches, and defining metrics to measure success. The document emphasizes that every environment is unique and input from IT teams is important to develop the right approach for each organization.