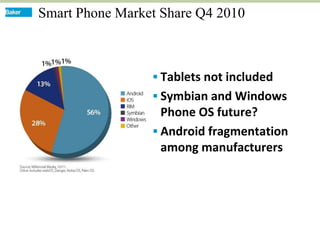
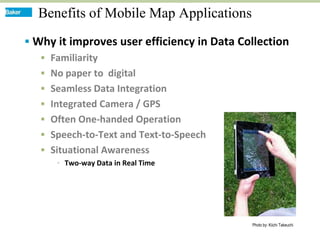
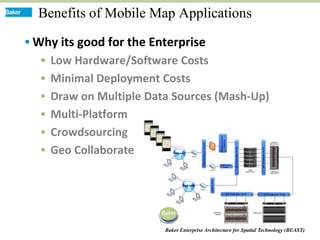
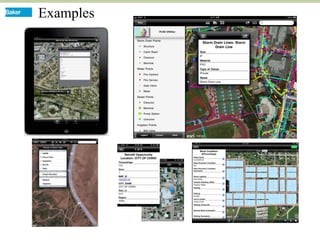
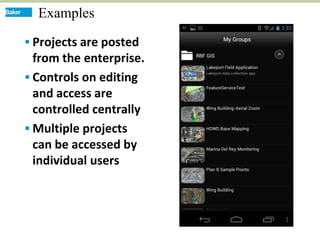
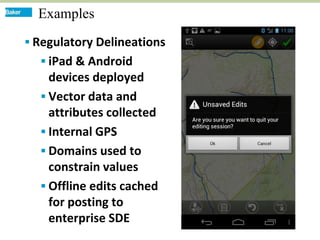
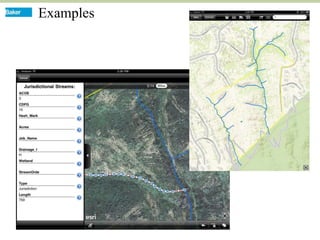
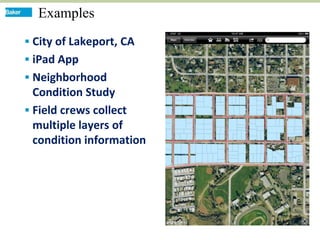
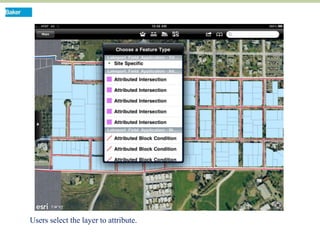
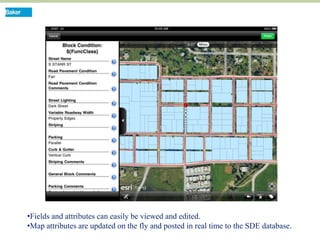
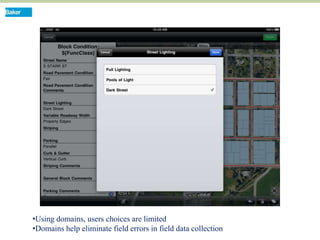
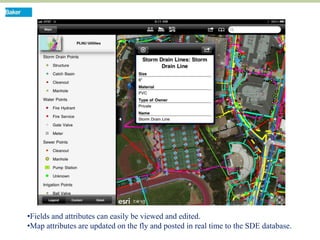
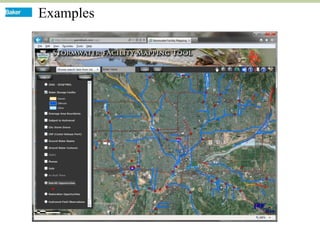
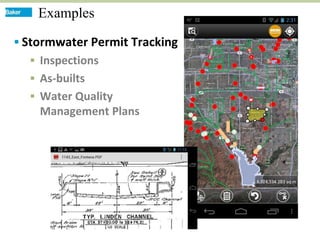
This document discusses how mobile phone applications can effectively collect and manage data. It provides examples of using mobile apps for tasks like public needs assessments, design work, and capturing or analyzing large amounts of data by leveraging mobile technologies. Specific considerations for deploying smartphone apps include platform choice, connectivity needs, ruggedness, battery life, and GPS accuracy. The document outlines benefits like improved user efficiency, low costs, and ability to integrate maps, cameras, and GPS. Examples illustrated include infrastructure condition assessments, regulatory delineations, and stormwater permit tracking using mobile GIS apps.