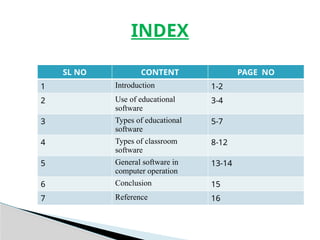
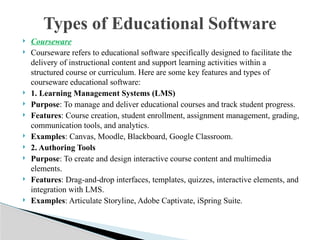
The document discusses the importance and various types of educational software, highlighting its benefits for teachers, students, and administrators. It covers categories such as educational games, learning management systems, and collaborative tools, along with specific software examples that enhance learning in classrooms. The conclusion emphasizes that effective use of educational software can significantly enrich the learning experience by making it more interactive and accessible.