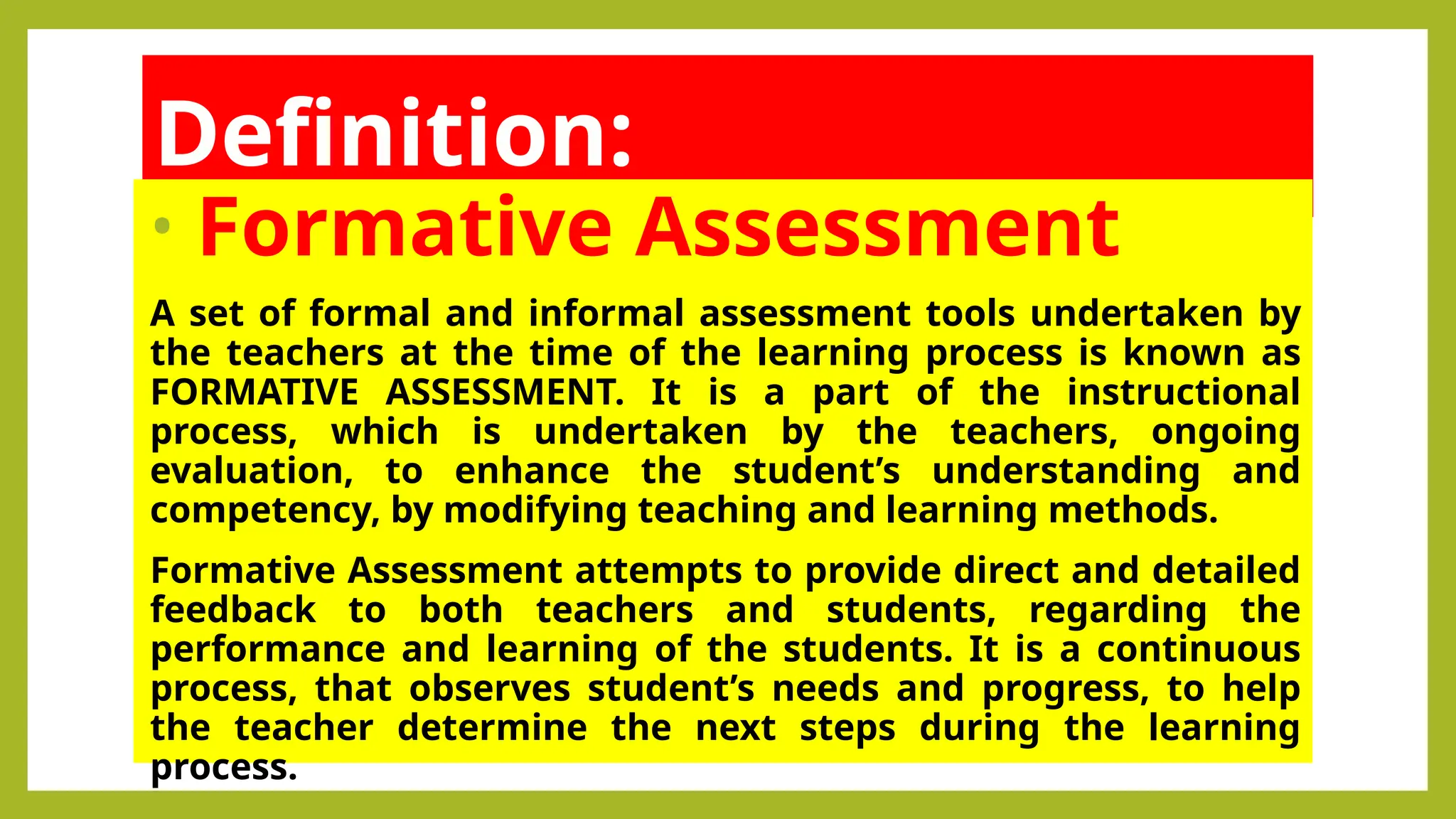
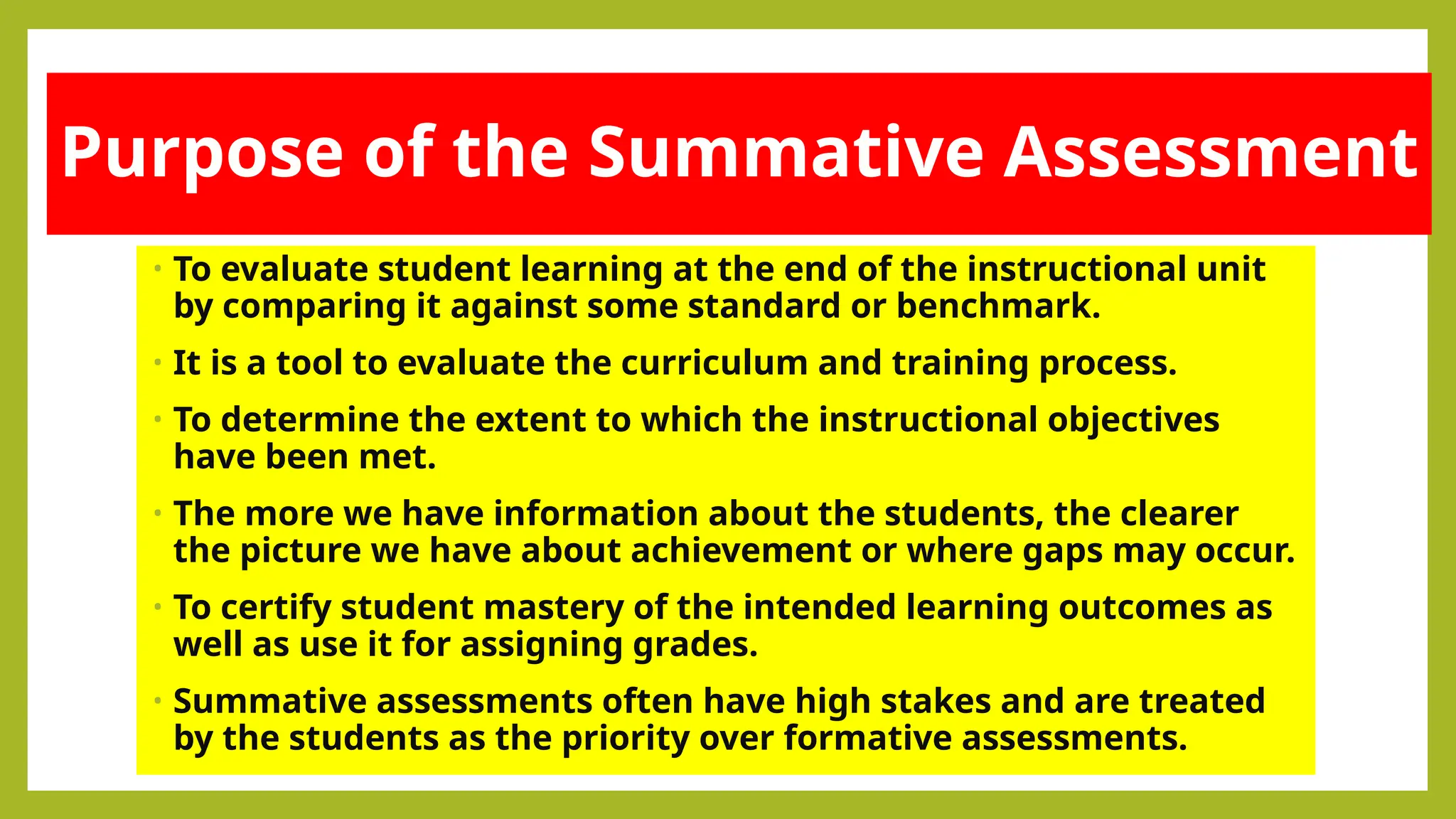
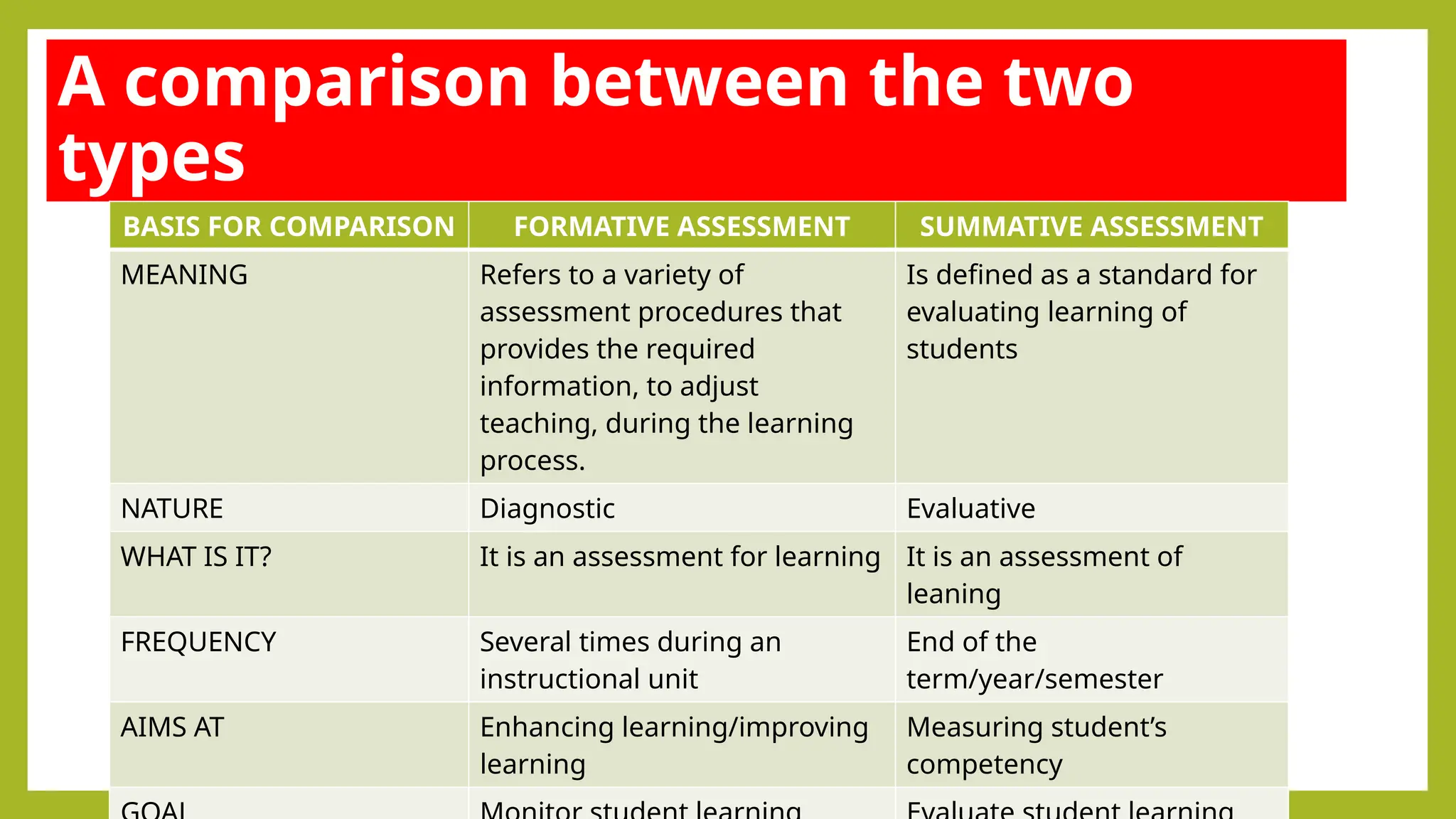
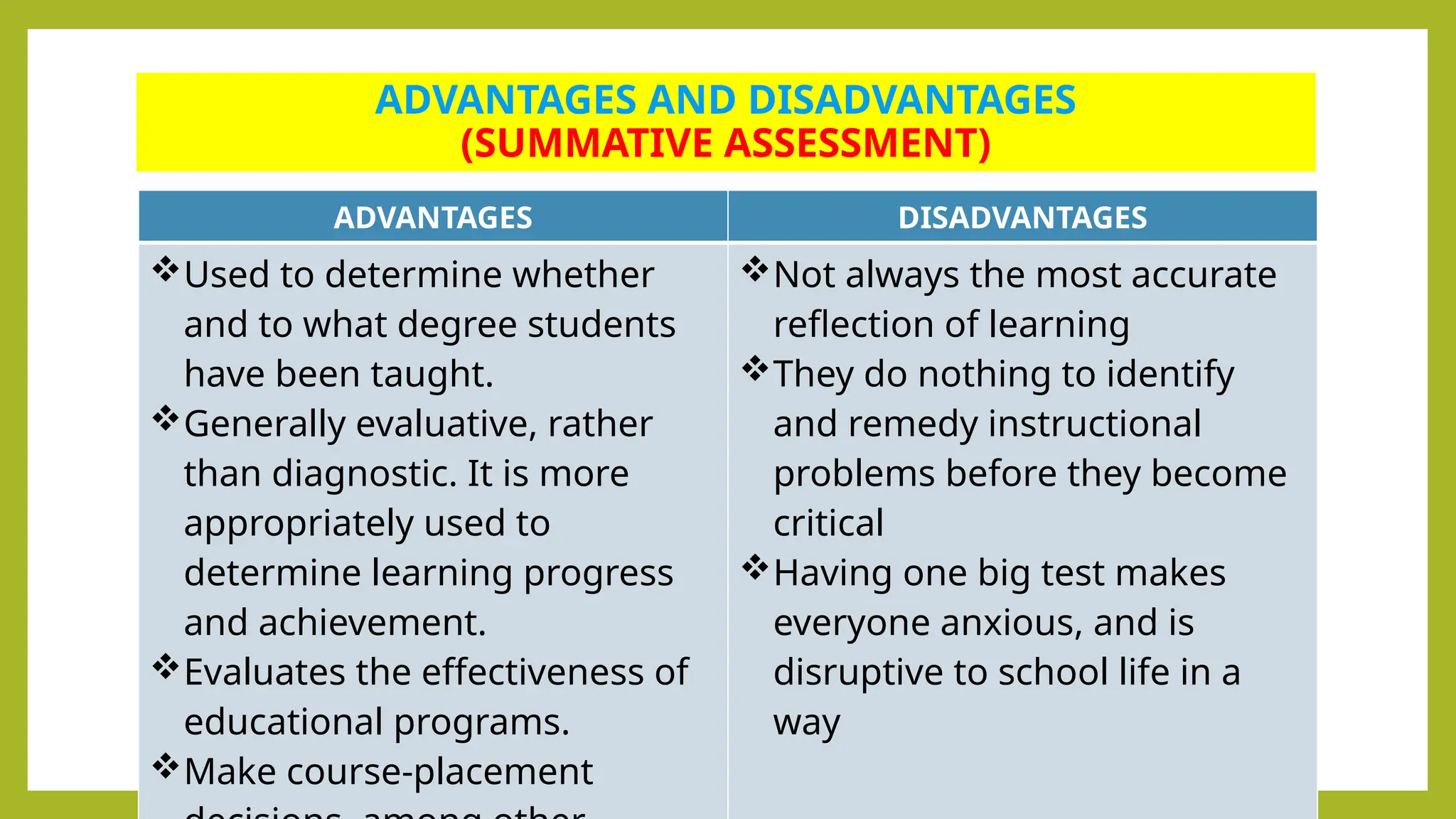
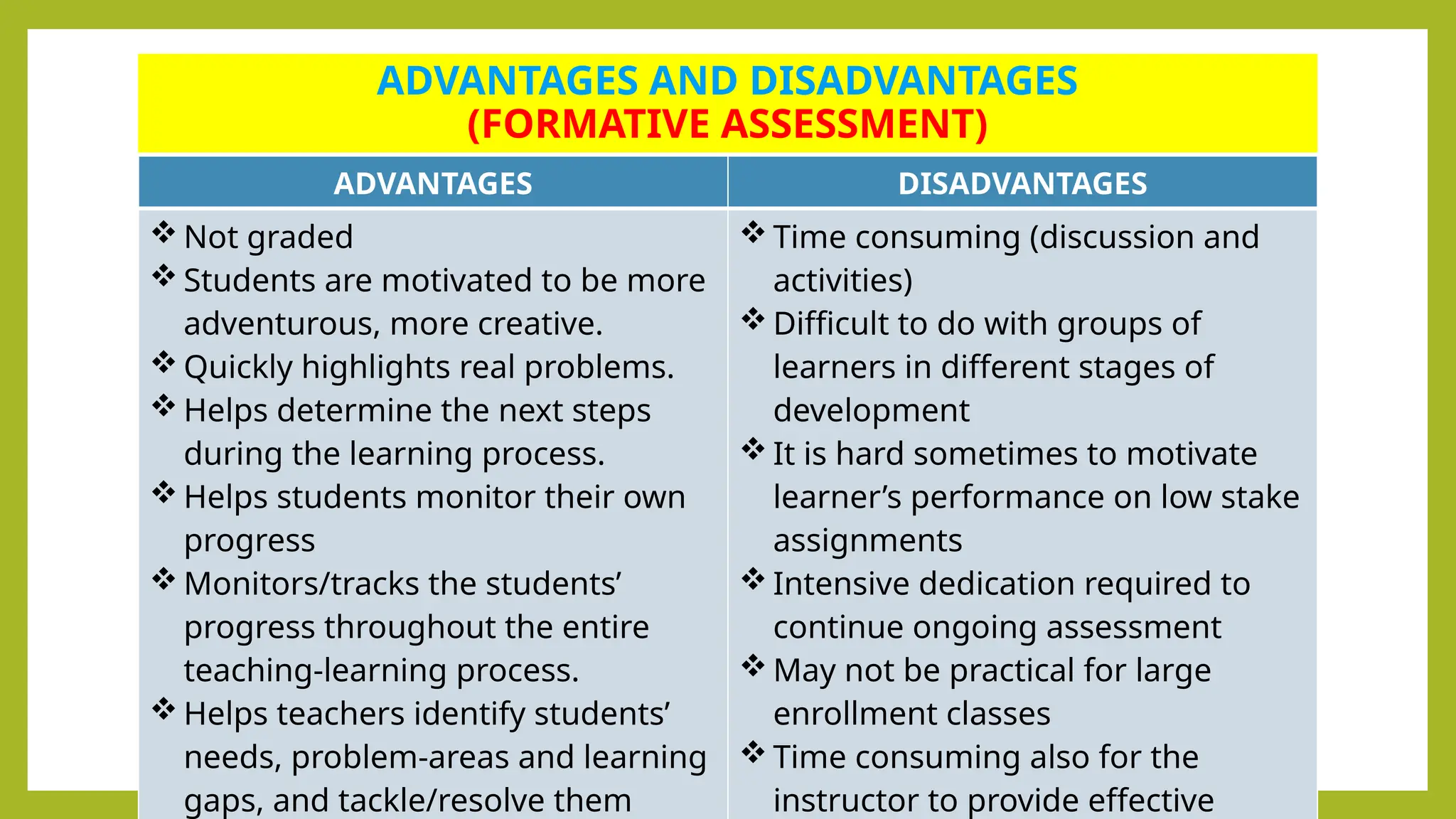
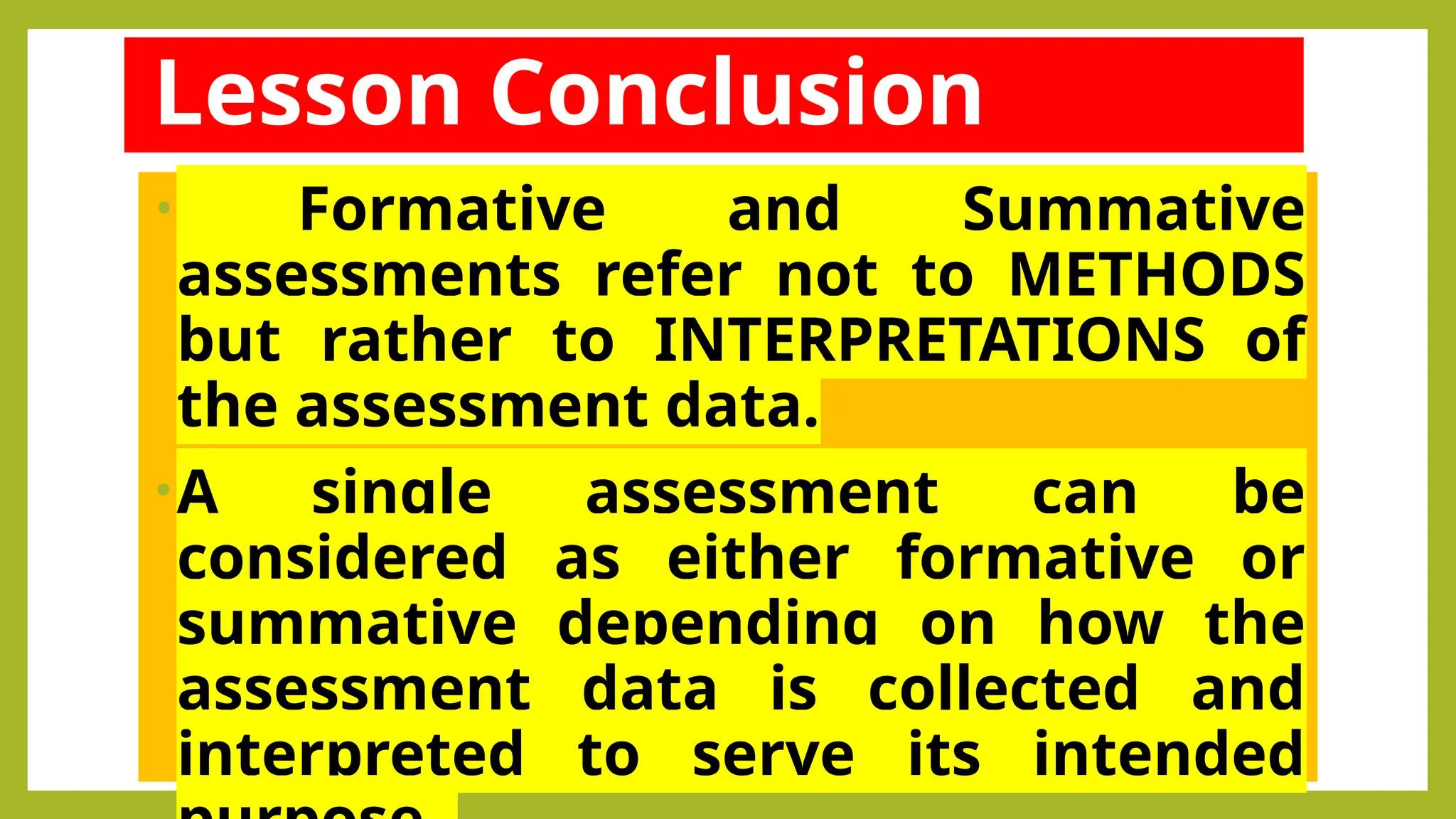
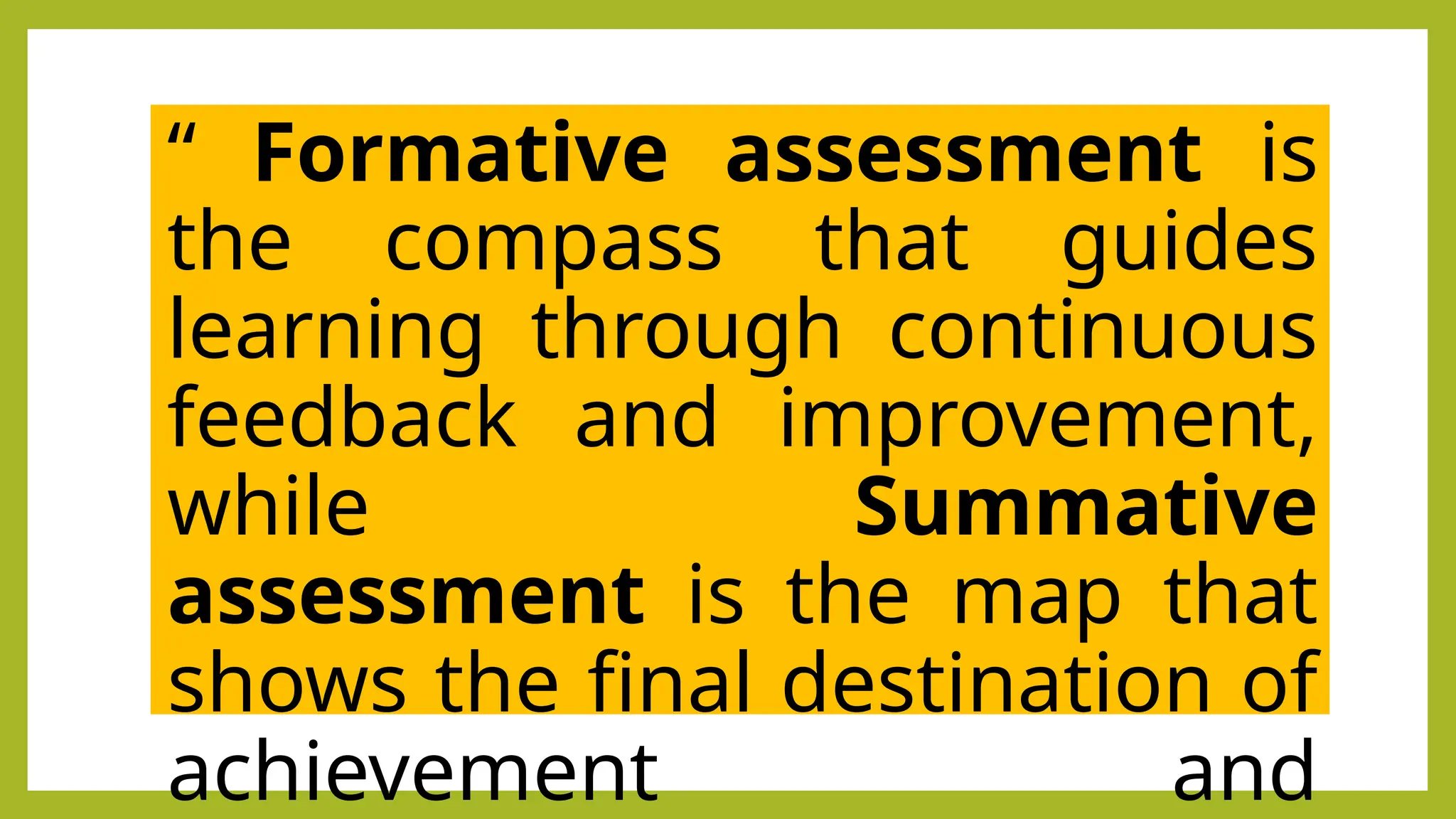
The document outlines the differences between formative and summative assessments, defining the former as ongoing evaluations aimed at enhancing student learning and the latter as periodic evaluations measuring knowledge retention. Formative assessments provide real-time feedback to both teachers and students, while summative assessments serve as a benchmark for learning at the end of instructional units. Advantages and disadvantages of each type are discussed, highlighting the importance of understanding their distinct roles in educational practice.