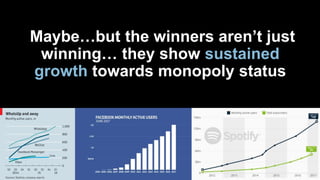
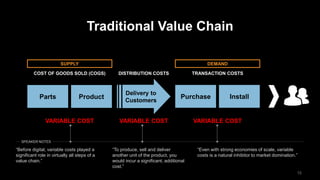
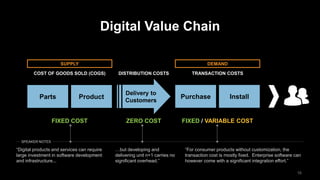
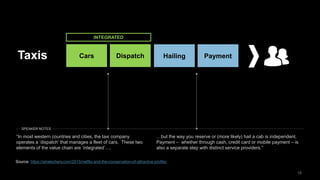
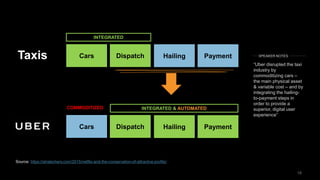
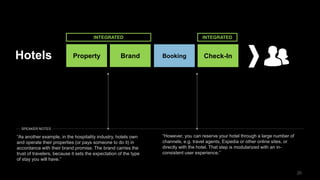
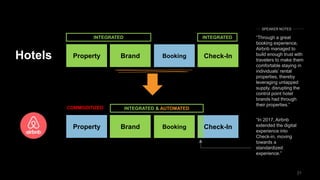
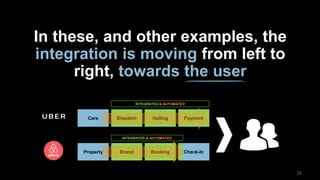
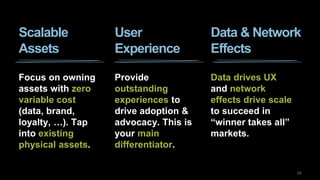
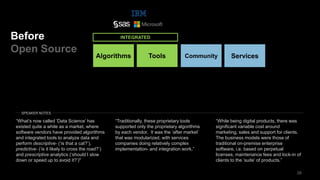
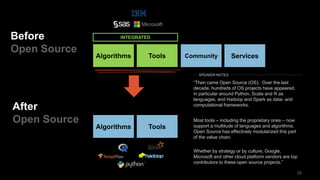
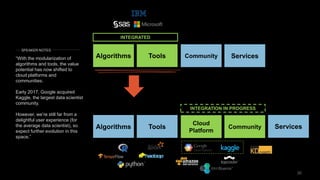
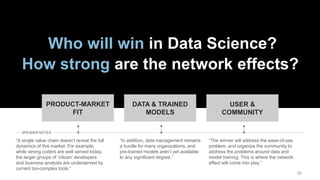
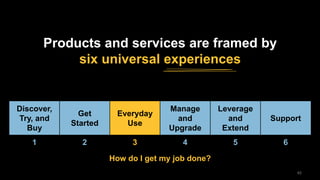
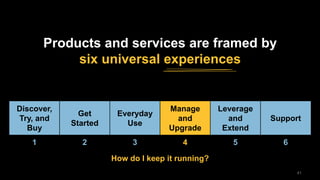
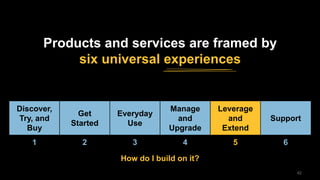
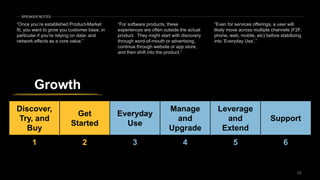
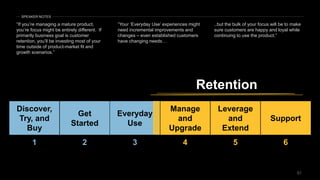
The document discusses the impact of digital disruption on various industries, highlighting how digital business models leverage technology to transform value chains and enhance user experiences. It emphasizes the importance of zero variable costs, user experience, and data-driven strategies in achieving competitive advantage. The analysis extends to specific industries such as transportation and hospitality, illustrating how companies like Uber and Airbnb have successfully disrupted traditional models through innovative digital approaches.