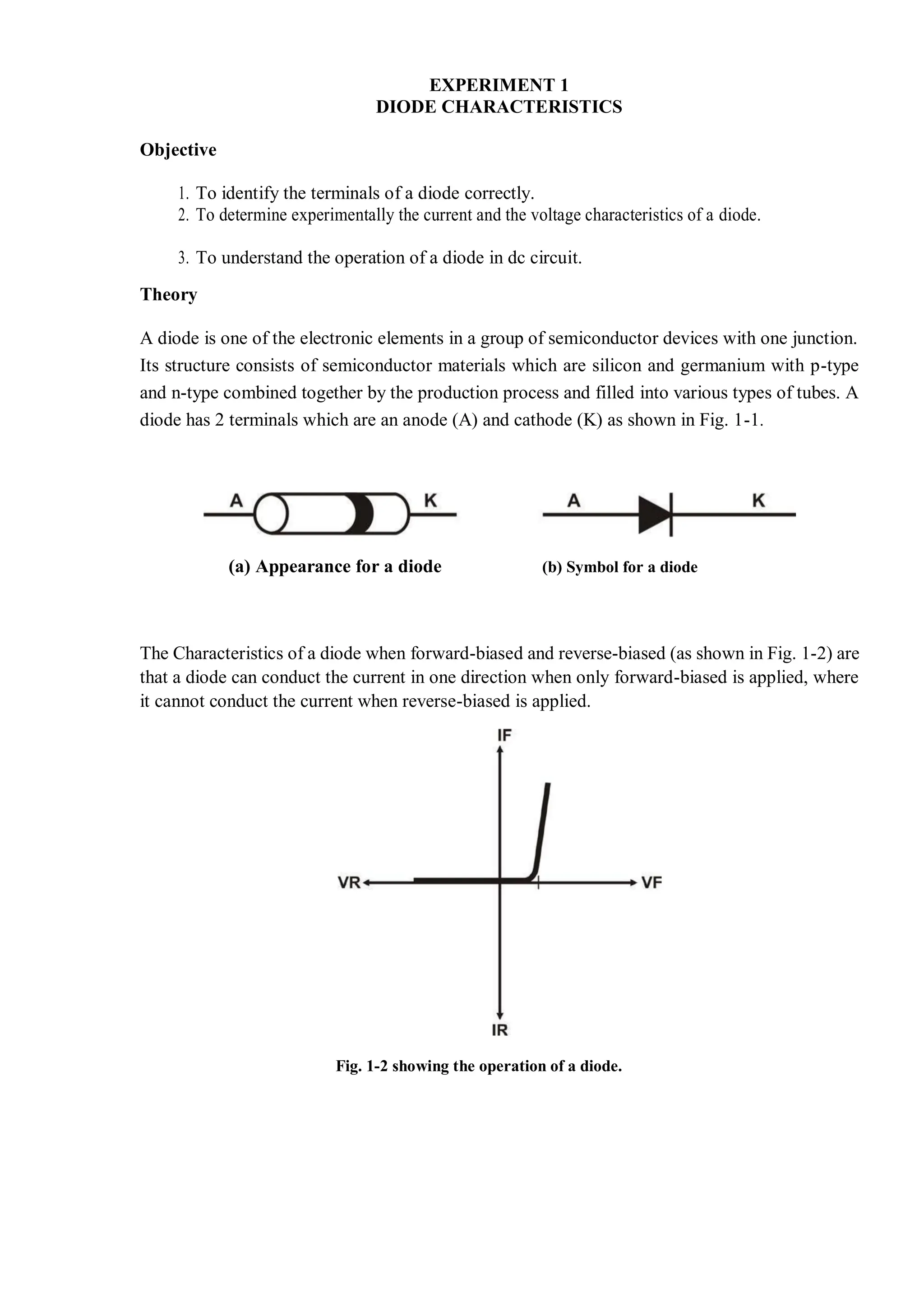
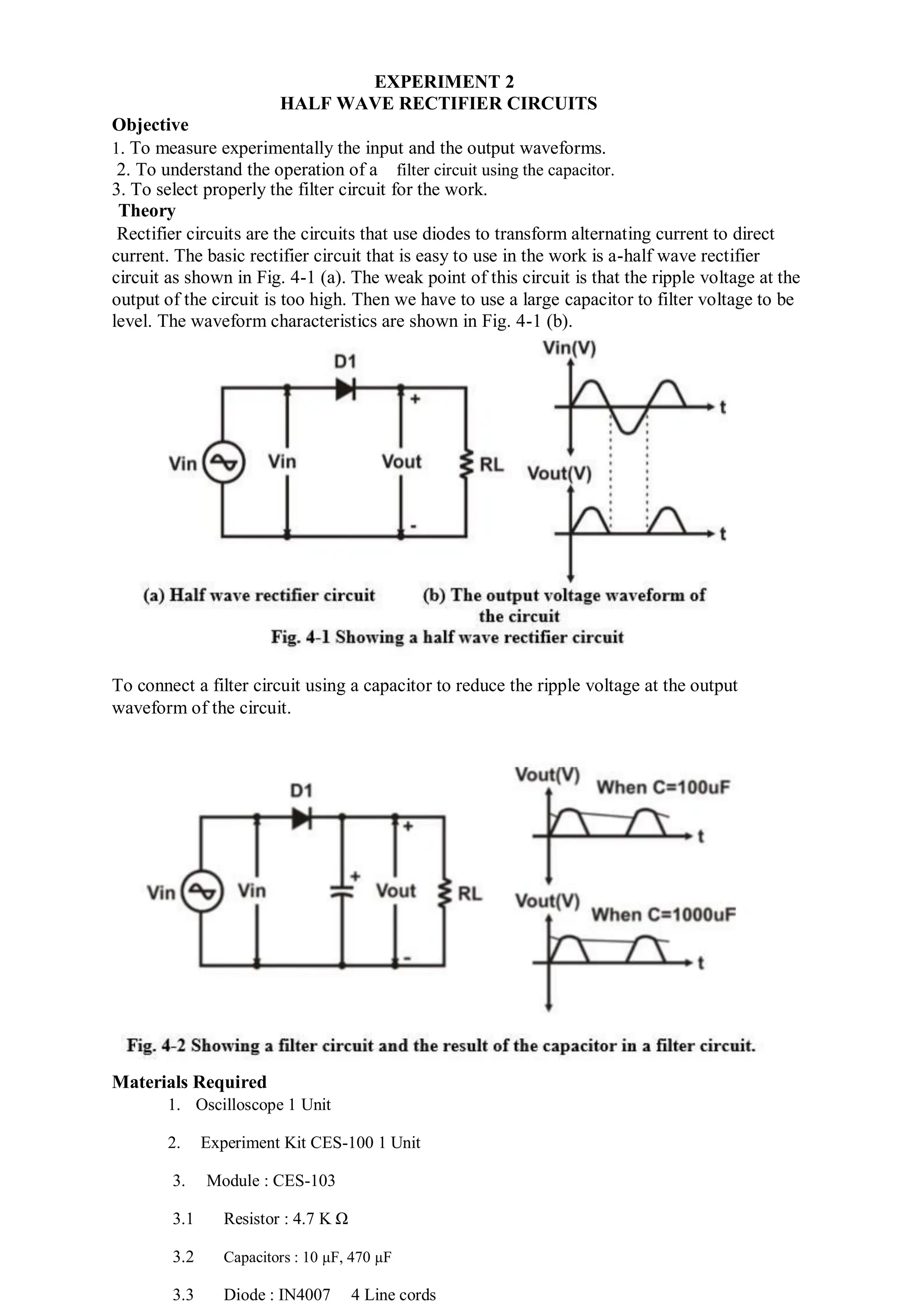
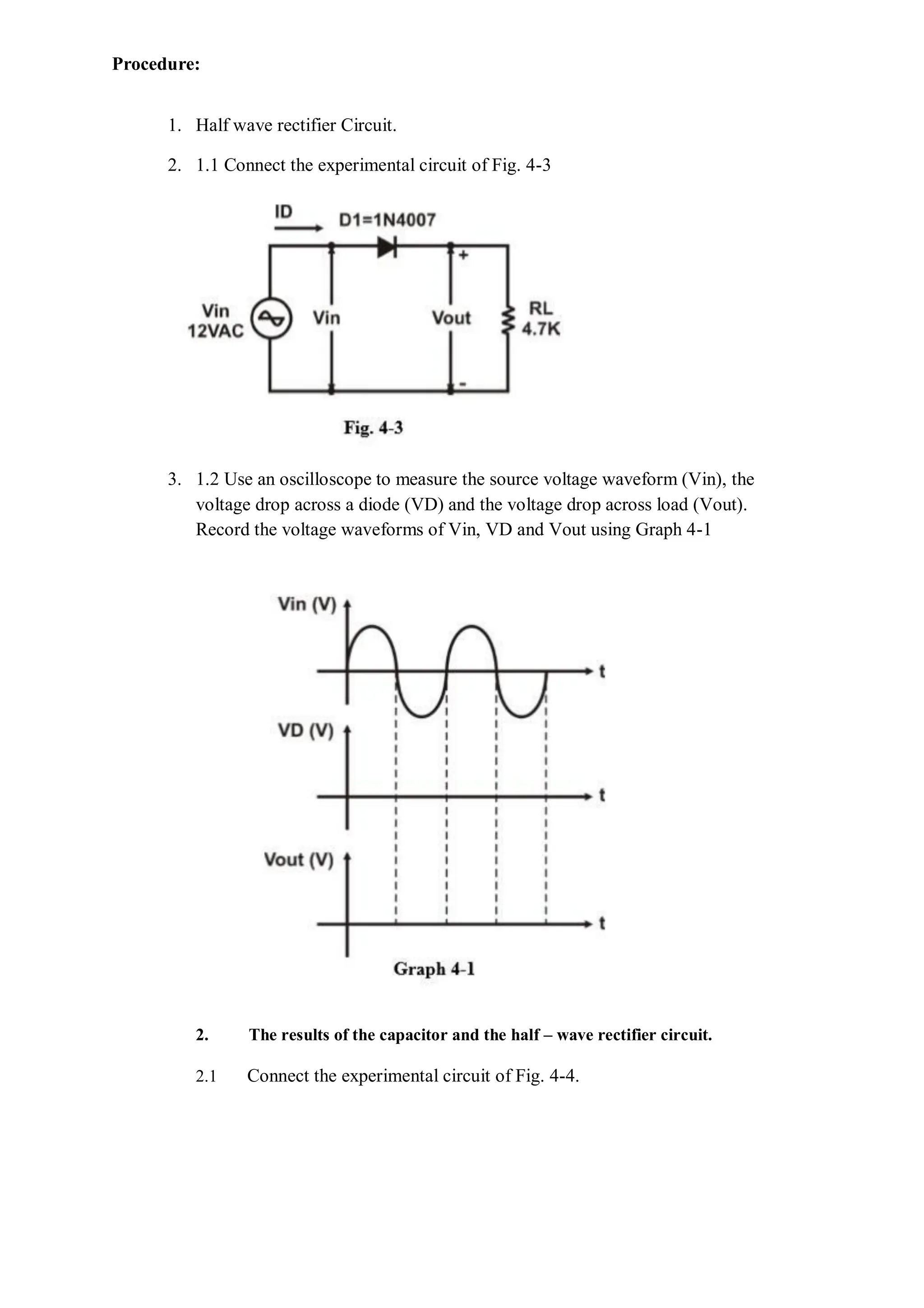
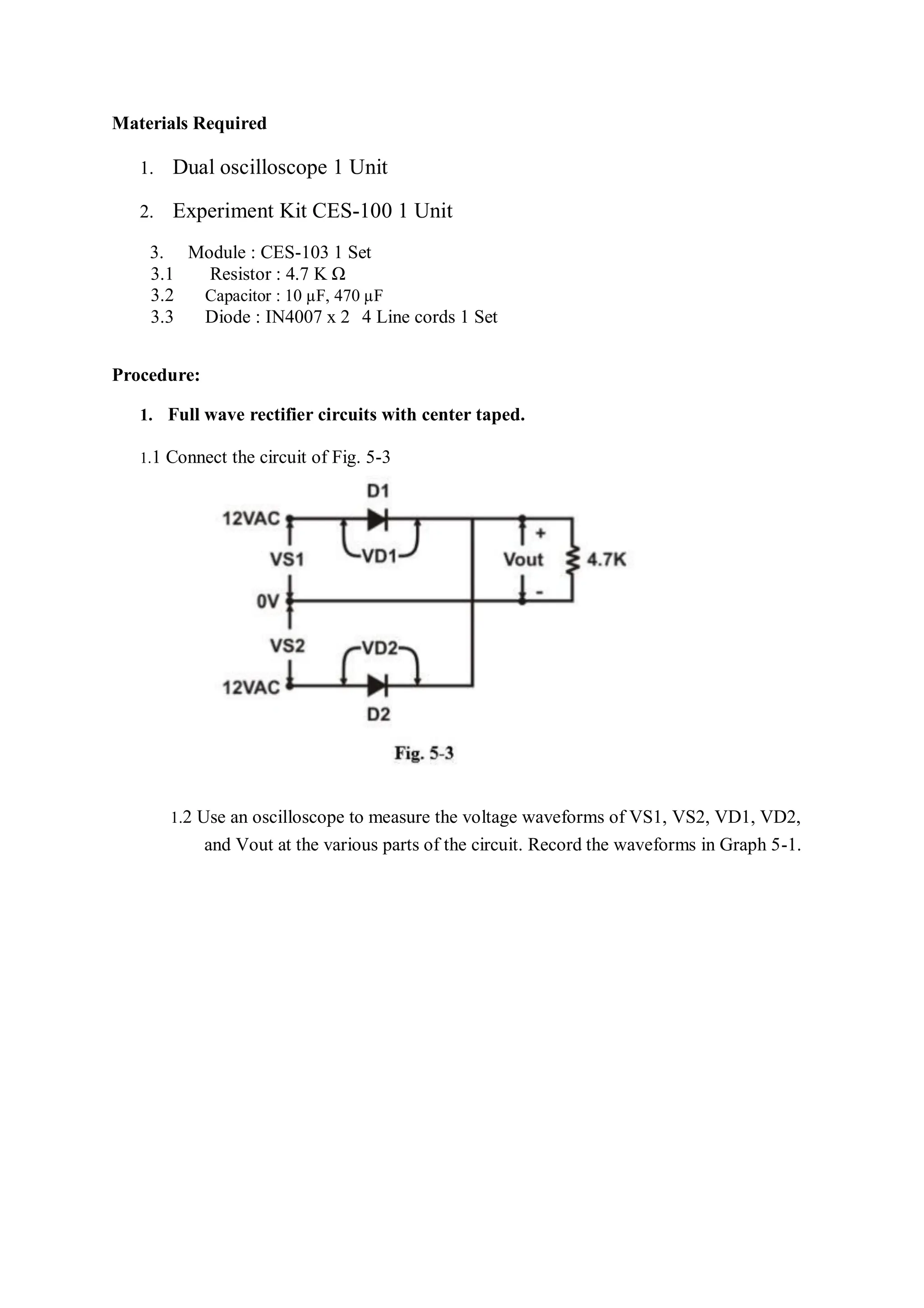
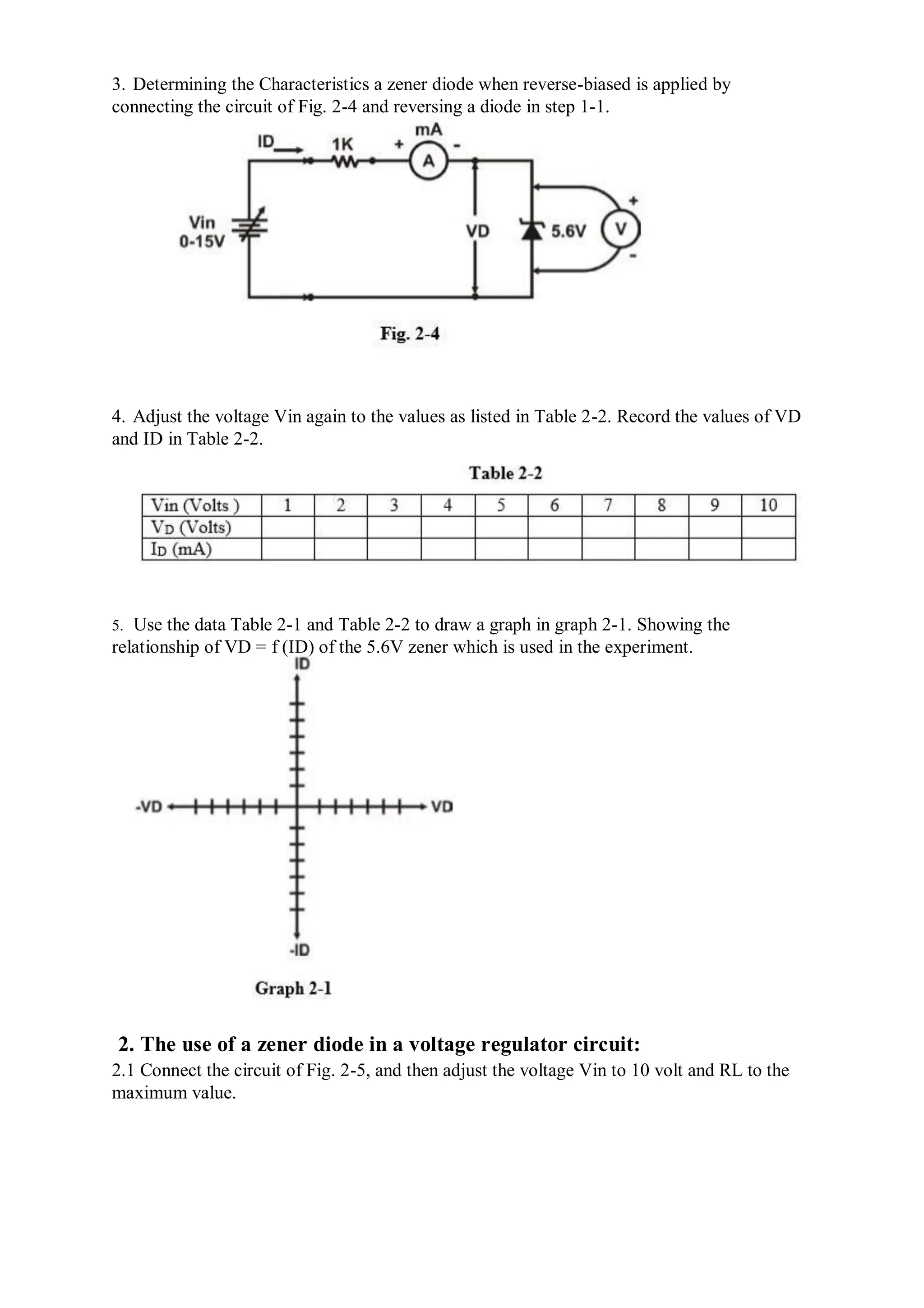
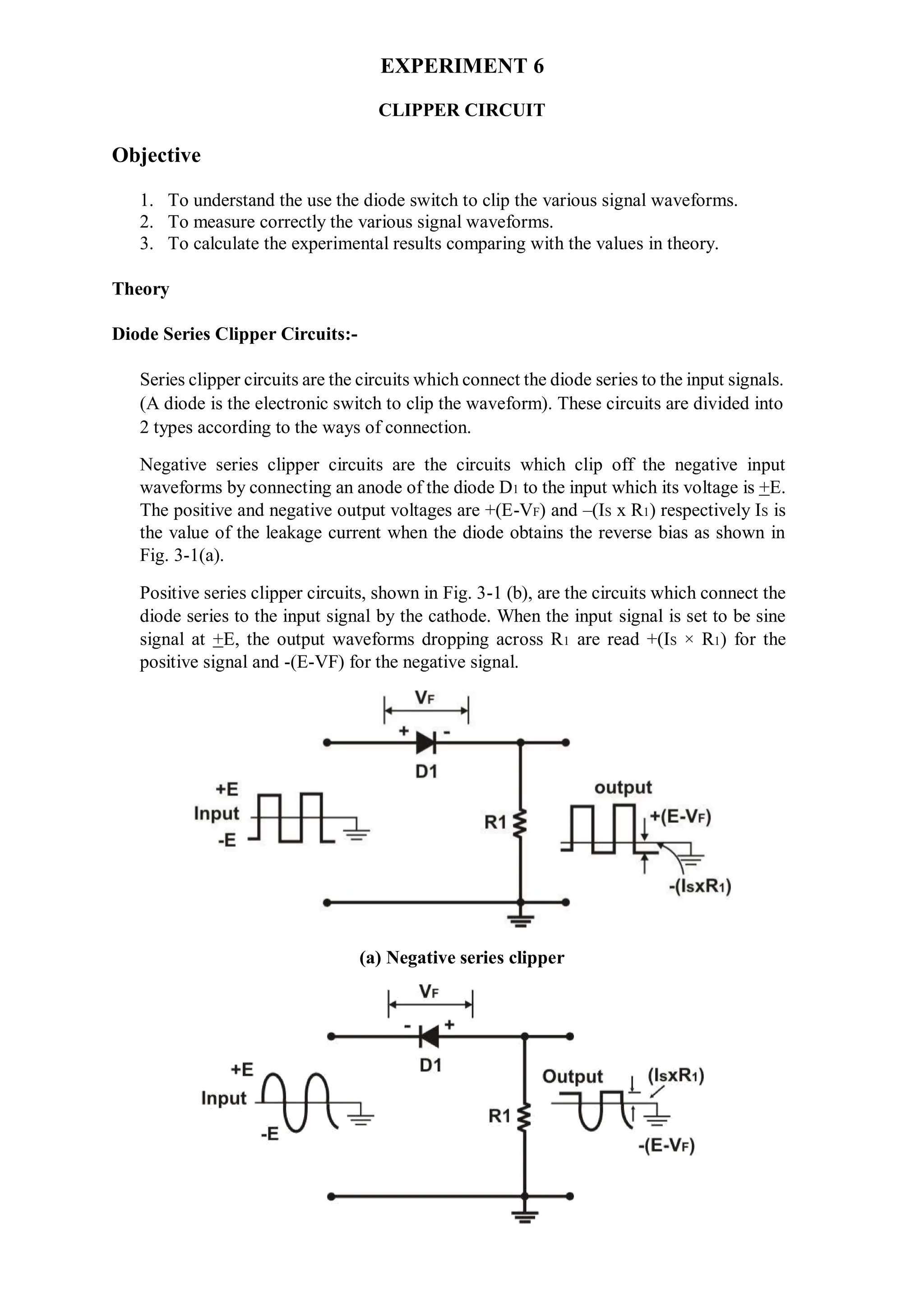
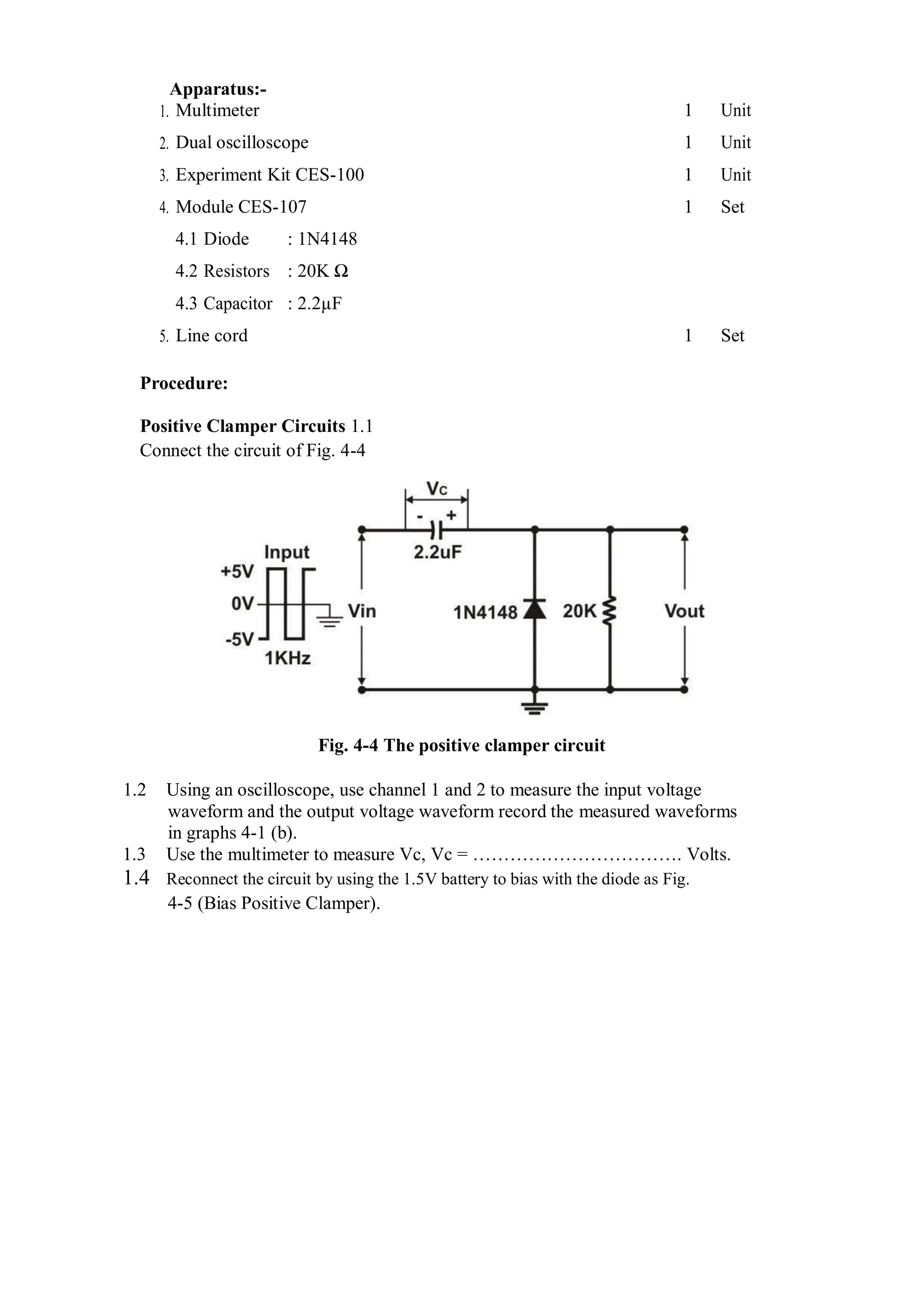
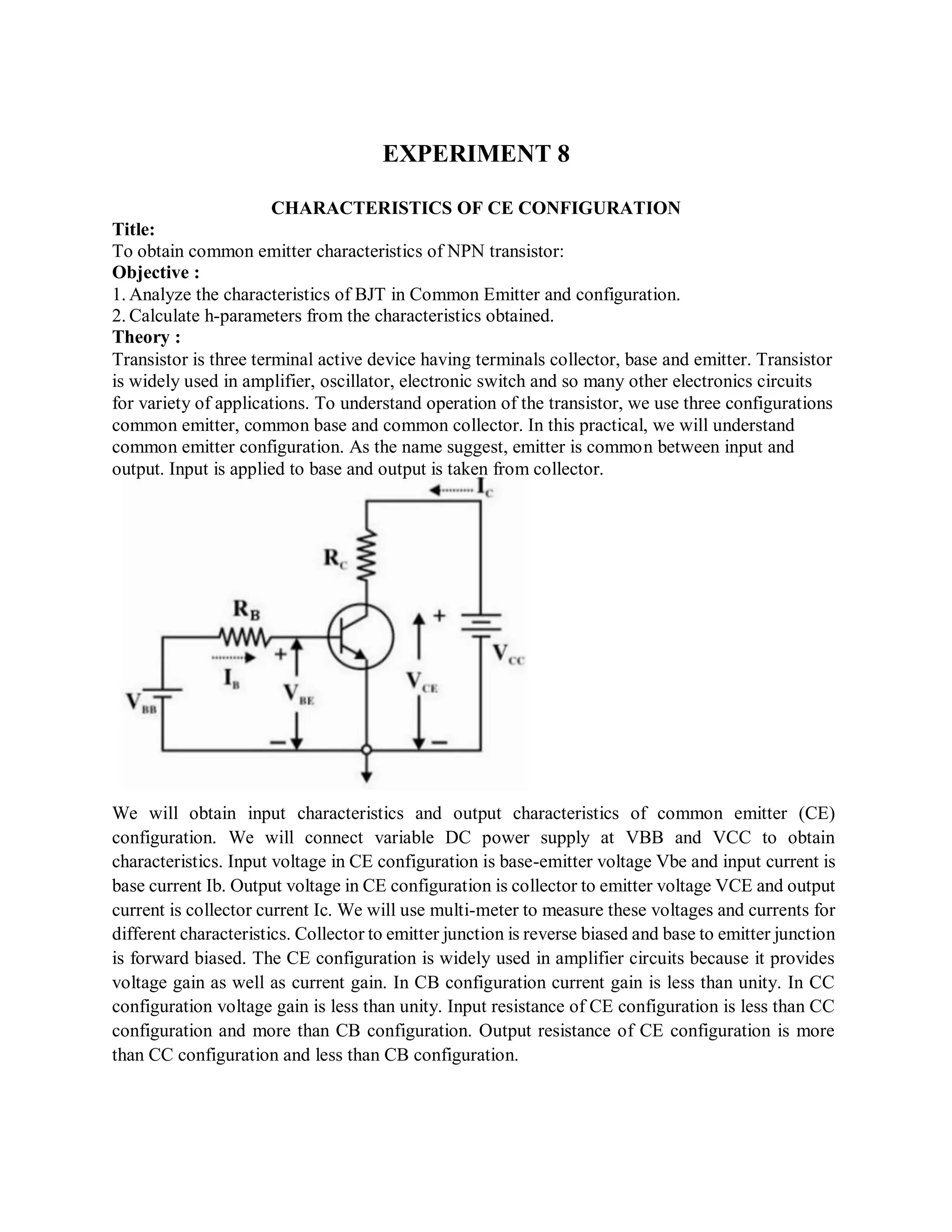
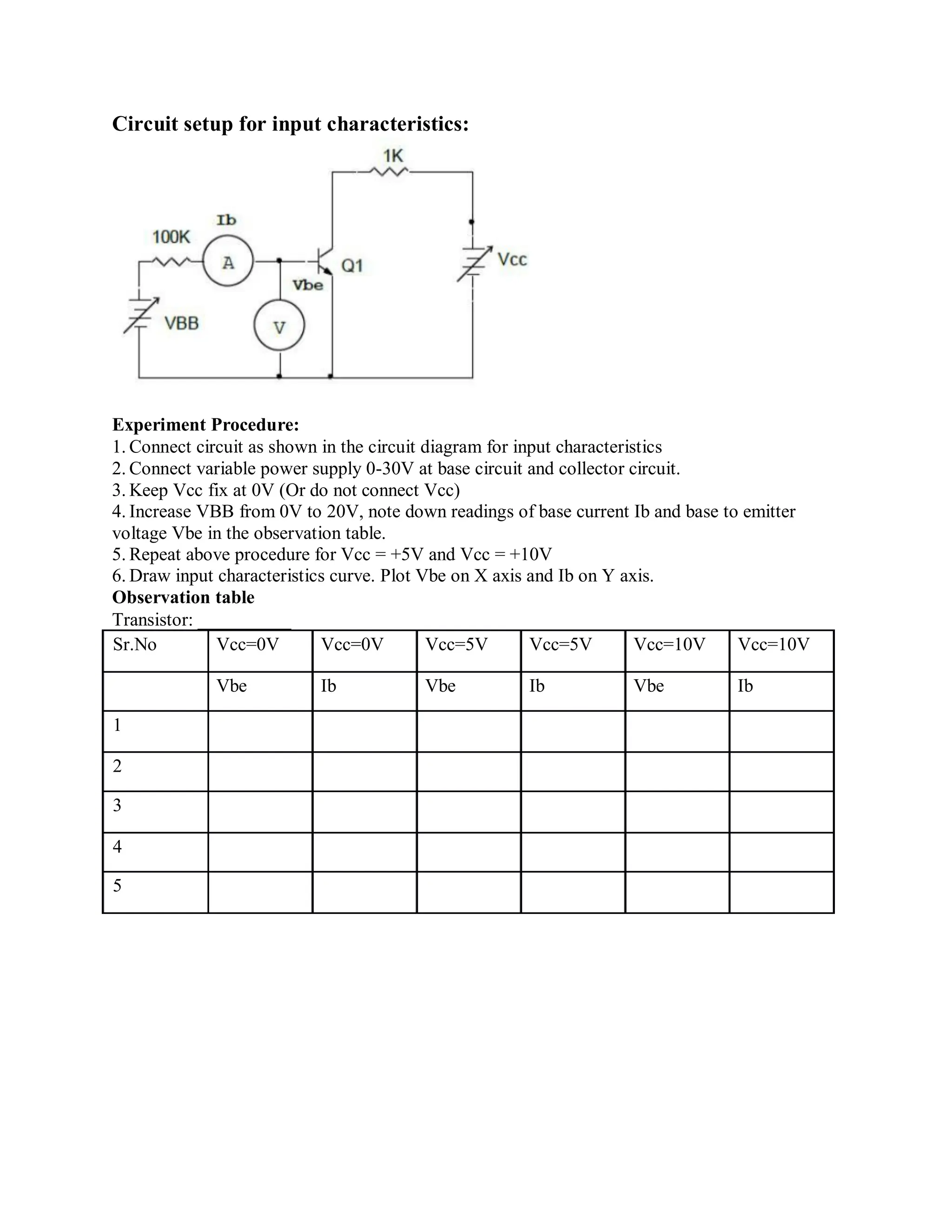
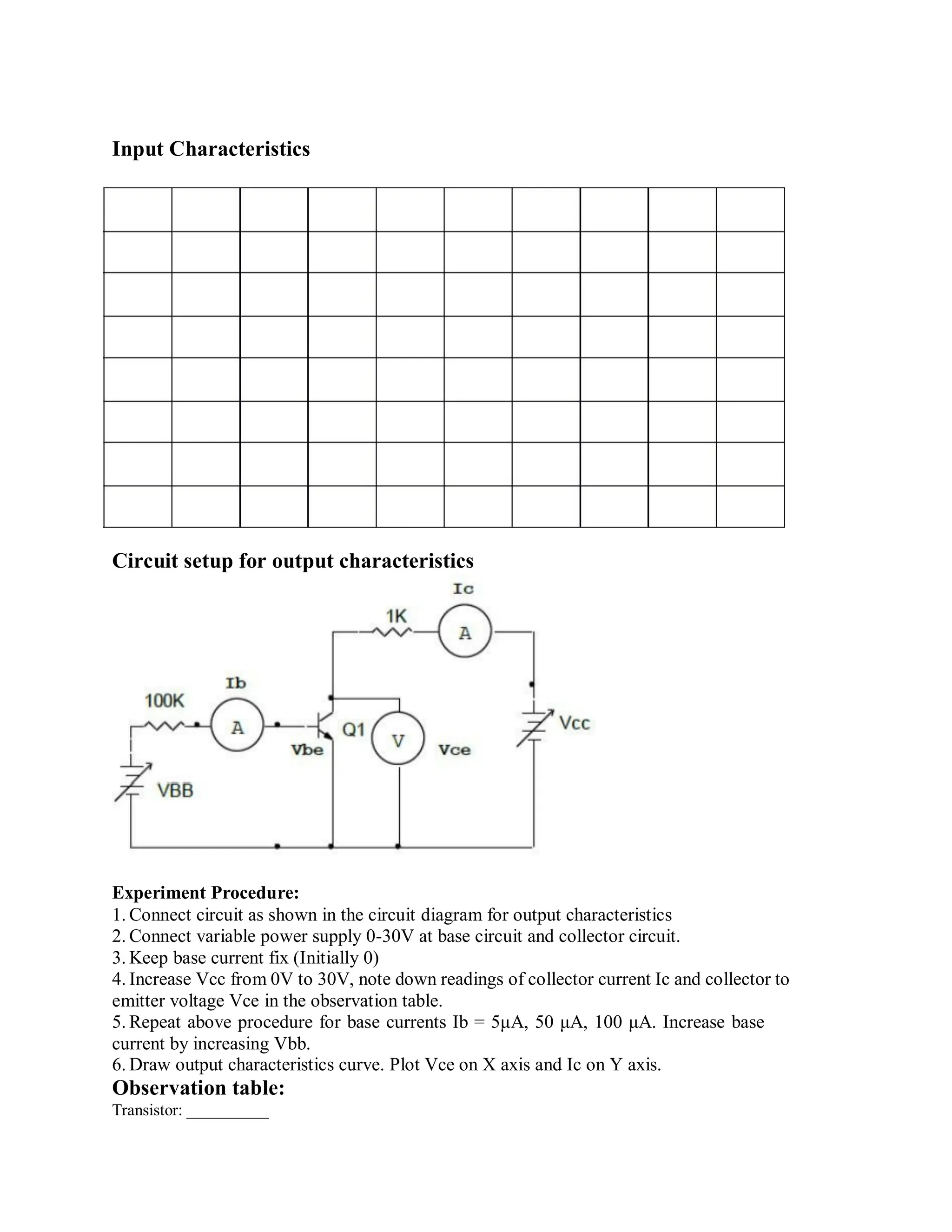
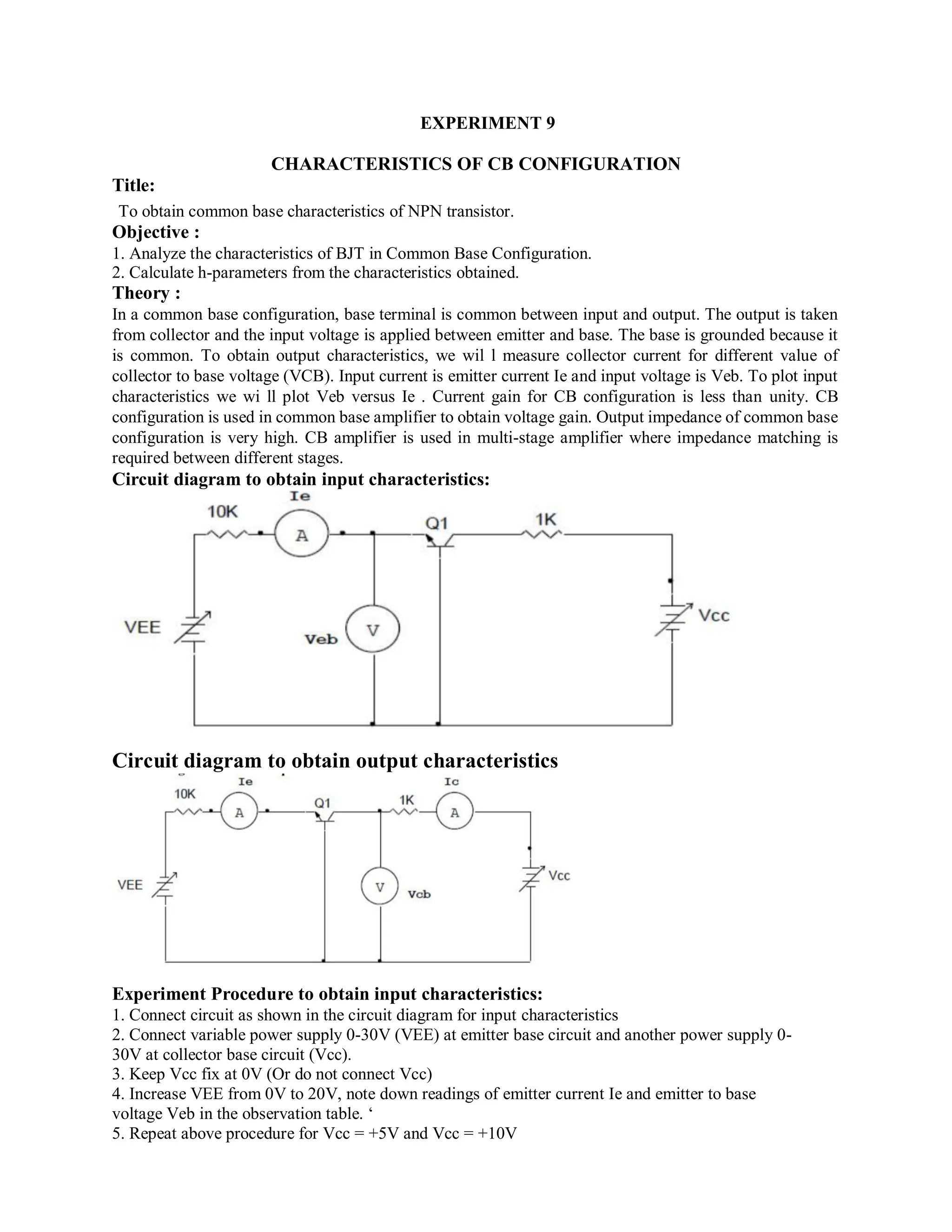
This document describes experiments on diode characteristics and applications. Experiment 1 involves identifying diode terminals and measuring the current-voltage characteristics of silicon and germanium diodes. Experiment 2 examines half-wave rectifier circuits and the effect of capacitors. Experiment 3 analyzes full-wave rectifier circuits with center tap and their voltage waveforms. Later experiments cover zener diode characteristics, clipper circuits, and clamper circuits. Diode switching is used to clip signal waveforms in various ways.