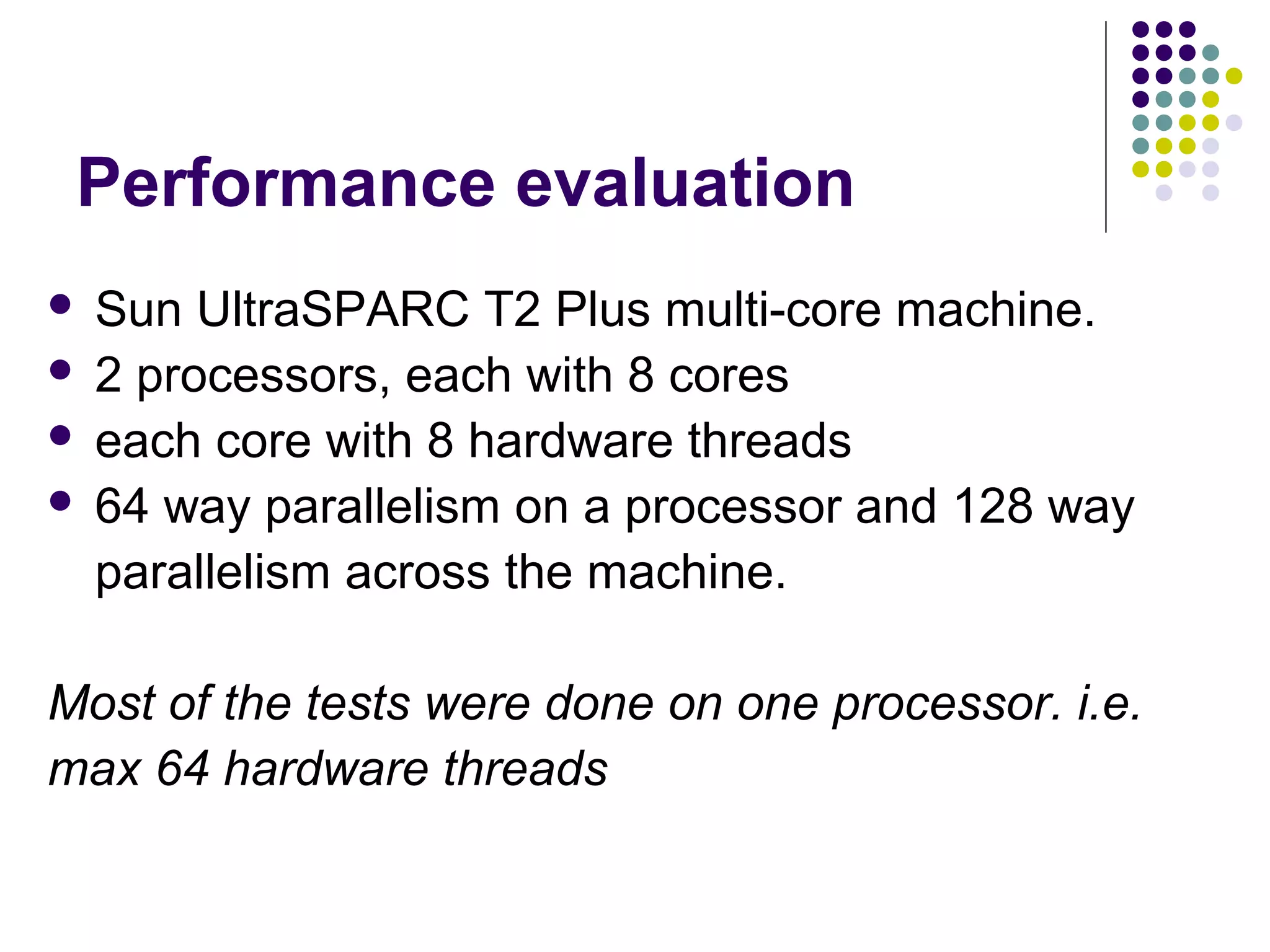
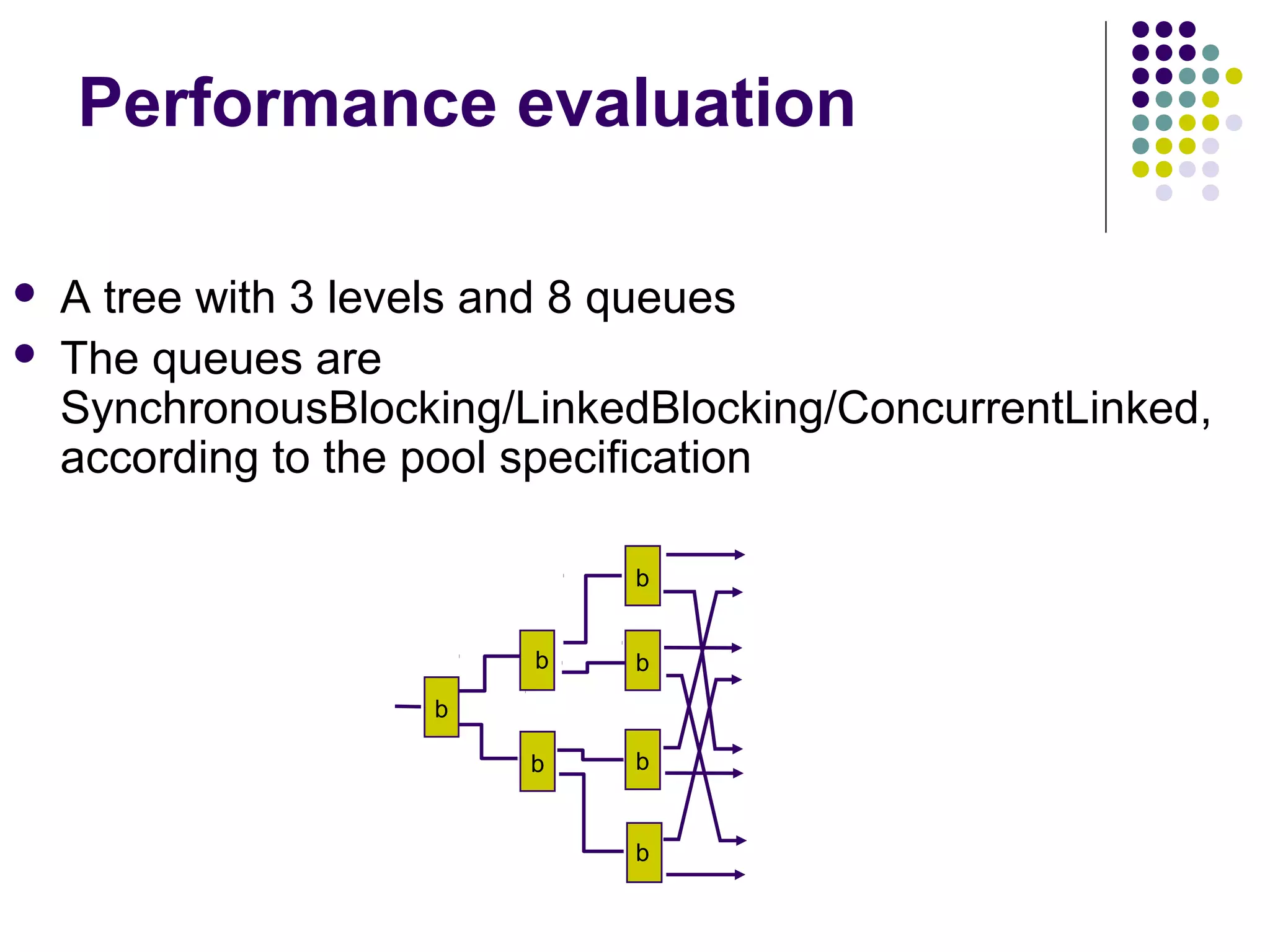
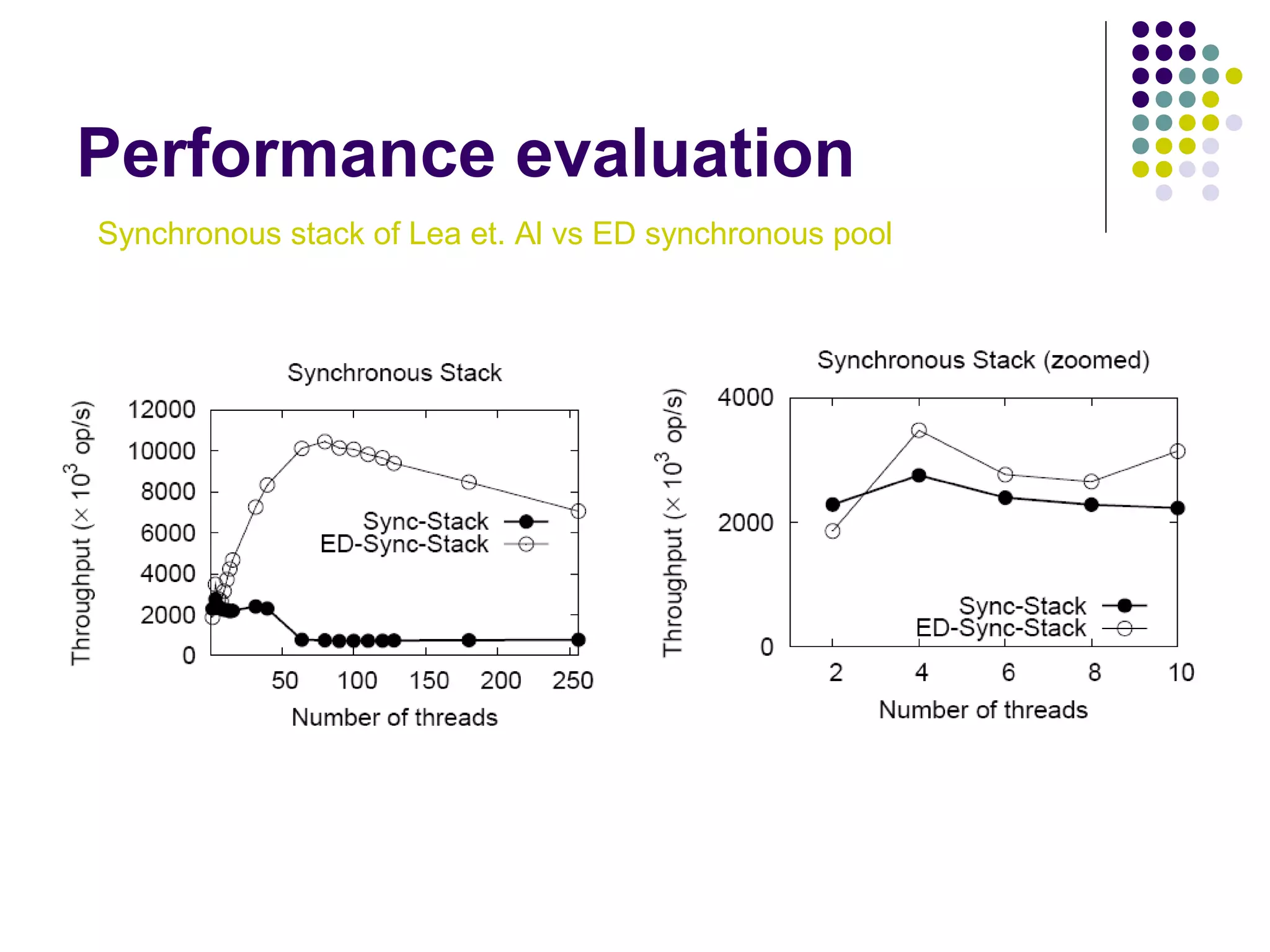
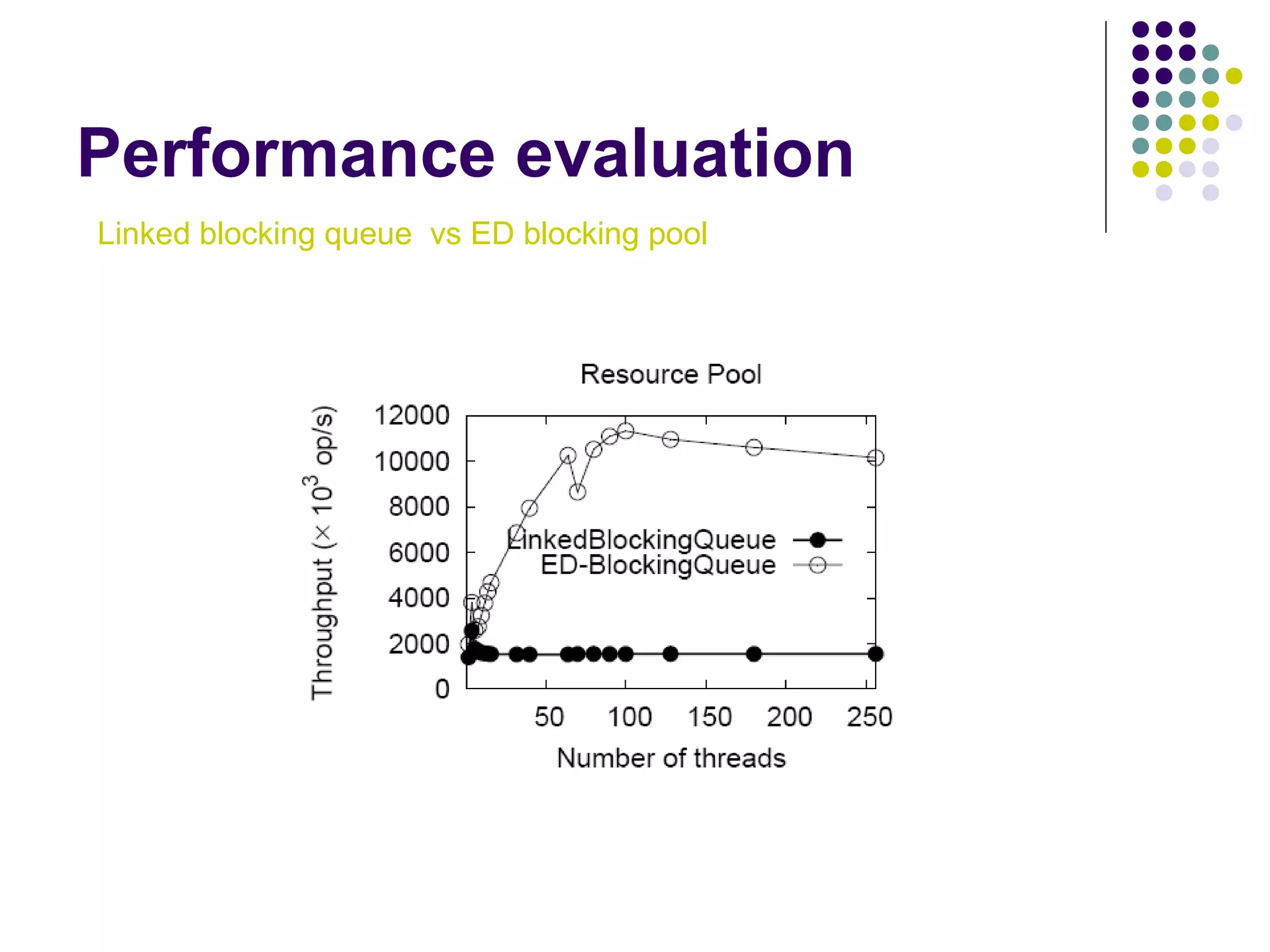
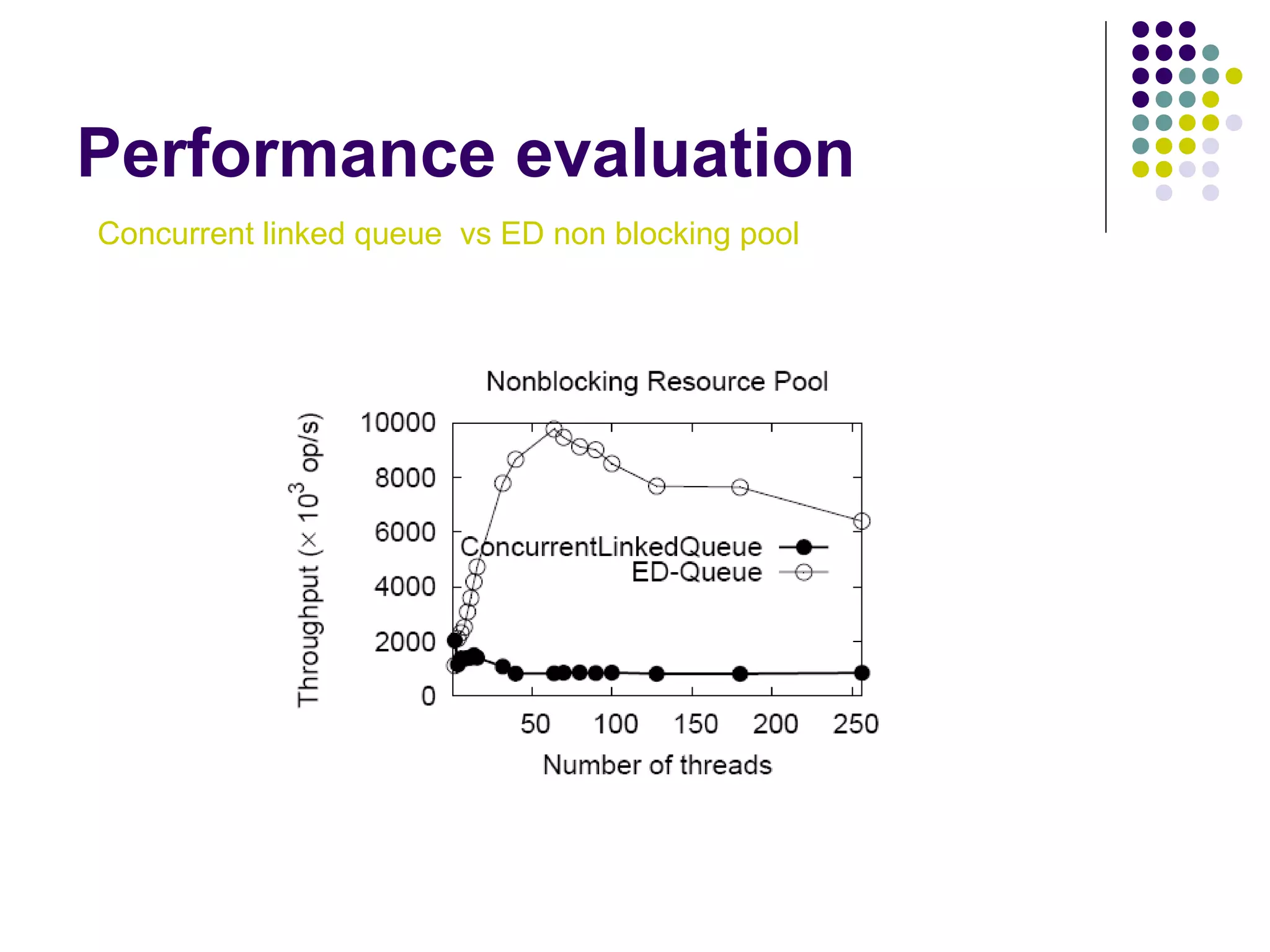
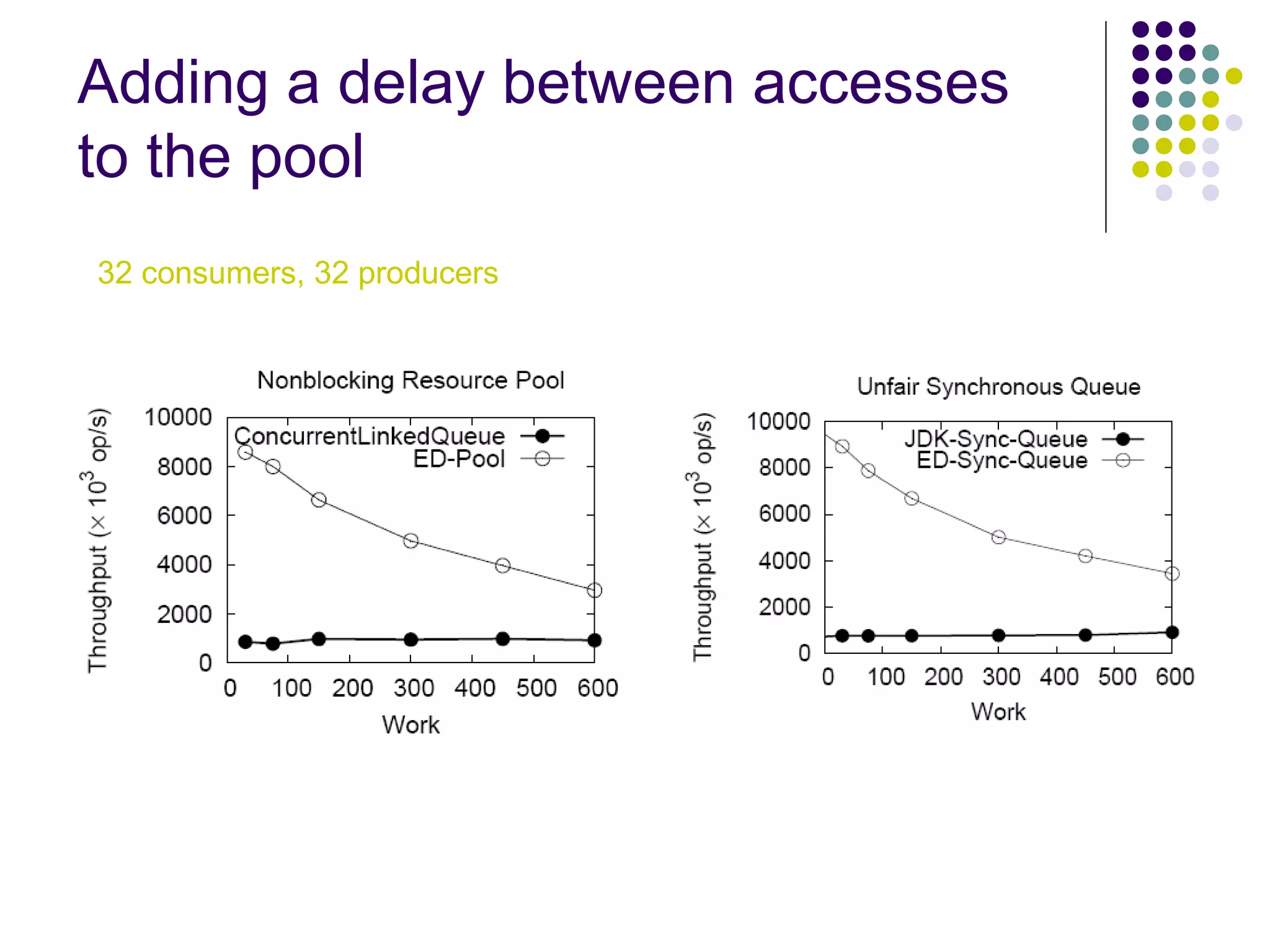
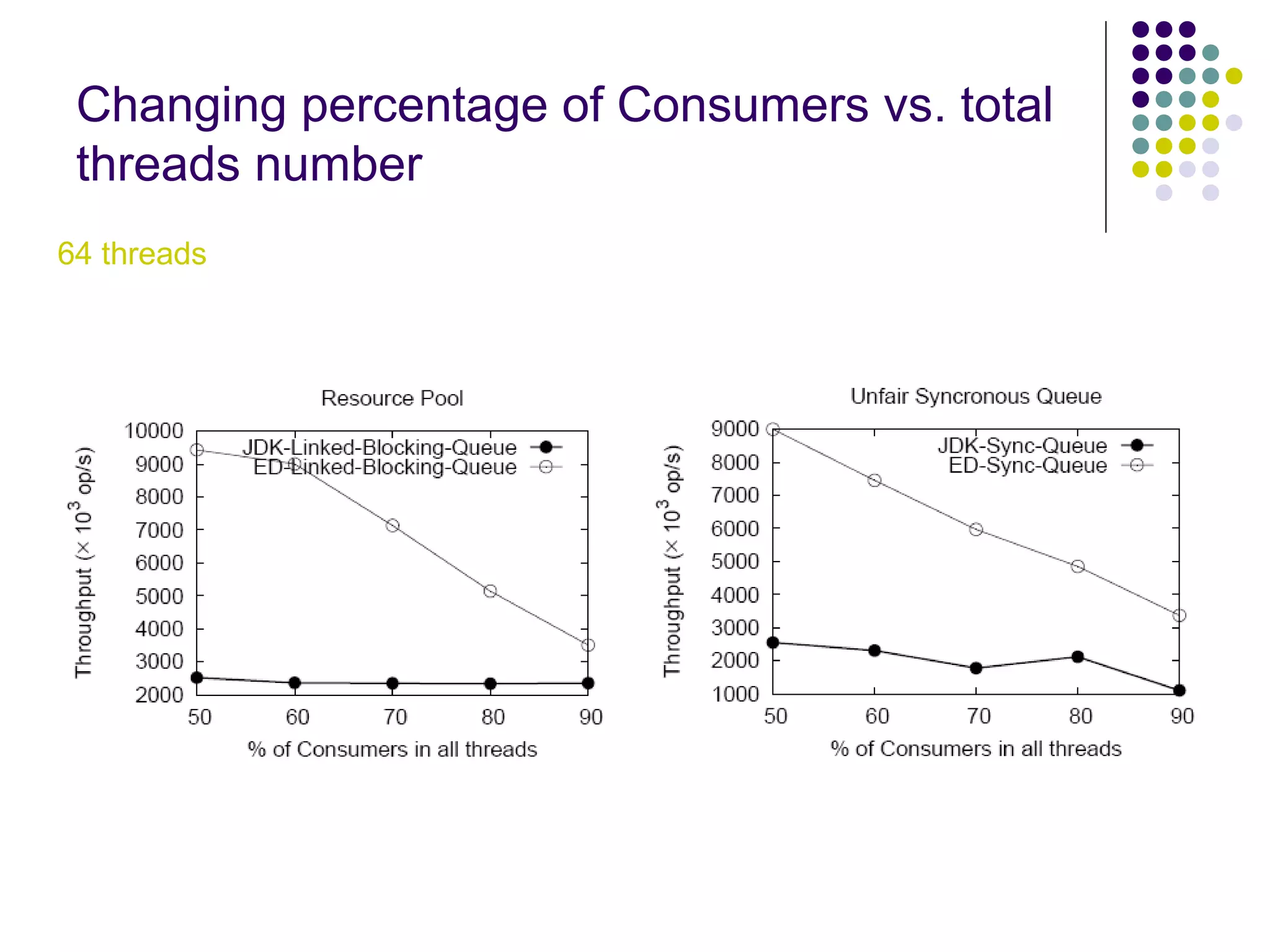
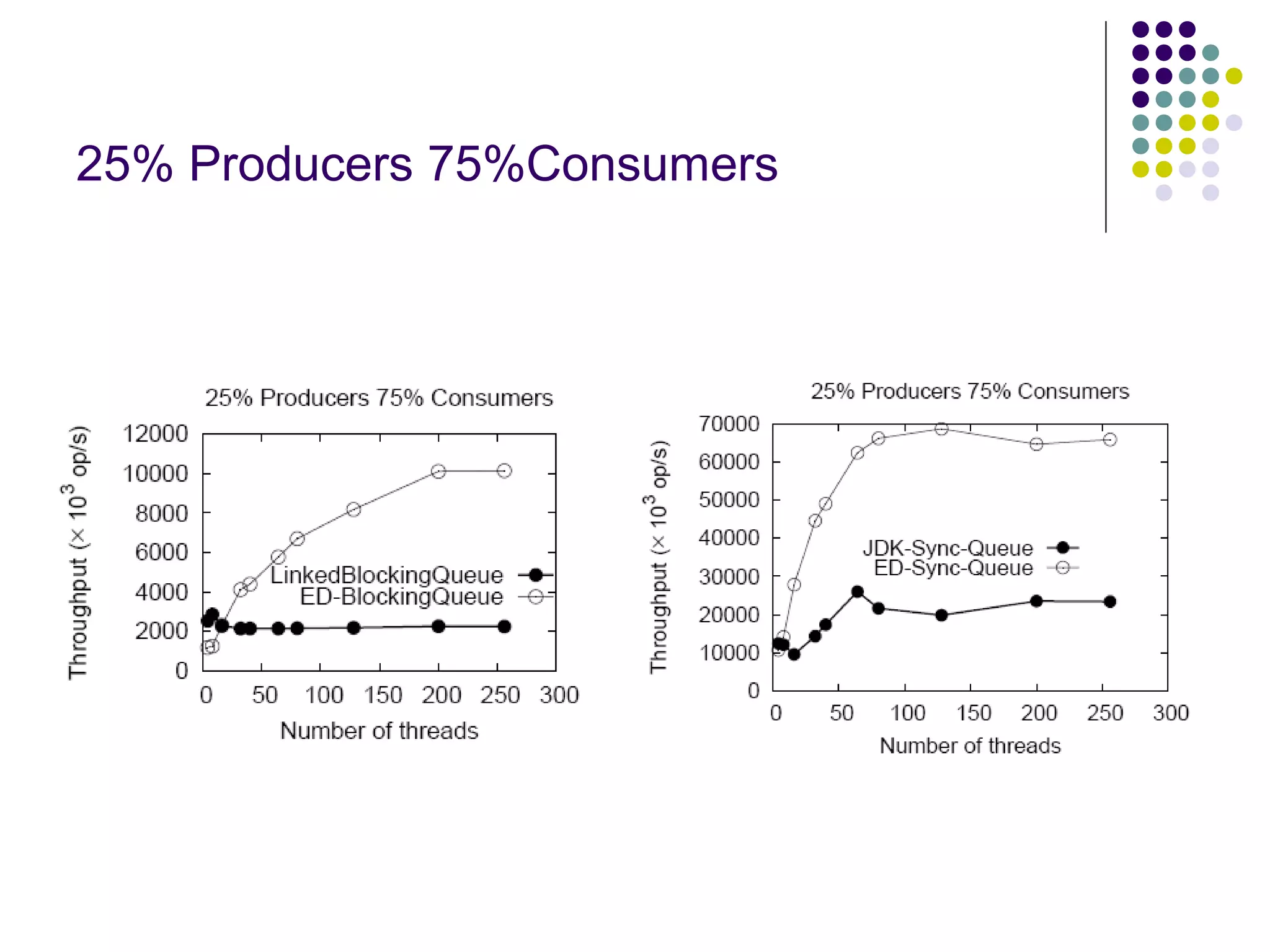
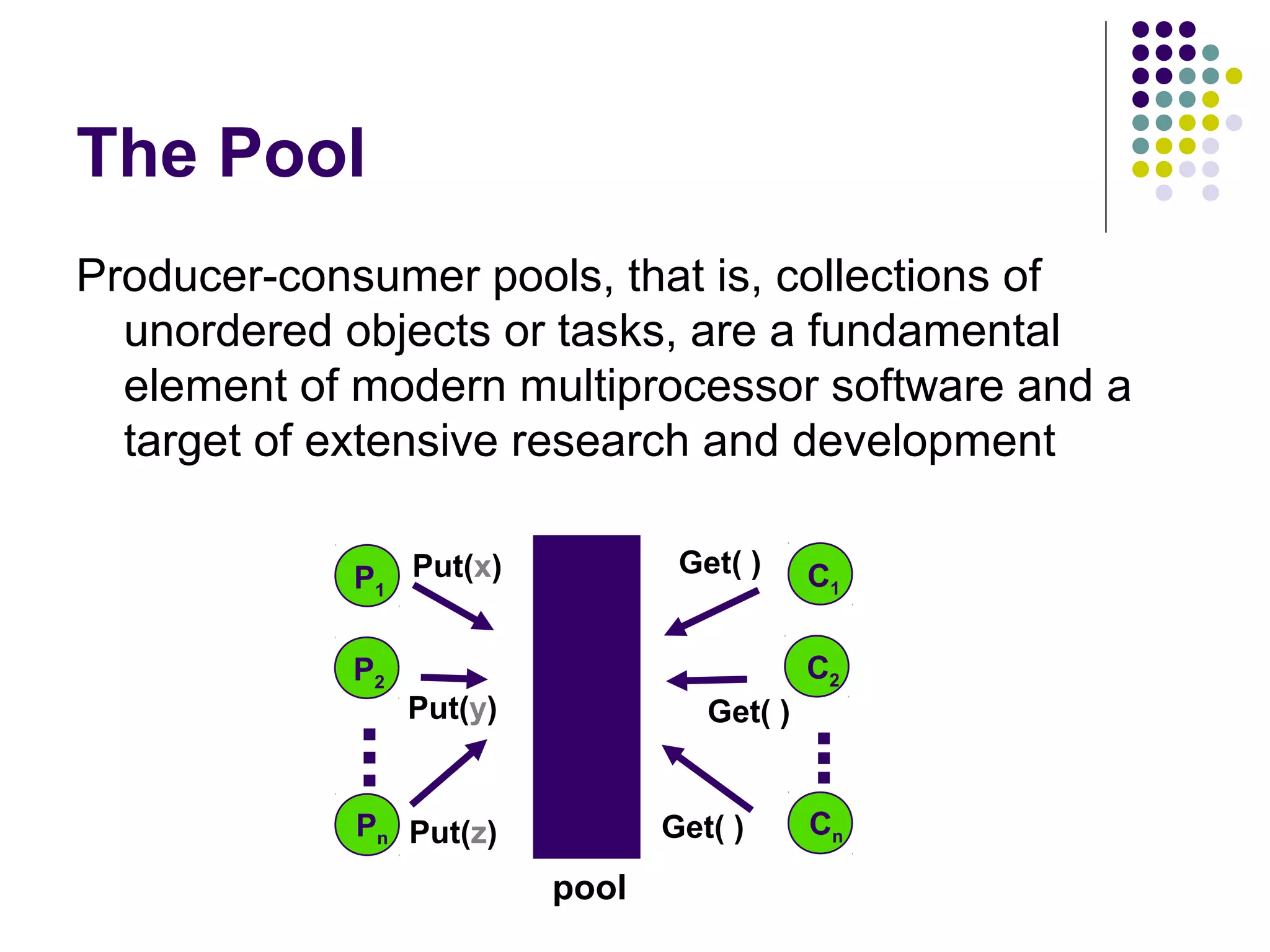
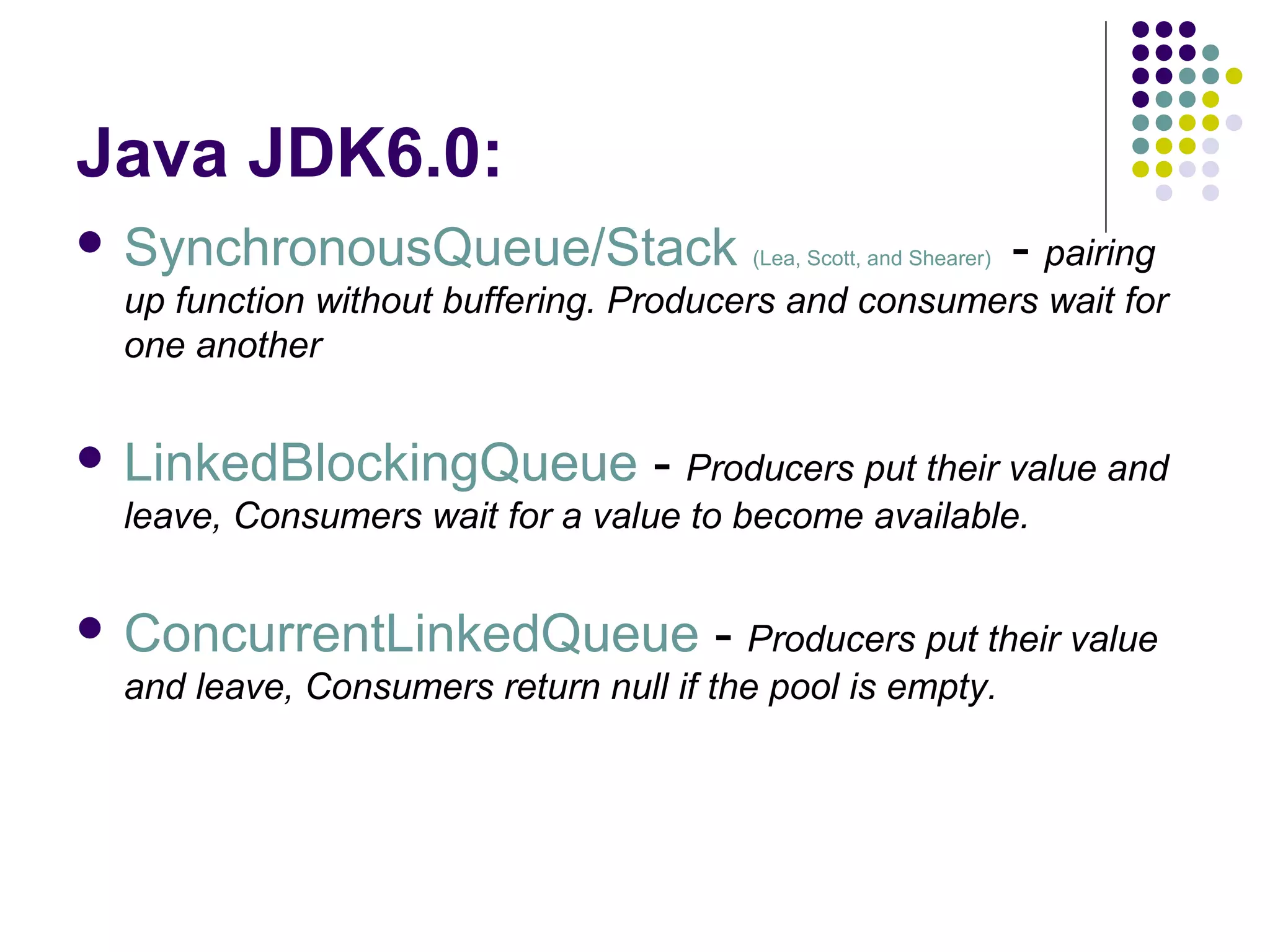
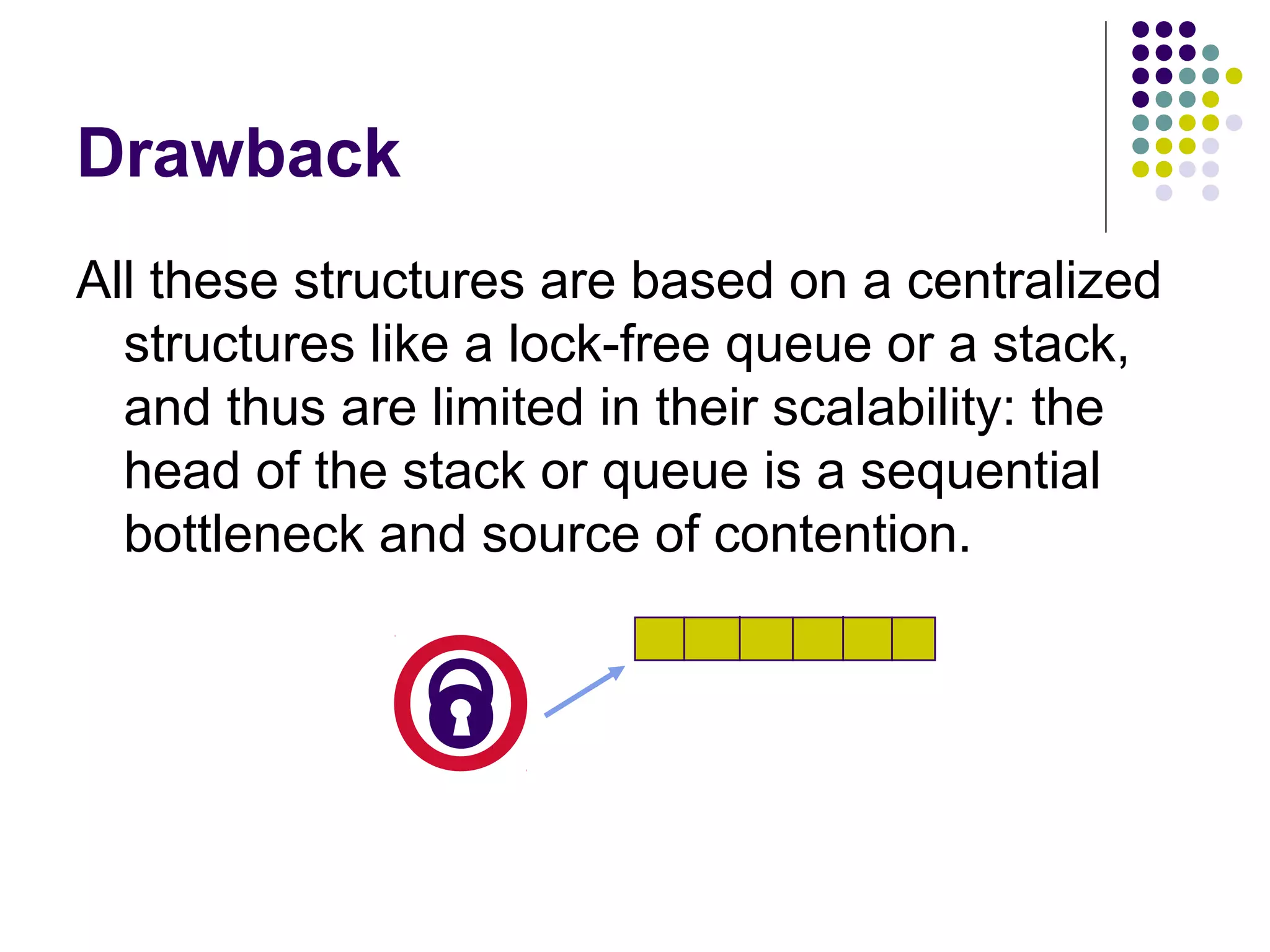
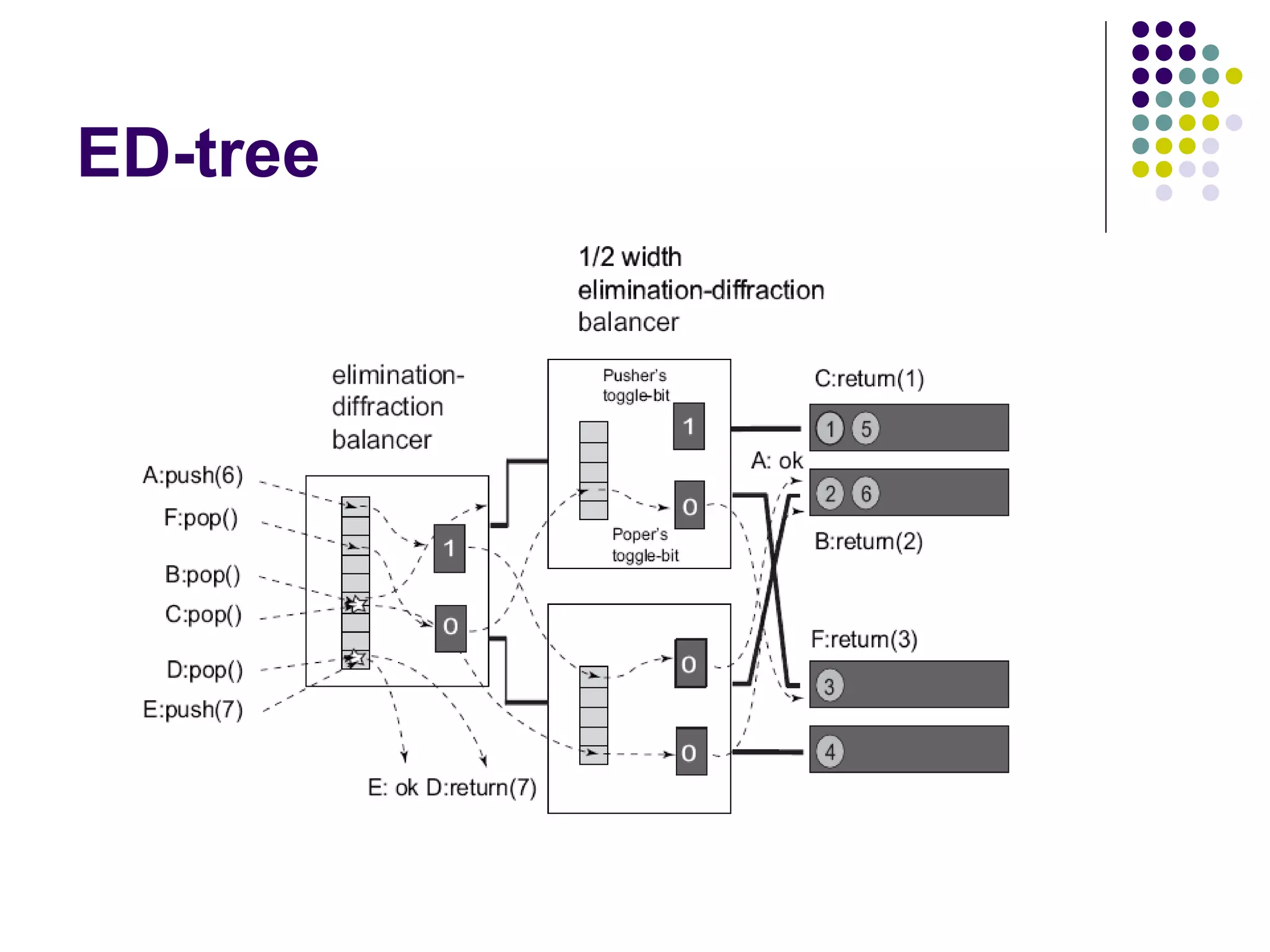
The document discusses the ED-tree, a novel distributed producer-consumer pool structure that combines elements of elimination-trees and diffraction-trees to enhance parallelism while reducing contention in multiprocessor environments. It critiques existing centralized structures for their scalability issues and presents the ED-tree as a solution that allows concurrent threads to interact without bottlenecks. The ED-tree adapts to varying load conditions and implements mechanisms to prevent starvation and enhance performance through a structured approach to managing thread collisions.




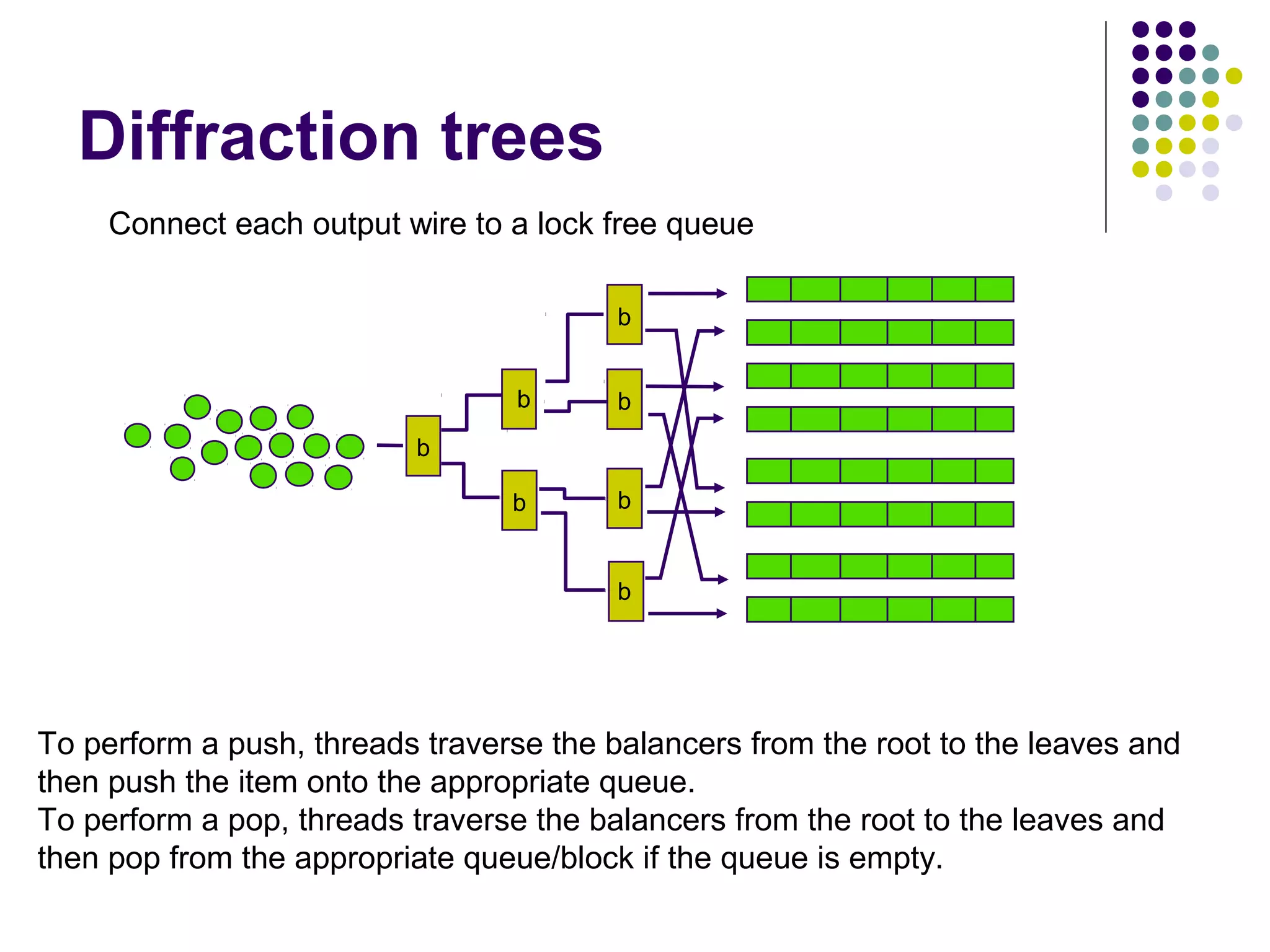
![Diffraction trees
A binary tree of objects called balancers [Aspnes-Herlihy-Shavit] with
a single input wire and two output wires
5
4
3
2
1
b
1
3
2
5
4
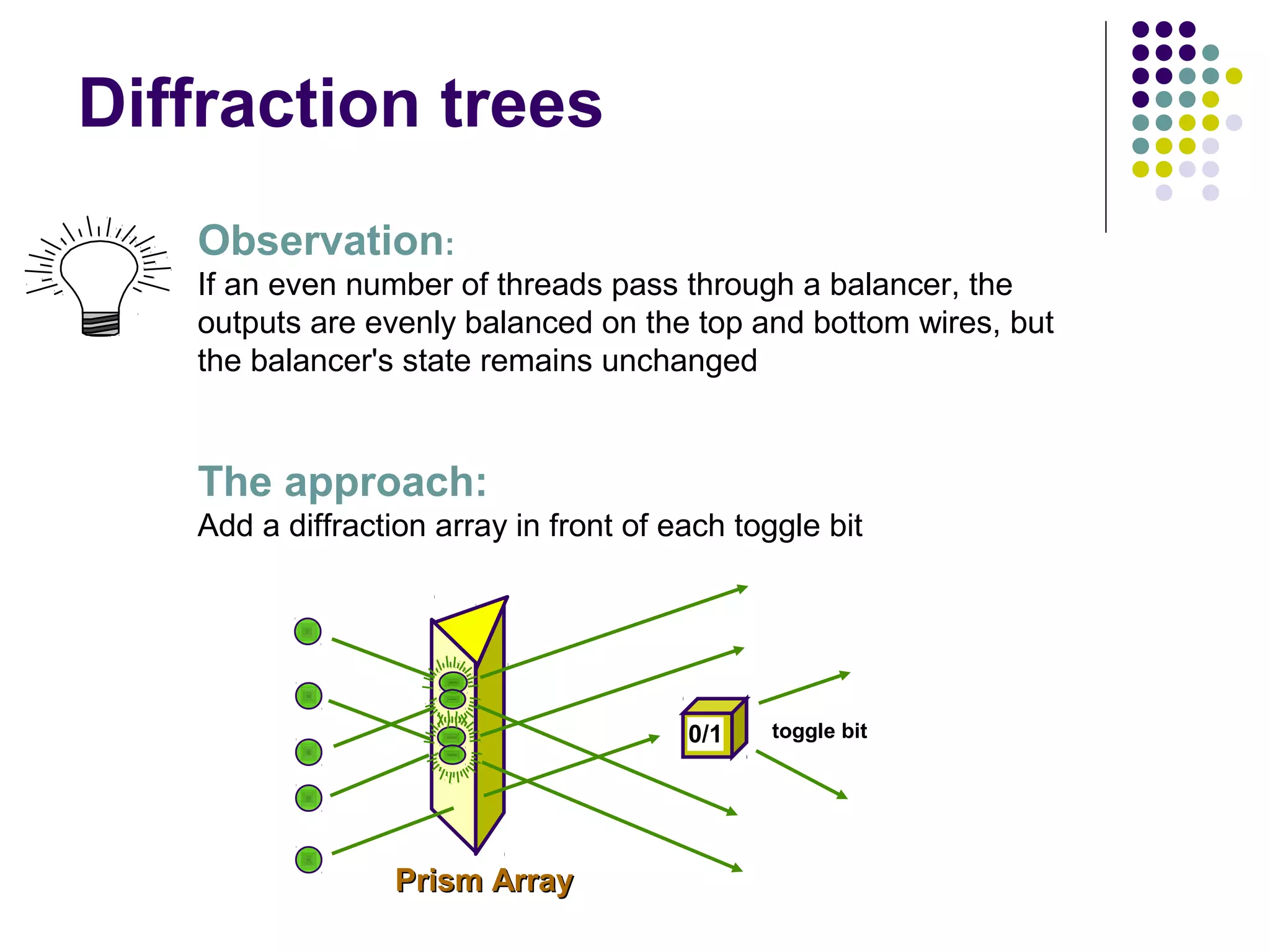
Threads arrive at a balancer and it repeatedly sends them left and right,
so its top wire always has maximum one more than the bottom one.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edtreepresentation-140211042259-phpapp02/75/Building-Scalable-Producer-Consumer-Pools-based-on-Elimination-Diraction-Trees-9-2048.jpg)
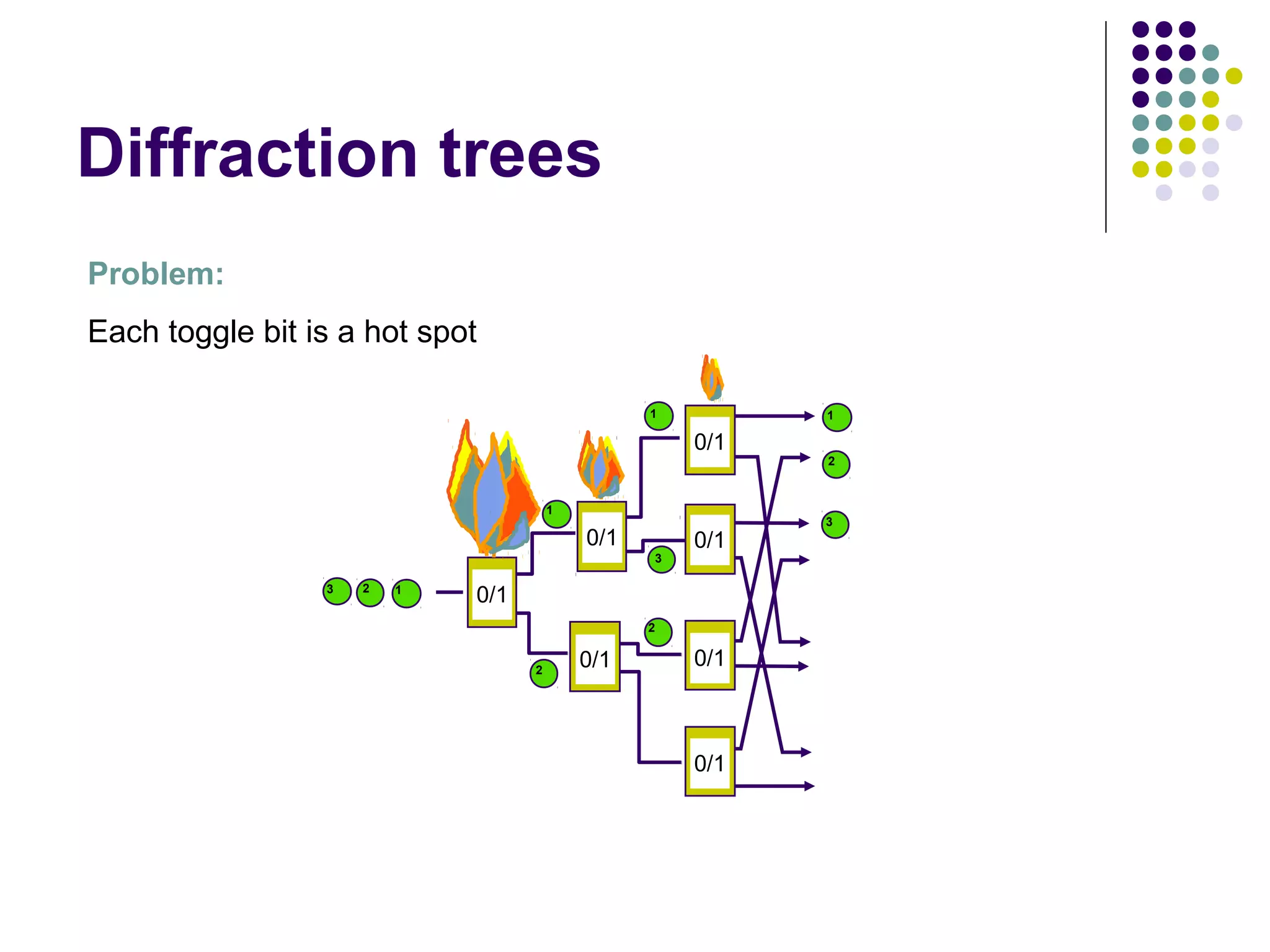
![Diffraction trees
1
[Shavit-Zemach]
b
b
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
b
9
2
10
3
4
b
b
b
5
6
7
b
8
In any quiescent state (when there are no threads in the tree), the tree
preserves the step property: the output items are balanced out so that the
top leaves outputted at most one more element than the bottom ones, and
there are no gaps.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edtreepresentation-140211042259-phpapp02/75/Building-Scalable-Producer-Consumer-Pools-based-on-Elimination-Diraction-Trees-10-2048.jpg)

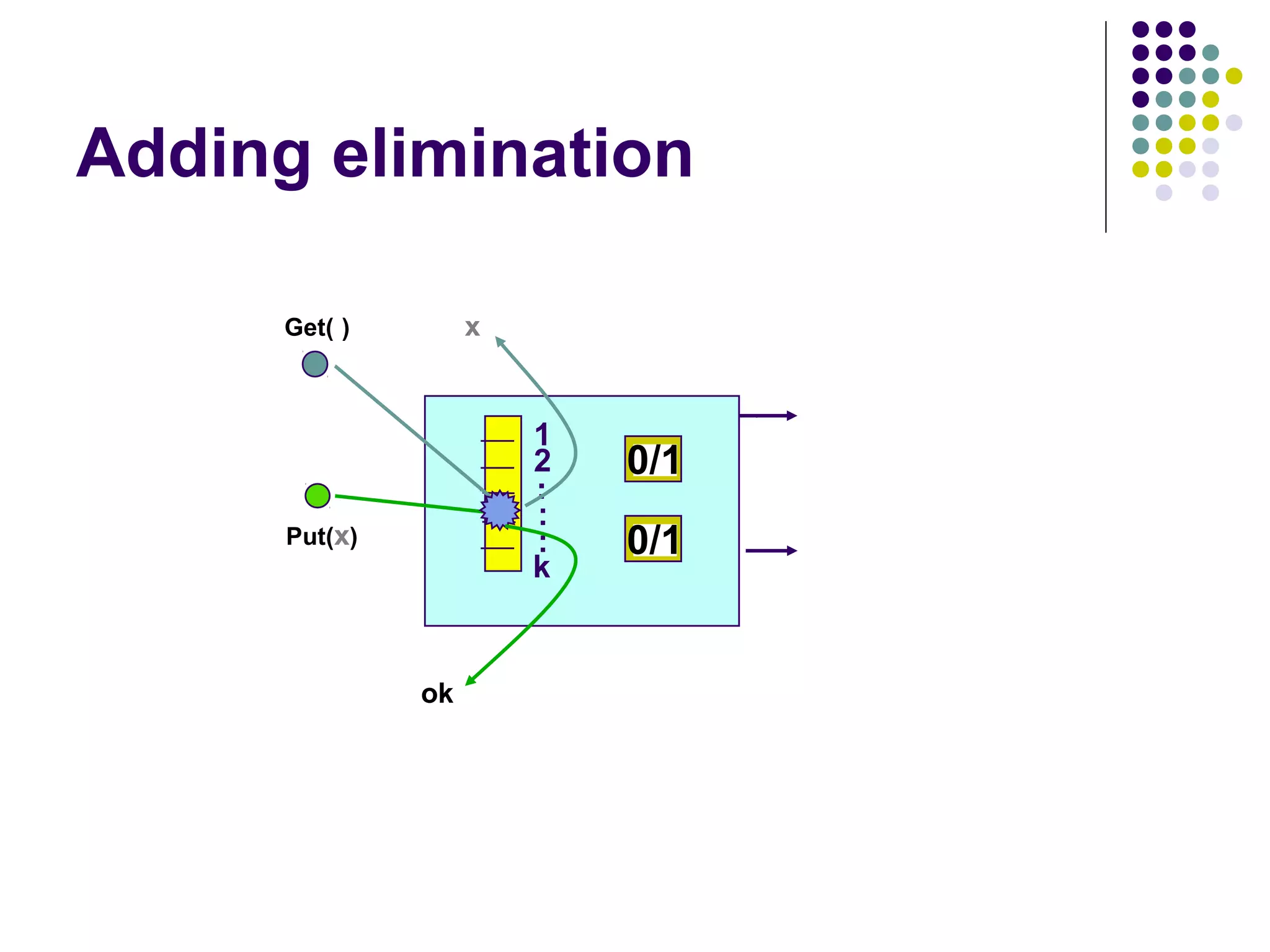




![Implementation
Each
balancer is composed from
an elimination array, a pair of toggle bits, and
two references one to each of its child nodes.
public class Balancer
{
ToggleBit producerToggle, consumerToggle;
Exchanger[] eliminationArray;
Balancer leftChild , rightChild;
ThreadLocal<Integer> lastSlotRange;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edtreepresentation-140211042259-phpapp02/75/Building-Scalable-Producer-Consumer-Pools-based-on-Elimination-Diraction-Trees-21-2048.jpg)