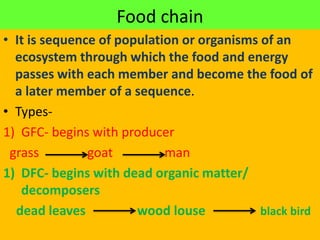
The document discusses ecosystems as functional units of nature comprising living organisms and abiotic components, divided into terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Key concepts include types of productivity (gross and net primary), factors affecting primary productivity, the process of decomposition, and the roles of producers and consumers within food chains and webs. It highlights the importance of environmental factors and species interactions in maintaining ecosystem structure and function.