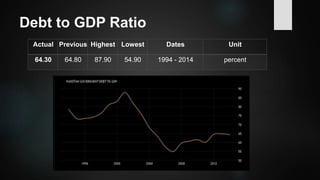
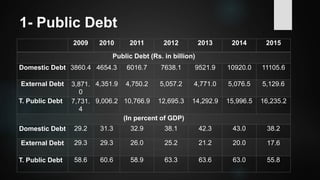
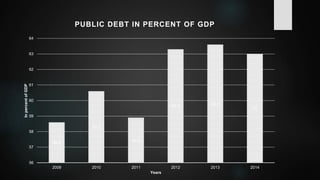
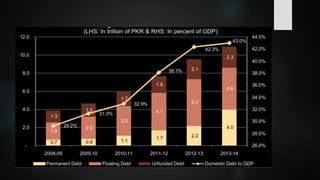
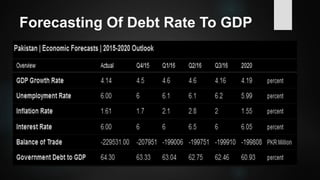
The document provides an overview of debt management in Pakistan, including definitions, types of debt, and the economic context of the country with specific metrics like GDP and debt-to-GDP ratio. It discusses the roles of various governmental bodies in managing public and external debts, along with the challenges faced in achieving effective debt management. The document also outlines policy recommendations to improve debt management strategies and mitigate the effects of growing debt on the economy.