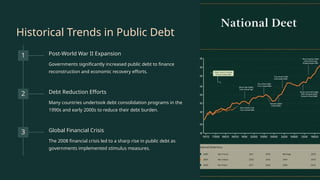
The document outlines the concept of public debt, which is the total amount a government owes to finance operations and spending, highlighting its importance for funding public services and stimulating the economy. It discusses historical trends, the drivers of public debt growth, and the objectives of effective public debt management, emphasizing the need for financial stability and risk mitigation. Additionally, it addresses challenges such as global economic conditions and demographic changes that can impact debt sustainability.
![SCHOOL OF COMMERCE,DAVV
SESION - 2023-2024
COURSE - B.COM [ATM] 4th SEM
TOPIC - PUBLIC DEBT AND ITS OBJECTIVES
SUBMITTED TO:- BHARTI ARYA Mam SUBMITTED BY:- KAJAL MALVIYA
ROLL NO. - BATM/22/2056](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/public-debt-and-its-objectives5-241116180535-d83d252c/75/Public-Debt-and-Its-Objectives-5-pptx-1-2048.jpg)