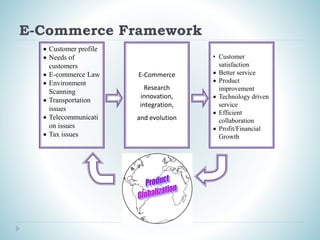
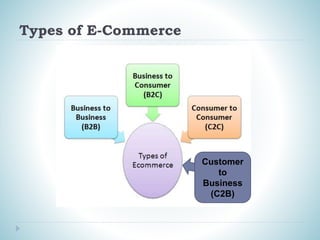
This document discusses e-commerce and globalization. It defines e-commerce as the buying and selling of goods and services over electronic networks like the internet. Globalization is described as the spread of people, ideas, and goods throughout the world. The document outlines an e-commerce framework involving customer profiling, needs assessment, and legal/environmental considerations. It also provides statistics on internet and e-commerce usage worldwide.