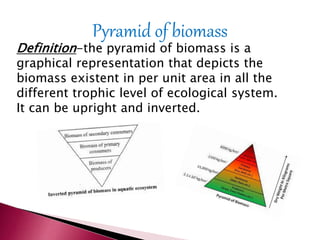
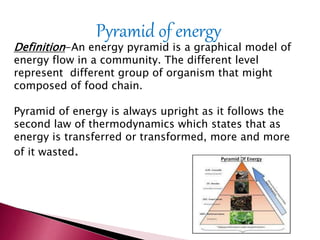
Ecological pyramids graphically represent biomass or productivity at trophic levels in an ecosystem. There are three main types: number, biomass, and energy. Pyramids of number show the population size at each level but don't account for size. Biomass pyramids depict the mass at each level and are more accurate but require killing organisms. Energy pyramids represent energy transfer between levels and always slope upwards due to energy loss, allowing ecosystem comparisons over time. Pyramids are important for understanding ecosystem structure and function but have limitations as food webs are more complex than simple chains.