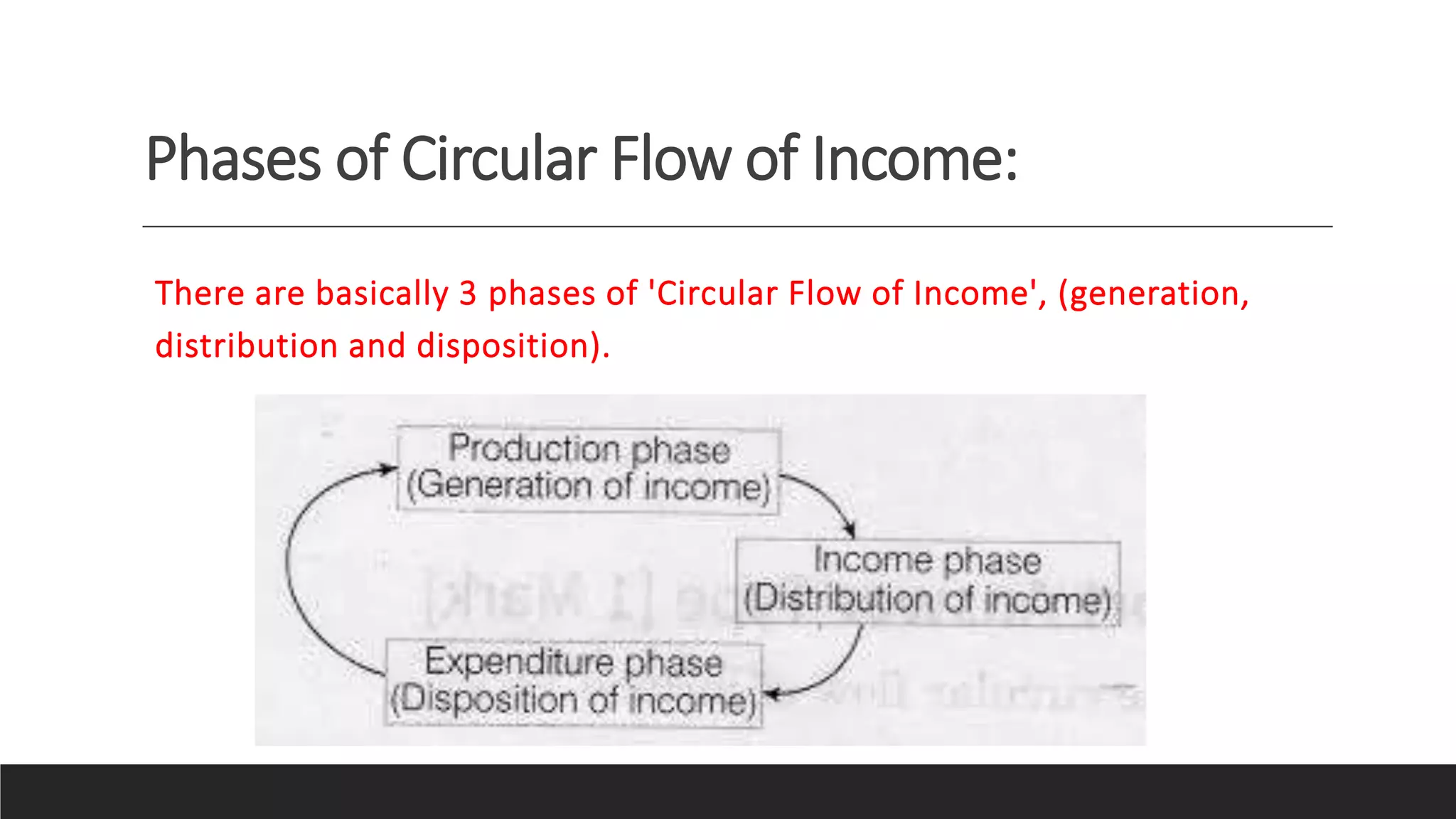
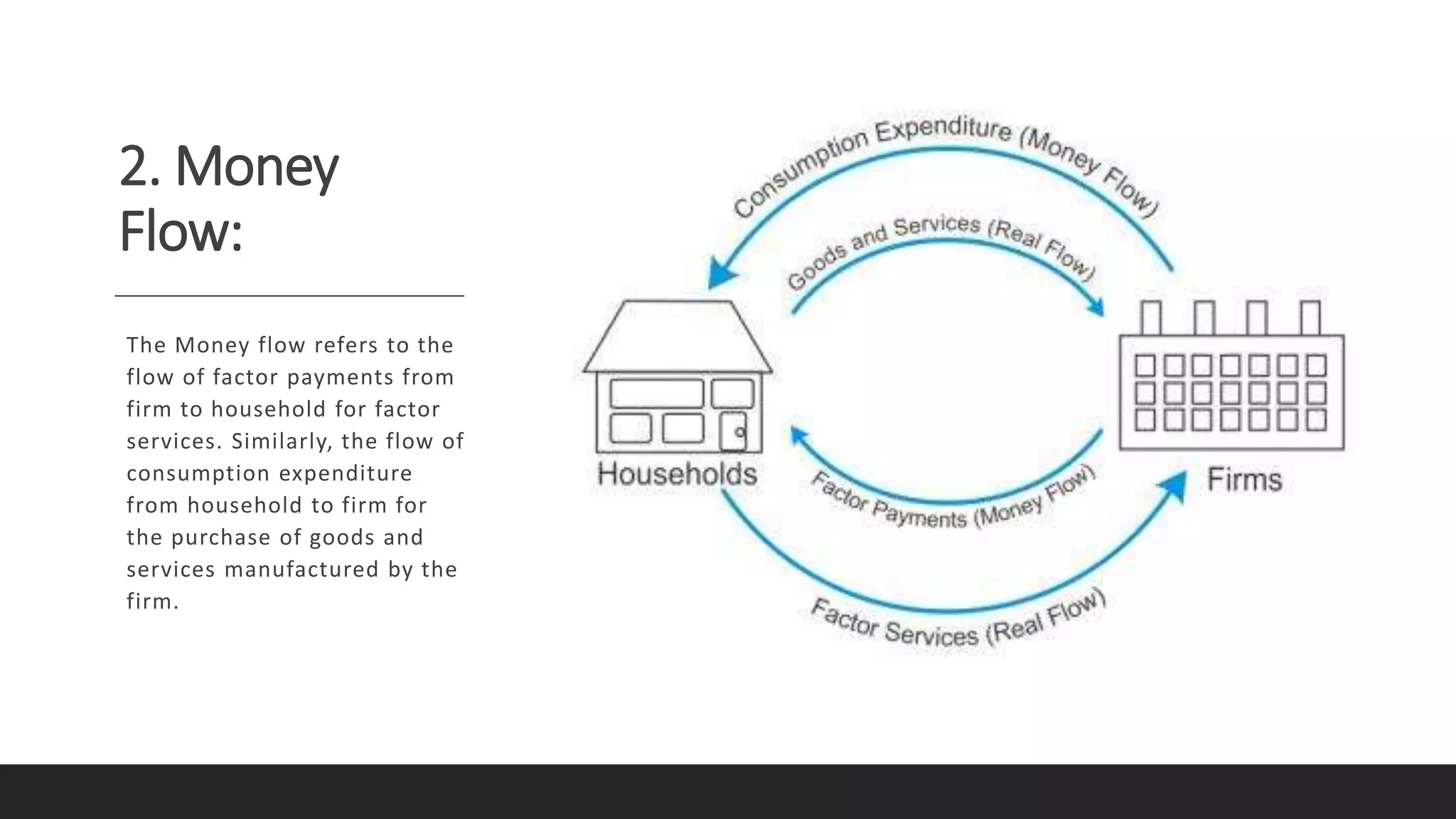
The circular flow of income model represents the major exchanges in an economy as flows of money, goods, and services between households and firms. There are three phases: 1) generation, where firms produce goods using inputs from households, 2) distribution, where firms pay households for inputs in the form of factor income, and 3) disposition, where households spend their income on goods from firms. The flows move in opposite directions, with real resources and financial capital flowing one way and payments flowing the other, forming a closed circuit.






![Circular Flow in
a Simple
Economy (Two-
sector
economy):
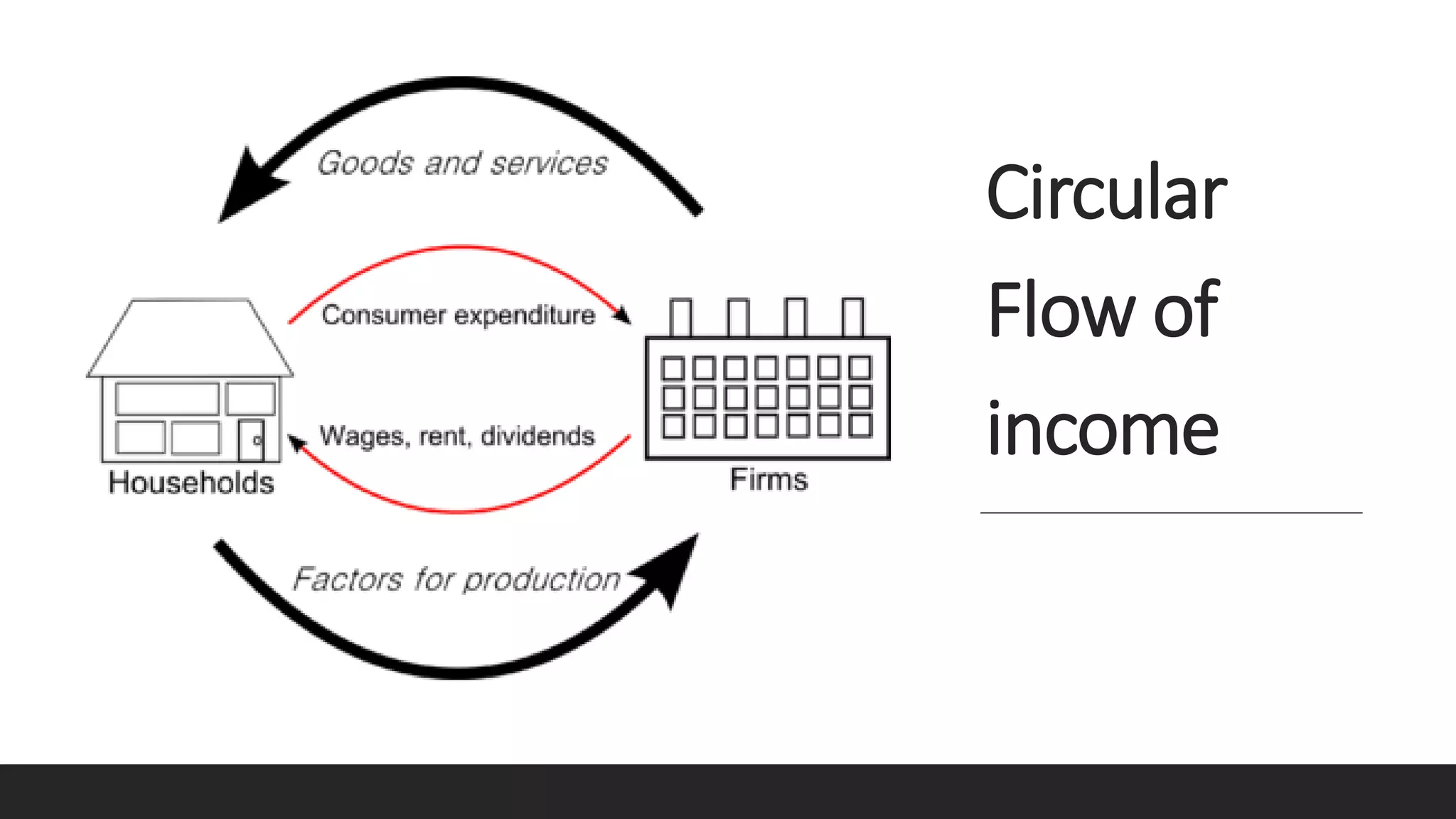
Simple economy assumes that there are only two
sectors, i.e., Firms and Households.
Households are the owners of factors of
production and consumers of goods and services.
Firms produce goods and services and sell them
to households.]
It is the simplest form of economy, where there is
no government and foreign trade.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecoslideshare-210314065325/75/Eco-slideshare-Chapter-Circular-Flow-of-Income-12-2048.jpg)
