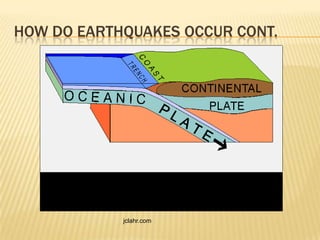
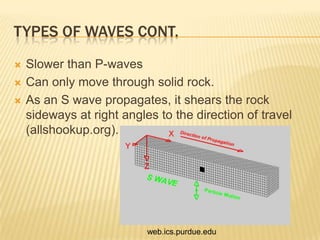
This document discusses earthquakes, including what they are, how they occur, where they occur, how they are measured, the types of waves associated with them, and how to protect yourself during one. Earthquakes happen along fault lines due to the sudden movement of tectonic plates. They are measured using the Richter scale and produce both P-waves and S-waves. Major fault types include strike-slip, normal, and reverse faults.