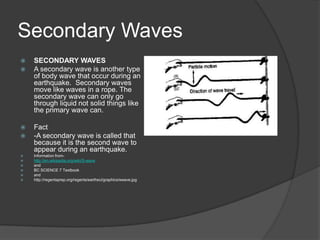
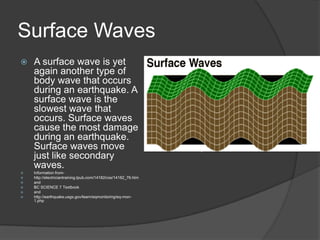
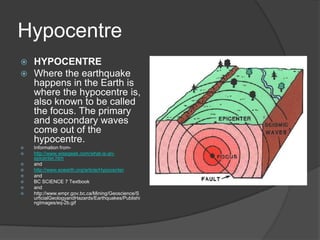
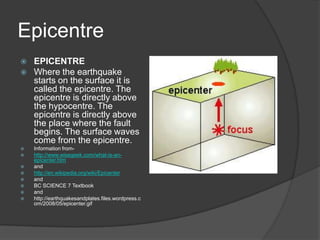
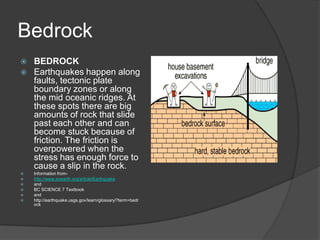
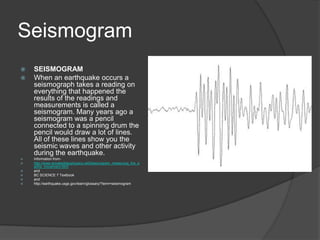
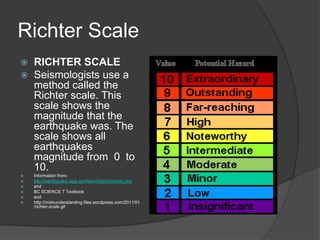
An earthquake occurs when rocks underground release stored energy, causing the ground to shake. Earthquakes are usually caused by the movement of tectonic plates. They can cause damage and loss of life through mechanisms like fires, landslides, floods, and tsunamis. Scientists measure earthquakes using seismographs which record seismic waves. The location and magnitude of quakes are determined by analyzing these wave recordings. Major quakes pose risks like liquefaction of soils and large tsunami waves.