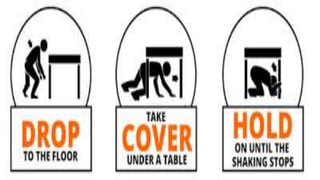
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of built-up energy in the Earth's crust. When tectonic plates or blocks of rock underground break along faults, seismic waves propagate, causing the shaking we experience during earthquakes. The location of the initial rock break is called the focus, while the point directly above on the surface is the epicenter. Earthquake intensity and magnitude characterize the severity and size of the shaking respectively. Proper preparation and following safety procedures during and after quakes can help minimize harm.