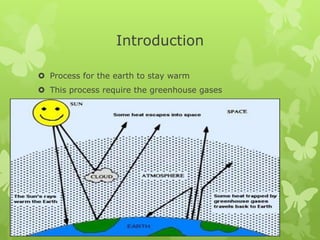
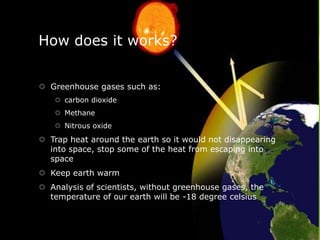
The greenhouse effect describes how greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap heat in the lower atmosphere, keeping the global average temperature about 60°F warmer than it would otherwise be. Without this natural greenhouse effect, the earth's temperature would be about -18°C. However, human activities that release additional greenhouse gases like burning fossil fuels are enhancing the greenhouse effect and causing global warming, with potential consequences including rising sea levels, changes in weather patterns, and difficulties for plants and animals.