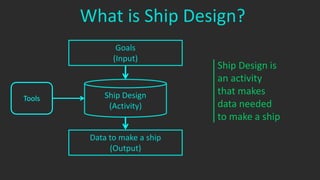
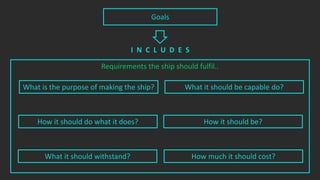
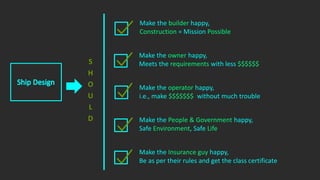
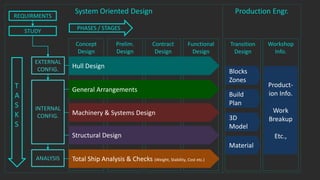
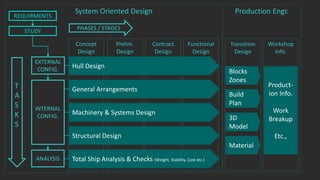
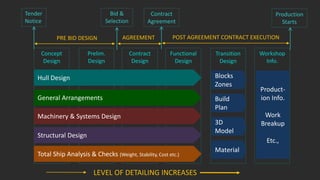
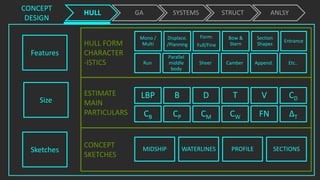
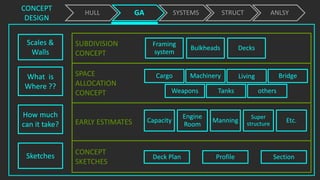
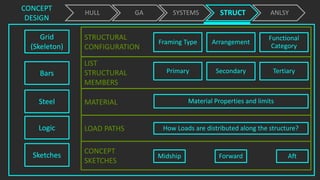
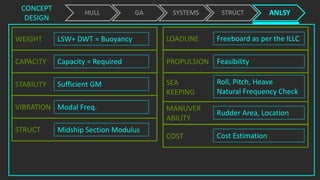
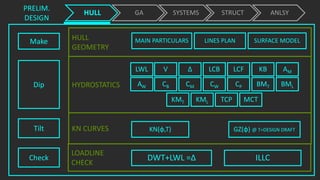
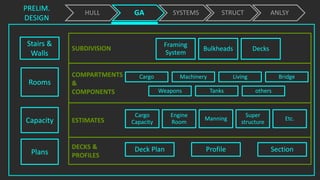
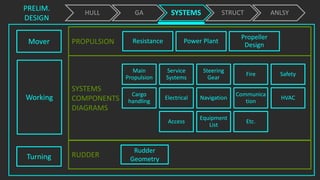
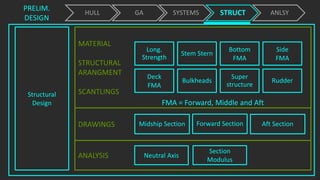
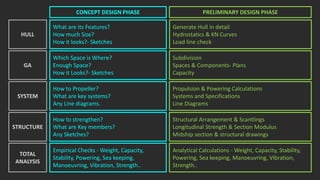
The document outlines the stages of ship design, focusing on the concept and preliminary design phases, emphasizing the importance of feasibility studies and owner requirements. It details specific tasks and considerations in designing a ship, including performance characteristics, structural configurations, and regulatory compliance. The design process is collaborative and systematic, involving multiple teams and phases to ensure the ship meets all operational and safety standards.