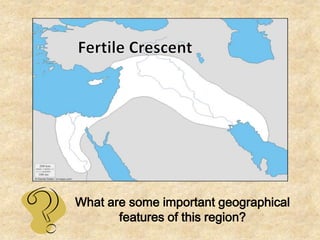
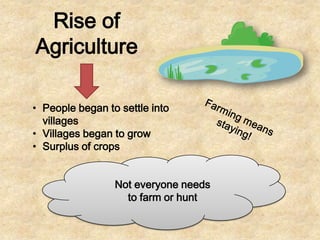
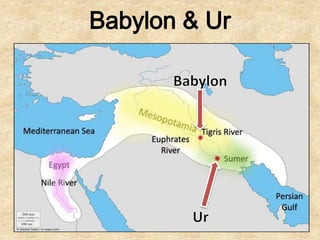
This document discusses the importance of rivers and seas in early civilizations. Rivers provided water for irrigation, allowing for easy transportation of water and the growth of crops. The dependable water supply and fertile soil from annual flooding encouraged people to settle into villages along rivers. As villages grew, not all residents needed to farm for subsistence, allowing specialization of jobs and the formation of social classes. This led to the development of early civilizations with features like centralized governments, public works, writing systems, organized religions, and urban cities. Sumer is highlighted as one of the earliest civilizations, consisting of independent city-states along the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in Mesopotamia, with cities like Ur serving