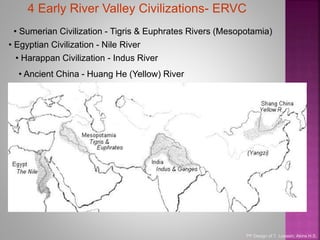
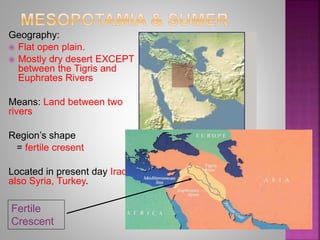
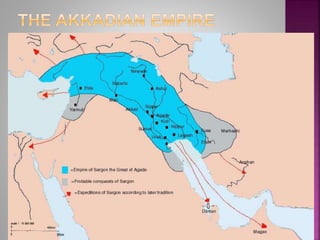
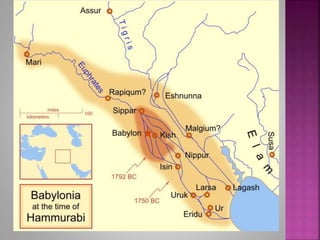
The document discusses four early river valley civilizations, focusing primarily on Sumer in Mesopotamia. Key aspects include the geography, social structure, religious beliefs, and significant achievements such as the creation of the cuneiform writing system and the establishment of empires under leaders like Sargon and Hammurabi. It highlights the importance of city-states, trade, and governance in shaping these ancient societies.