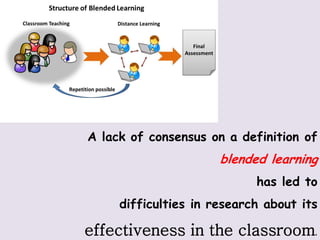
E-learning involves using computers and electronic devices to deliver educational content online or in a blended format. It allows students to learn remotely on their own schedule. Blended learning combines online learning with traditional in-person classes, allowing students some flexibility over pacing. M-learning uses mobile devices to provide educational content anywhere, anytime through social and content interactions. Research has found blended learning improves student satisfaction and attitudes, but students must stay engaged and not fall behind on materials.