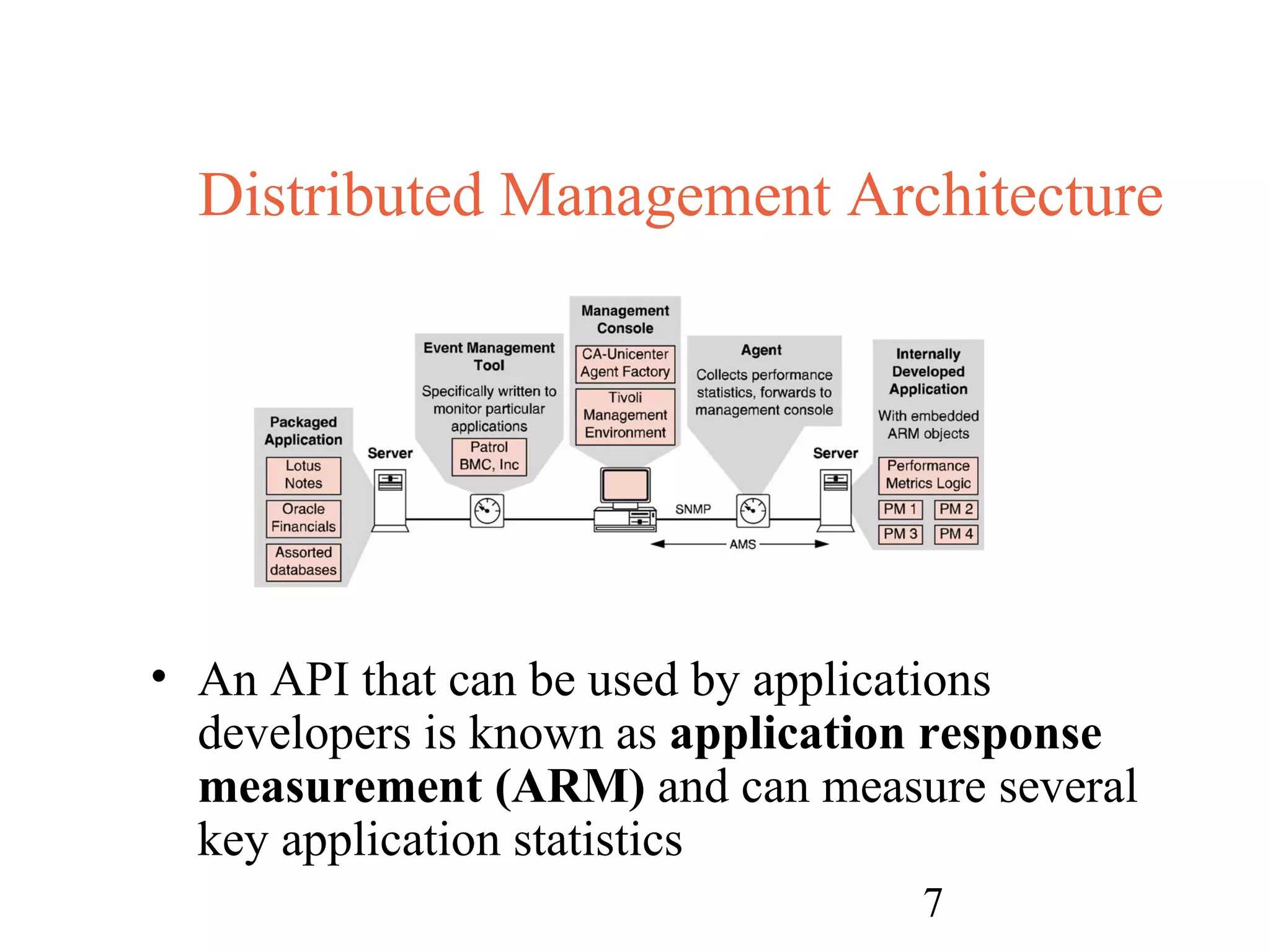
The document discusses various elements of IT infrastructure that require management, including enterprise networks, servers, desktops, databases, and applications. It describes several standards and technologies used for managing these elements, such as SNMP, WBEM, DMI, and application response measurement. It also covers challenges around managing distributed and laptop/mobile environments.