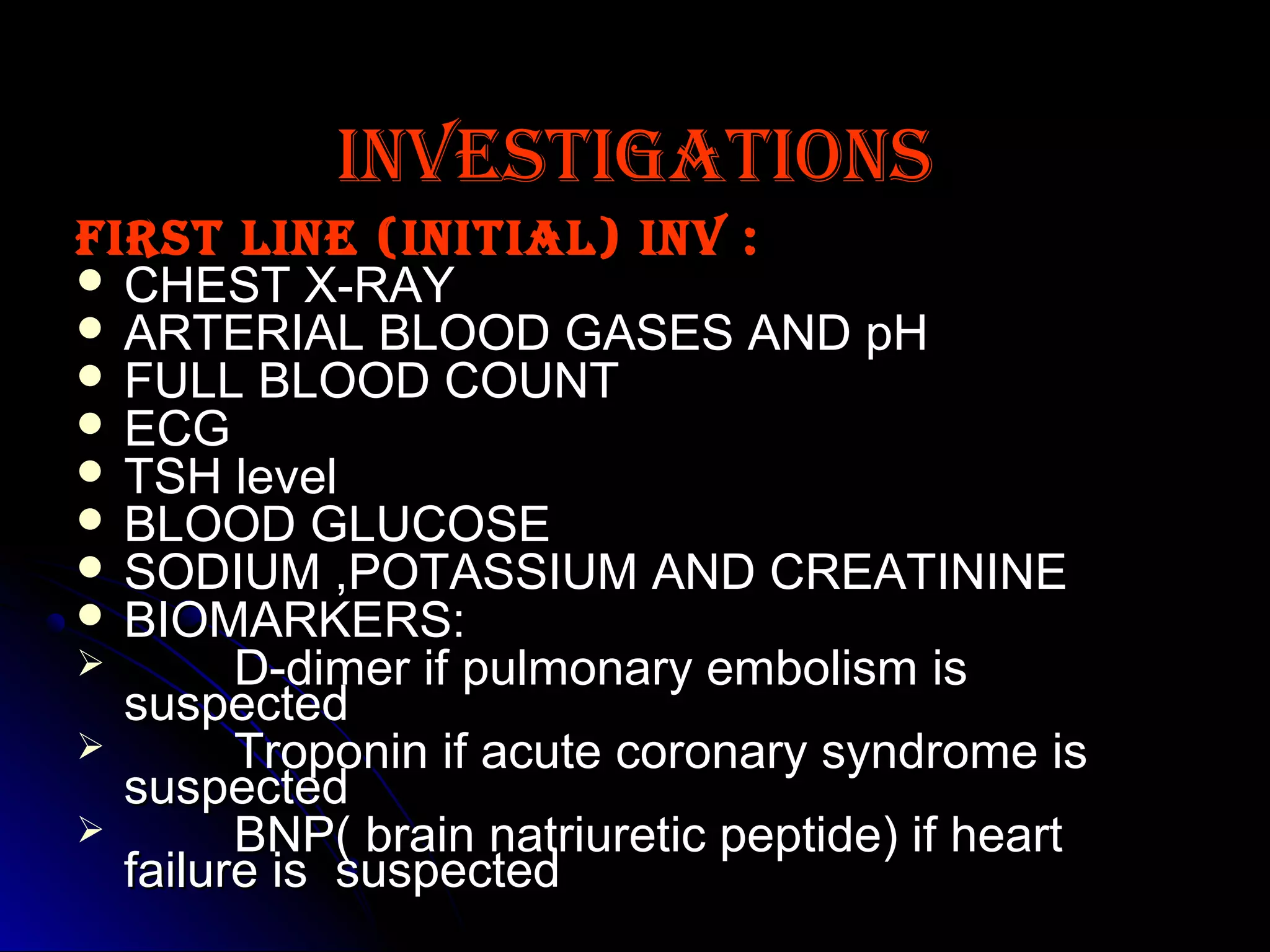
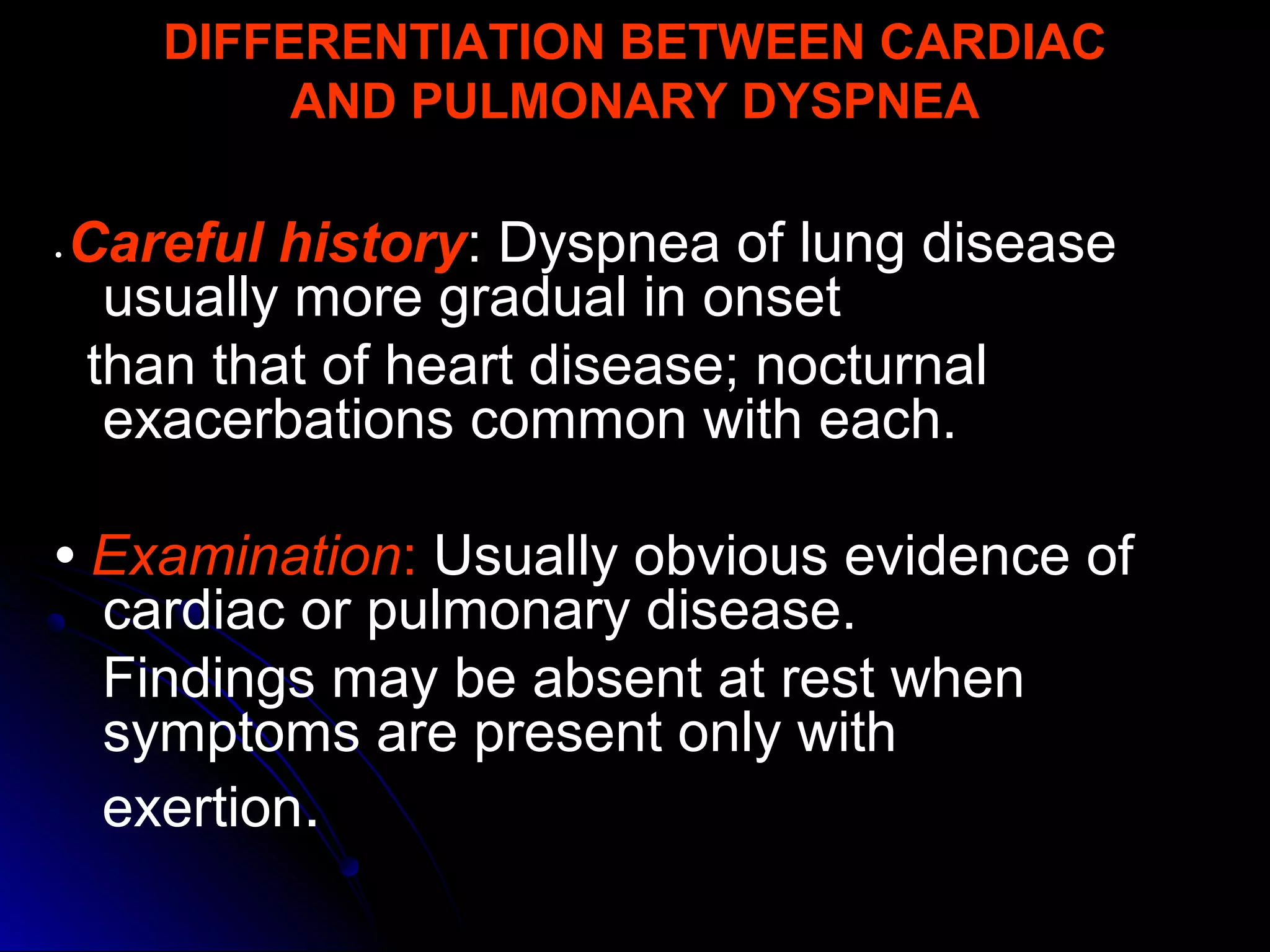
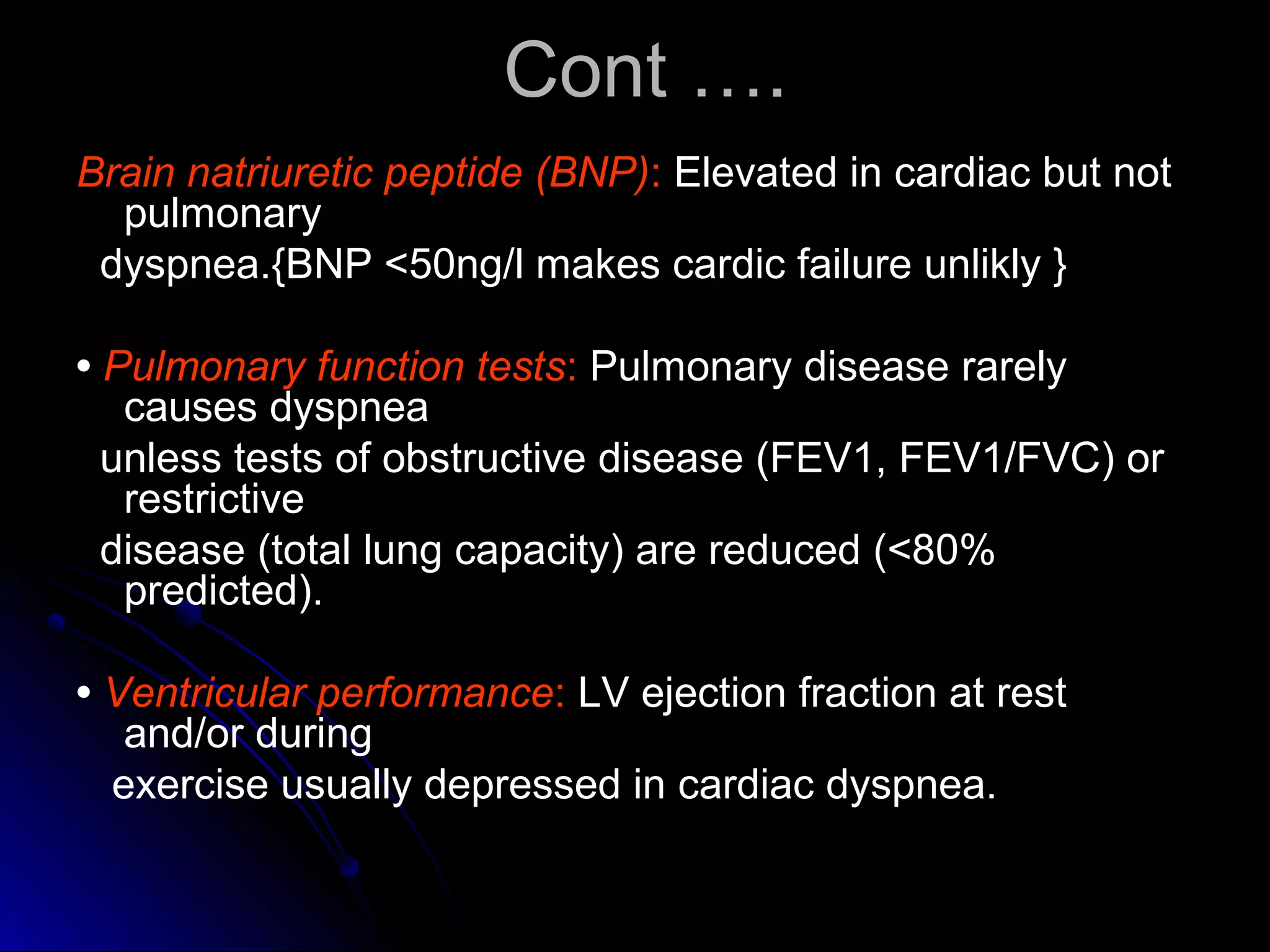
This document provides guidance on evaluating patients presenting with dyspnea (shortness of breath). It defines dyspnea and lists some specific types based on position. Common causes are outlined for pulmonary, cardiac, mixed, and non-cardiopulmonary origins. A clinical approach is described beginning with vital signs and history, followed by physical exam focusing on respiratory, cardiac, and fluid status findings. Initial investigations include chest X-ray, blood gases, ECG, and blood tests. Further tests may include lung function, exercise testing, and biomarkers to differentiate cardiac from pulmonary causes when the chest X-ray is normal. Careful history taking and physical exam remain important to identify underlying conditions.













![MRC Breathlessness Scale
Grade Degree of dysponea
1 Breathless when hurrying on the level or
walking up a slight hill
2 Breathlessness when walking with people of
own age or on level ground
3 Walks slower than peers or stops when
walking on the flat at own pace
4 Stops after walking 100 meters or a few
minuters on the level
5
[5b]
Too breathless to leave the house
Too breathless to wash or dress](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dyspnoea2-161103182417/75/Dyspnoea-2-15-2048.jpg)