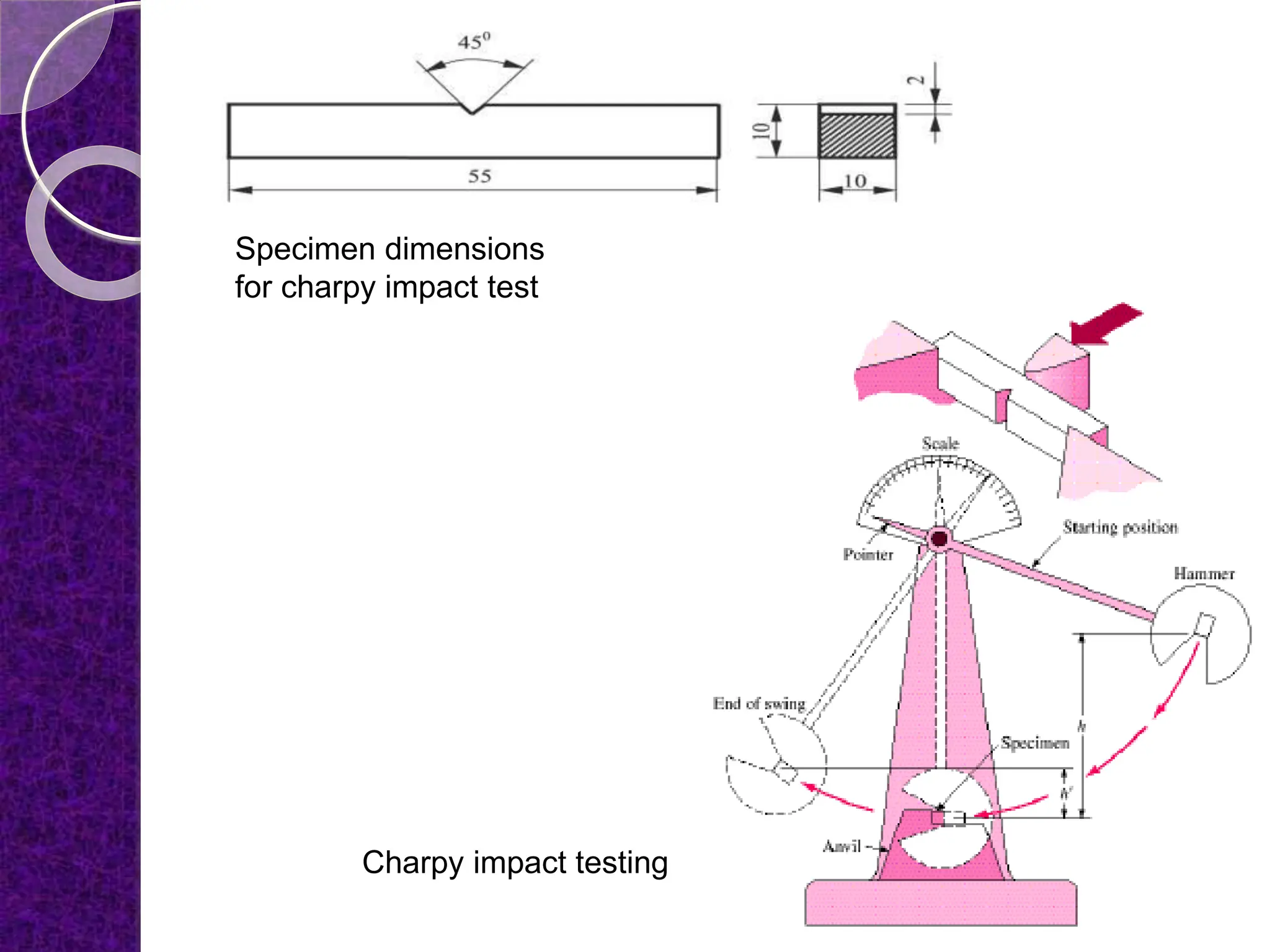
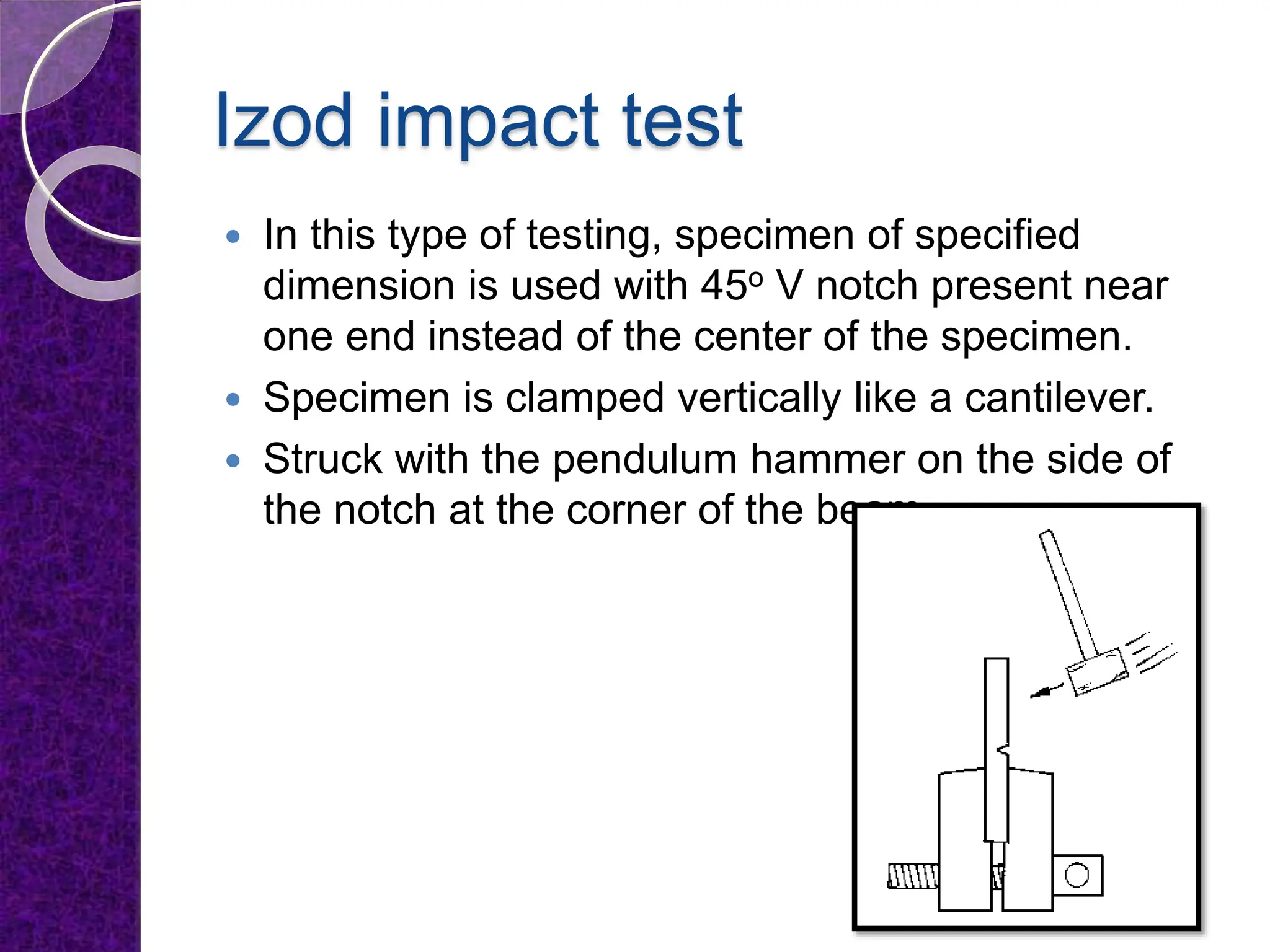
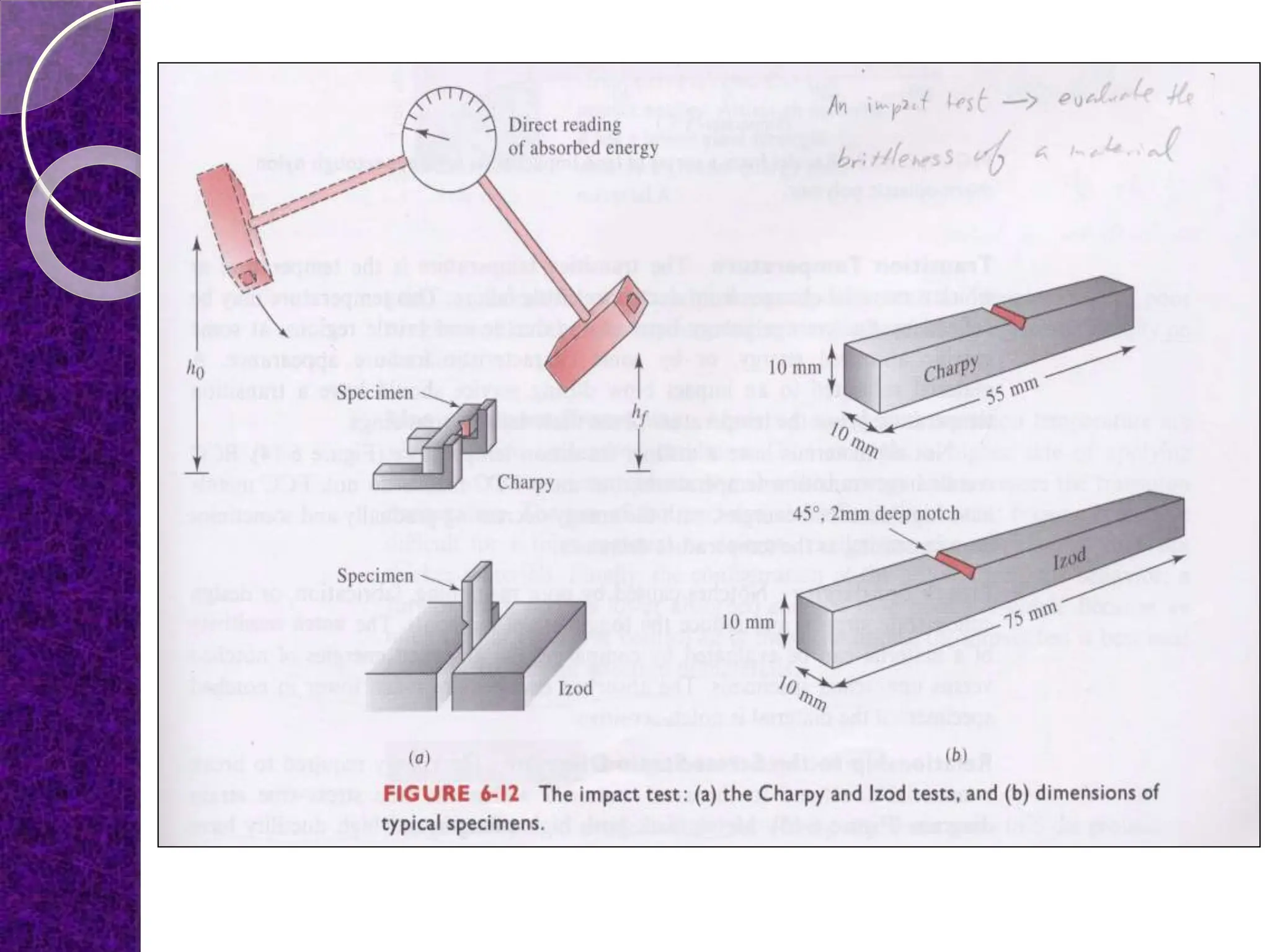
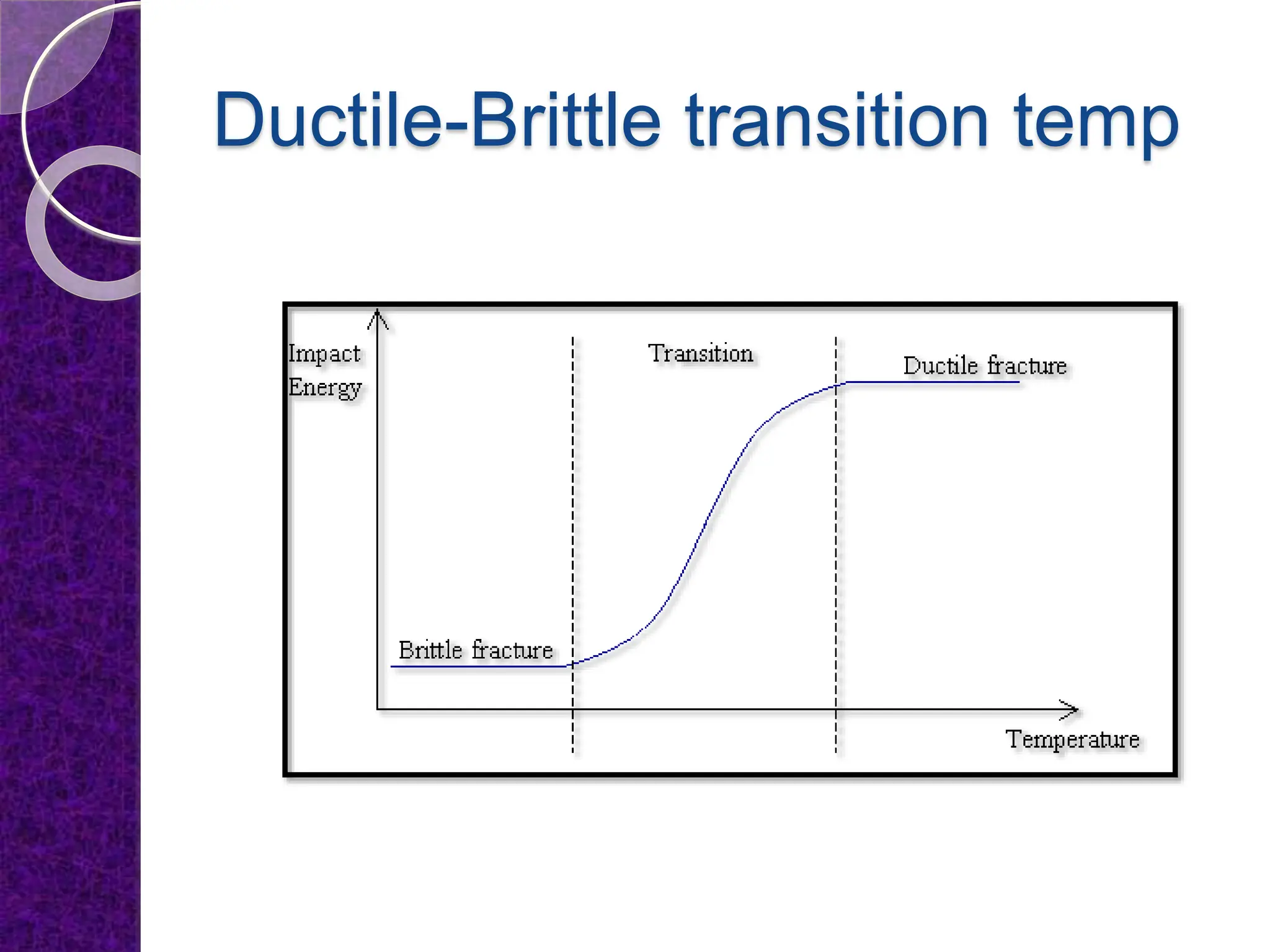
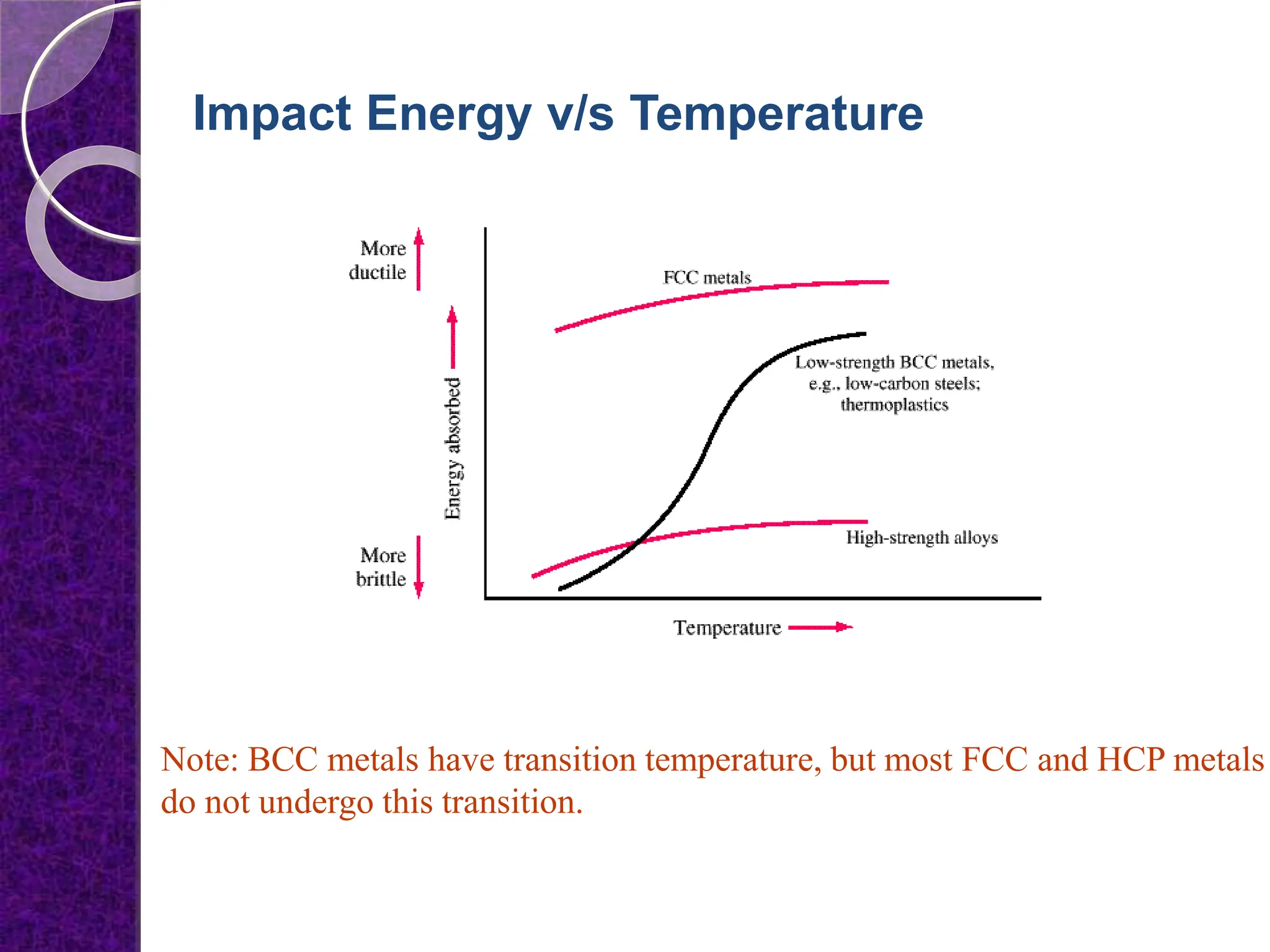
The document discusses the ductile to brittle transition, highlighting the historical context of brittle failures in shipping during World War II due to low temperatures, high strain rates, and stress concentration. It explains the importance of impact testing, specifically the Charpy and Izod tests, to measure a material's toughness and determine the temperature at which ductile materials exhibit brittle behavior. The transition occurs over a range of temperatures rather than a specific point, making it challenging to define a single ductile-brittle transition temperature.