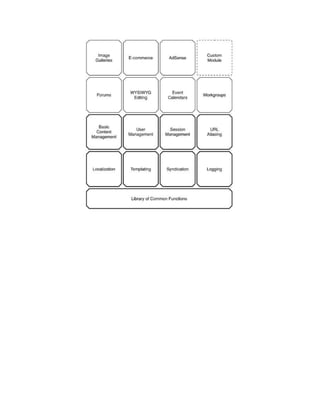
This document provides an overview of the Drupal core default installation including descriptions of what is contained in folders like includes, profiles, scripts, and sites. It also summarizes the Drupal bootstrap process which initializes the database, loads variables, initializes sessions, and sends HTTP headers to fully load Drupal.